The Renaissance marked a profound cultural rebirth igniting advancements in art, science, and philosophy across Europe. Emphasizing human potential and creativity, this era redefined societal values and inspired groundbreaking achievements. Explore the article to uncover how the Renaissance continues to influence Your world today.
Table of Comparison
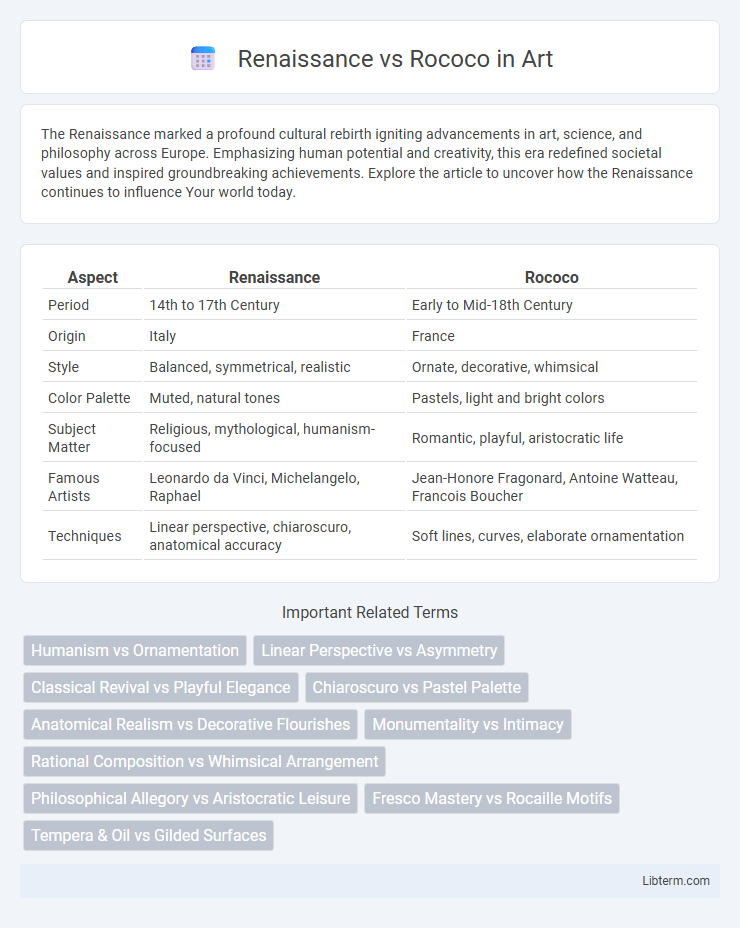
| Aspect | Renaissance | Rococo |
|---|---|---|
| Period | 14th to 17th Century | Early to Mid-18th Century |
| Origin | Italy | France |
| Style | Balanced, symmetrical, realistic | Ornate, decorative, whimsical |
| Color Palette | Muted, natural tones | Pastels, light and bright colors |
| Subject Matter | Religious, mythological, humanism-focused | Romantic, playful, aristocratic life |
| Famous Artists | Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael | Jean-Honore Fragonard, Antoine Watteau, Francois Boucher |
| Techniques | Linear perspective, chiaroscuro, anatomical accuracy | Soft lines, curves, elaborate ornamentation |
Origins and Historical Context
The Renaissance art movement originated in the 14th century in Italy, emphasizing humanism, classical antiquity, and balanced composition inspired by the revival of Greco-Roman culture. Rococo emerged in early 18th-century France as a reaction against the grandeur of Baroque, characterized by ornate decoration, lightness, and playful themes reflecting the aristocratic lifestyle during the reign of Louis XV. Both movements mirror their historical contexts: Renaissance art aligns with the cultural rebirth and scientific inquiry of the period, while Rococo embodies the social and political climate of pre-revolutionary Europe marked by elegance and frivolity.
Key Philosophies and Ideals
The Renaissance emphasized humanism, balance, and classical ideals, promoting rationality, proportion, and the revival of Greco-Roman art and philosophy. Rococo, in contrast, celebrated ornamental elegance, playful themes, and emotional expressiveness, reflecting aristocratic leisure and a lighter, more decorative aesthetic. Key philosophies of Renaissance centered on intellectual pursuit and harmony, while Rococo embraced extravagance and whimsical beauty.
