Surrealism explores the unconscious mind through dream-like imagery and unexpected juxtapositions, challenging conventional perceptions of reality. This artistic movement influences literature, visual arts, and film, offering a unique way to express complex emotions and ideas. Discover how surrealism can transform your creativity by diving deeper into its fascinating facets throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
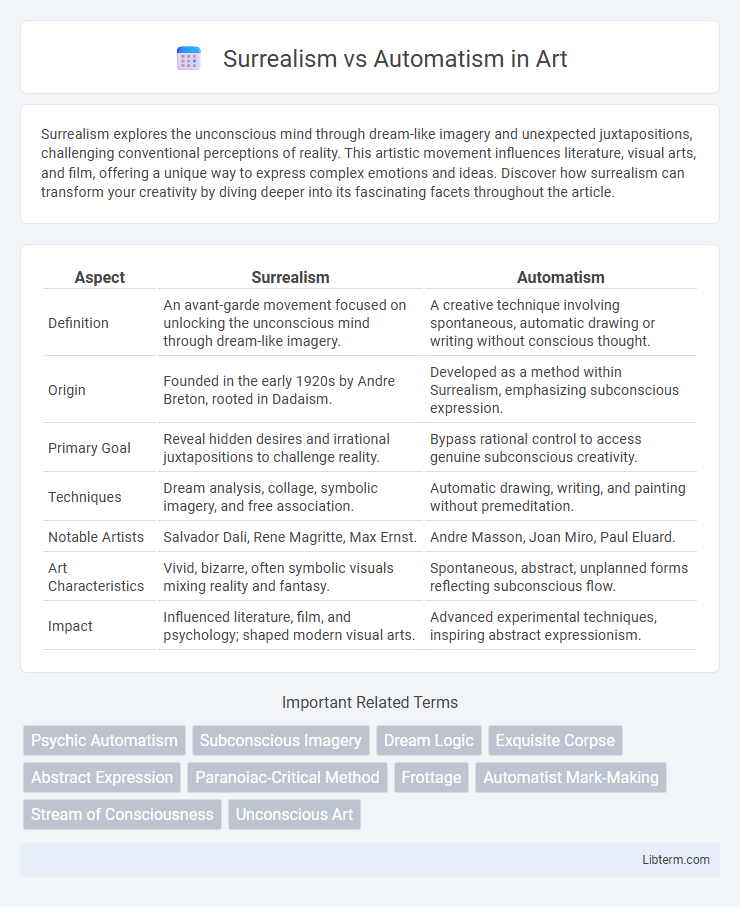
| Aspect | Surrealism | Automatism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An avant-garde movement focused on unlocking the unconscious mind through dream-like imagery. | A creative technique involving spontaneous, automatic drawing or writing without conscious thought. |
| Origin | Founded in the early 1920s by Andre Breton, rooted in Dadaism. | Developed as a method within Surrealism, emphasizing subconscious expression. |
| Primary Goal | Reveal hidden desires and irrational juxtapositions to challenge reality. | Bypass rational control to access genuine subconscious creativity. |
| Techniques | Dream analysis, collage, symbolic imagery, and free association. | Automatic drawing, writing, and painting without premeditation. |
| Notable Artists | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst. | Andre Masson, Joan Miro, Paul Eluard. |
| Art Characteristics | Vivid, bizarre, often symbolic visuals mixing reality and fantasy. | Spontaneous, abstract, unplanned forms reflecting subconscious flow. |
| Impact | Influenced literature, film, and psychology; shaped modern visual arts. | Advanced experimental techniques, inspiring abstract expressionism. |
Introduction to Surrealism and Automatism
Surrealism, an influential 20th-century avant-garde movement, explores the unconscious mind through dream-like imagery and irrational juxtapositions, aiming to unlock deeper creative potential beyond rational thought. Automatism, a core technique within Surrealism, involves spontaneous, unplanned creation to bypass conscious control and reveal the subconscious. This method enables artists to produce raw, unfiltered expressions that challenge traditional artistic conventions.
