Understanding art criticism enhances your appreciation by revealing the deeper meanings, techniques, and cultural contexts behind artworks. It bridges the gap between the artist's intention and the viewer's interpretation, fostering a more informed and enriched experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how art criticism can transform your engagement with art.
Table of Comparison
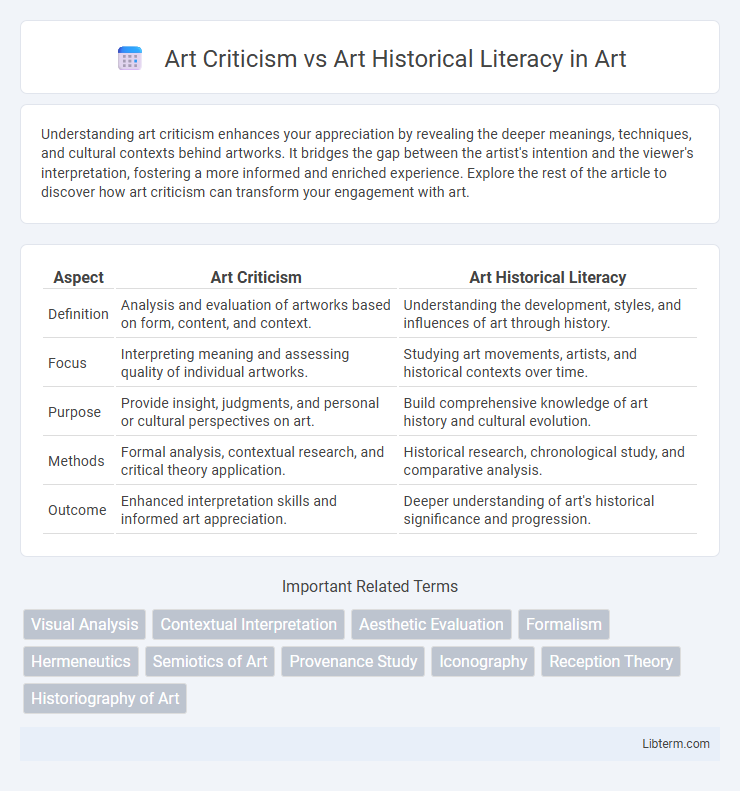
| Aspect | Art Criticism | Art Historical Literacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analysis and evaluation of artworks based on form, content, and context. | Understanding the development, styles, and influences of art through history. |
| Focus | Interpreting meaning and assessing quality of individual artworks. | Studying art movements, artists, and historical contexts over time. |
| Purpose | Provide insight, judgments, and personal or cultural perspectives on art. | Build comprehensive knowledge of art history and cultural evolution. |
| Methods | Formal analysis, contextual research, and critical theory application. | Historical research, chronological study, and comparative analysis. |
| Outcome | Enhanced interpretation skills and informed art appreciation. | Deeper understanding of art's historical significance and progression. |
Defining Art Criticism and Art Historical Literacy
Art criticism involves evaluating and interpreting artworks based on aesthetic principles, emotional impact, and cultural context, aiming to provide reasoned judgments about an artwork's value and meaning. Art historical literacy refers to the knowledge and understanding of art's development over time, including styles, movements, influential artists, and socio-historical factors shaping art history. While art criticism emphasizes subjective evaluation and immediate response, art historical literacy offers a broader, contextual framework that informs deeper comprehension of artistic evolution.
The Origins and Evolution of Art Criticism
Art criticism originated in ancient Greece, evolving from early aesthetic theories by philosophers like Plato and Aristotle, who emphasized beauty and form. During the Renaissance, art criticism expanded with scholars analyzing technique, symbolism, and cultural context, laying the groundwork for art historical literacy. The Enlightenment and Modernism further transformed art criticism into a formal discipline, integrating historical knowledge with evaluative judgments that continue to shape contemporary understanding.
Foundations of Art Historical Literacy
Foundations of art historical literacy encompass the ability to analyze and interpret artworks within their cultural, historical, and social contexts, integrating knowledge of artistic movements, key figures, and stylistic developments. This literacy enables a deeper understanding of art's evolving meanings and functions, moving beyond subjective evaluation to informed, evidence-based insights. Art criticism, while focused on evaluating aesthetic and conceptual qualities, relies on art historical literacy to contextualize works and articulate their significance accurately.
Key Differences: Approach and Methodology
Art criticism centers on the immediate evaluation and interpretation of artworks, emphasizing subjective judgment and aesthetic experience through personal and cultural lenses. In contrast, art historical literacy involves systematic research and contextual analysis of art within historical, social, and cultural frameworks, relying on evidence-based methodologies and scholarly discourse. The primary difference lies in art criticism's focus on contemporary response and meaning, whereas art history prioritizes understanding the evolution, provenance, and significance of art across time.
The Role of Subjectivity in Art Criticism
Art criticism relies heavily on subjectivity, as it involves personal interpretation, emotional response, and individual taste in evaluating artworks. In contrast, art historical literacy emphasizes objective analysis through context, chronology, and cultural significance to understand a piece within its historical framework. The interplay between subjective art criticism and structured art historical knowledge enriches the dialogue surrounding artistic value and meaning.
Contextual Understanding through Art History
Art criticism emphasizes evaluating the aesthetic and conceptual qualities of artworks, while art historical literacy provides a deep contextual understanding through the study of historical movements, cultural influences, and artist biographies. Contextual understanding through art history enables a comprehensive interpretation of art by situating works within their socio-political environments and artistic traditions. Mastery of art historical literacy enriches critical analysis by revealing the nuanced meanings and historical significance embedded in artistic expression.
Intersections: When Criticism Meets History
Art criticism and art historical literacy converge by providing a comprehensive framework for understanding art's cultural and temporal contexts. Critical analysis evaluates aesthetic and conceptual qualities while historical knowledge situates artworks within broader movements, ideologies, and social dynamics. This intersection enriches interpretation, offering nuanced insights that reflect both immediate artistic impact and long-term historical significance.
Practical Applications in the Art World
Art criticism involves evaluating and interpreting artworks to inform audiences and influence market trends, while art historical literacy provides contextual understanding essential for authentic curation and preservation. Practical applications in the art world include gallery exhibitions, where critics shape public perception, and museums, where art historians ensure accurate historical representation. Mastering both disciplines enhances decision-making for collectors, curators, and educators, driving informed engagement with art.
Impact on Art Appreciation and Education
Art criticism sharpens analytical skills by engaging viewers in evaluating aesthetics, techniques, and cultural contexts, enriching personal interpretation and emotional connection to artworks. Art historical literacy provides foundational knowledge of artistic movements, historical contexts, and cultural influences, enabling a deeper understanding of an artwork's significance and evolution. Combining both approaches enhances art education, fostering critical thinking, cultural awareness, and a comprehensive appreciation of visual art.
Looking Forward: The Future of Both Disciplines
Art criticism and art historical literacy are evolving through digital technologies and interdisciplinary approaches, fostering greater accessibility and diverse perspectives. Emerging tools like AI-driven analysis and virtual reality enable deeper engagement with art, enhancing both evaluative and contextual understanding. Collaboration between critics and historians promises a more integrated future, blending interpretive insight with historical knowledge to enrich art appreciation and scholarship.
Art Criticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com