Artistic Characteristics and Styles
Renaissance art emphasizes symmetry, proportion, and human anatomy, showcasing balanced compositions and realistic perspective techniques that highlight classical themes and religious subjects. Rococo style features ornate decoration, pastel colors, and playful, light-hearted themes, with intricate details and asymmetrical designs that convey elegance and movement. While Renaissance art strives for harmony and idealized beauty, Rococo favors decorative exuberance and emotional expressiveness.
Major Artists and Influential Figures
Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael were major artists of the Renaissance, known for their mastery in realistic human anatomy, perspective, and balanced composition. Rococo featured influential figures like Francois Boucher, Jean-Honore Fragonard, and Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, who emphasized decorative elegance, playful themes, and elaborate ornamentation. Both movements significantly shaped Western art history, with Renaissance focusing on classical harmony and Rococo highlighting ornate exuberance.
Architectural Innovations
Renaissance architecture emphasized symmetry, proportion, and geometry, featuring innovations such as the use of domes, columns, and pilasters inspired by classical Roman and Greek orders, exemplified in structures like Brunelleschi's Florence Cathedral dome. Rococo architecture, emerging in the 18th century, introduced intricate ornamental designs, light pastel colors, and asymmetrical forms with extensive stucco work, as seen in the Amalienburg Pavilion in Munich. While Renaissance focused on rational structural clarity and harmony, Rococo prioritized decorative elegance and playful spatial effects.
Iconic Artworks and Masterpieces
Renaissance art is epitomized by masterpieces such as Leonardo da Vinci's "Mona Lisa" and Michelangelo's "David," celebrated for their realistic human forms, balanced composition, and emphasis on classical ideals. Rococo artworks, exemplified by Jean-Honore Fragonard's "The Swing" and Francois Boucher's "Madame de Pompadour," showcase ornate detail, pastel colors, and playful, frivolous themes reflecting aristocratic elegance. The contrast between Renaissance's structured realism and Rococo's decorative exuberance highlights distinct shifts in artistic focus from humanism to ornamental fantasy.
Color Palettes and Visual Motifs
Renaissance art prominently features a balanced and harmonious color palette with rich, deep hues such as crimson, gold, and dark green, emphasizing naturalism and classical themes with motifs like mythological figures and religious iconography. Rococo contrasts this with a lighter, pastel-based palette including soft pinks, light blues, and creamy whites, highlighting playful, ornate visual motifs like floral patterns, decorative shells, and intricate scrollwork. These differences reflect Renaissance's focus on realism and symmetry versus Rococo's emphasis on elegance, lightness, and decorative extravagance.
Cultural Impact and Legacy
The Renaissance period revolutionized Western culture by emphasizing humanism, scientific inquiry, and artistic realism, laying the foundation for modern philosophy, literature, and visual arts. Rococo, emerging in the 18th century, reflected the aristocratic indulgence and playful elegance of its time, influencing interior design, fashion, and decorative arts with its ornate and light-hearted aesthetic. Both movements significantly shaped cultural heritage: the Renaissance fueled intellectual progress and artistic standards, while Rococo left a lasting imprint on aesthetics and social customs in European high society.
Decorative Arts and Furniture Design
Renaissance decorative arts emphasized symmetry, proportion, and classical motifs inspired by ancient Greek and Roman designs, often featuring rich wood carvings and inlaid marquetry in furniture. Rococo furniture design shifted towards lighter, more ornamental styles with asymmetrical forms, intricate floral patterns, and pastel color palettes, highlighting curves, gilding, and elaborate scrollwork. Both periods reflect distinct cultural values, with Renaissance art focusing on humanism and order, while Rococo embraced playfulness, elegance, and decorative extravagance.
Lasting Influence on Modern Art
Renaissance art introduced principles of realism, perspective, and anatomical accuracy that remain foundational in modern artistic techniques. Rococo's emphasis on ornate detail, lightness, and playful themes influenced decorative art and interior design styles in contemporary culture. The balanced harmony of Renaissance and the expressive elegance of Rococo continue to inspire modern art movements and aesthetics.
Renaissance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com