Historical Origins of Surrealism
Surrealism emerged in the early 1920s as a revolutionary cultural movement founded by Andre Breton, who sought to unlock the unconscious mind through art and literature. Influenced by Freudian psychoanalysis and Dadaism, Surrealism aimed to challenge rational thought and promote spontaneous creation, which directly led to the development of automatism as a key technique. Automatism, characterized by automatic writing and drawing, became a practical method within Surrealism to access the subconscious without censorship or intellectual control.
The Birth of Automatism in Art
The birth of automatism in art emerged from Surrealism as a revolutionary technique that emphasized spontaneous creation without conscious control, allowing the subconscious mind to guide artistic expression. Automatism was pioneered by artists like Andre Breton and Joan Miro, who sought to bypass rational thought to reveal deeper psychological truths and unlock creative potential. This method contrasted with traditional Surrealism by prioritizing free association and unfiltered impulses over symbolic or dream-like imagery.
Key Philosophies: Surrealism vs Automatism
Surrealism emphasizes unlocking the unconscious mind through dream imagery and irrational juxtapositions to challenge reality and provoke deeper truths. Automatism focuses on spontaneous, unplanned creation, allowing the subconscious to guide artistic expression without interference from rational thought. Surrealism often uses automatism as a technique but places greater importance on symbolic meaning and the exploration of hidden desires.
Influential Artists in Surrealism and Automatism
Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte are critical figures in Surrealism, renowned for their dreamlike imagery and symbolic content that challenge reality. Automatism thrives on artists like Andre Masson and Joan Miro, who emphasize spontaneous, subconscious expression through unpremeditated creation techniques. Both movements significantly influenced 20th-century art, with Surrealism focusing on deliberate imagery and Automatism privileging intuitive creation.
Techniques and Methods Compared
Surrealism employs techniques like dream analysis, symbolic imagery, and juxtaposition to unlock the unconscious mind, whereas Automatism relies on spontaneous, unplanned creation such as automatic writing or drawing to bypass rational control. Surrealist methods often involve deliberate interpretation to reveal hidden meanings, while Automatism emphasizes raw, unedited expression as a direct channel to the subconscious. Both approaches prioritize the unconscious but differ in structure--Surrealism balances control and spontaneity, whereas Automatism champions pure immediacy and reflexive creativity.
The Role of the Unconscious Mind
Surrealism deeply explores the unconscious mind by harnessing dreams and free association to unlock hidden desires and emotions. Automatism serves as a key technique within Surrealism, enabling artists to bypass conscious control and tap directly into subconscious thoughts through spontaneous creation. This method reveals the unfiltered psyche, emphasizing the significance of the unconscious in generating authentic, imaginative art.
Impact on Modern and Contemporary Art
Surrealism's impact on modern and contemporary art is profound, as it challenged traditional representations by emphasizing dream imagery and the unconscious mind, influencing artists like Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte. Automatism, a key technique within Surrealism, pioneered spontaneous creation without rational control, which directly inspired abstract expressionists such as Jackson Pollock to explore freeform gestures and subconscious expression. Both movements reshaped artistic practices by prioritizing psychological depth and unfiltered creativity, laying foundational principles for contemporary explorations in visual and kinetic art.
Criticisms and Controversies
Surrealism faced criticism for its perceived reliance on irrationality and dream logic, often challenging traditional artistic boundaries and provoking debates about the role of consciousness in creativity. Automatism, a central Surrealist technique involving spontaneous, unfiltered expression, sparked controversy due to its emphasis on subconscious impulses, raising questions about the legitimacy and coherence of art produced without deliberate control. Critics argued that automatism risked reducing art to mere randomness, undermining skilled craftsmanship and intellectual intention.
Conclusion: Surrealism and Automatism’s Legacy
Surrealism and Automatism have profoundly influenced modern art by challenging traditional notions of creativity and unlocking the subconscious mind. Their legacy endures in contemporary artistic practices emphasizing spontaneity, dream imagery, and psychological depth. Artists continue to explore automatism's free-form techniques within surrealism's broader framework, fostering innovative expressions that redefine reality and imagination.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com