A binder is a crucial component in paints and coatings, responsible for holding pigment particles together and ensuring adhesion to surfaces. The medium, often a liquid carrier, controls the paint's viscosity and flow, impacting application and drying time. Explore the article to understand how choosing the right binder and medium can enhance your painting projects.
Table of Comparison
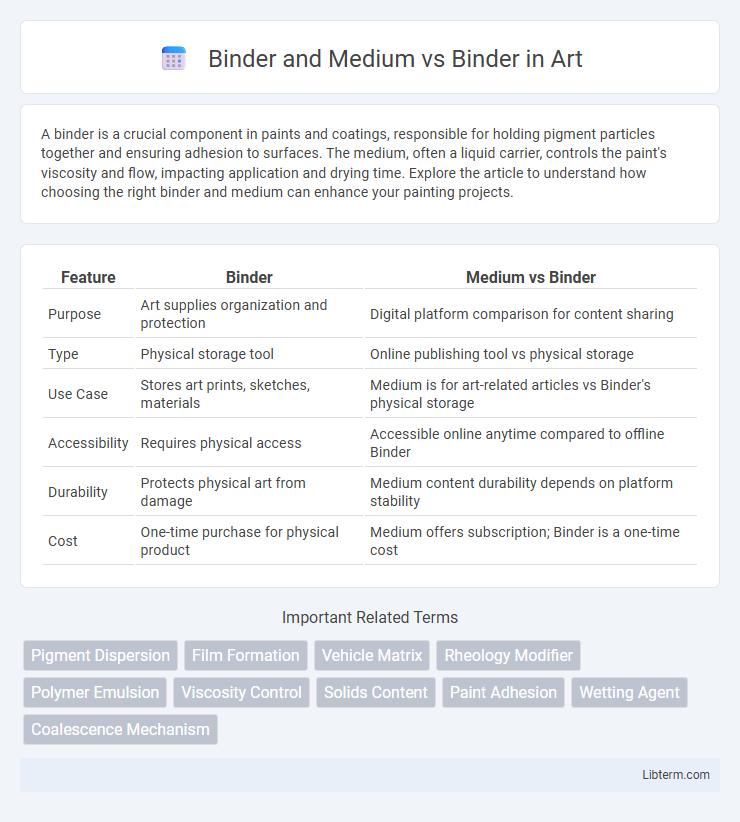
| Feature | Binder | Medium vs Binder |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Art supplies organization and protection | Digital platform comparison for content sharing |
| Type | Physical storage tool | Online publishing tool vs physical storage |
| Use Case | Stores art prints, sketches, materials | Medium is for art-related articles vs Binder's physical storage |
| Accessibility | Requires physical access | Accessible online anytime compared to offline Binder |
| Durability | Protects physical art from damage | Medium content durability depends on platform stability |
| Cost | One-time purchase for physical product | Medium offers subscription; Binder is a one-time cost |
Understanding Binders: Definitions and Roles
Binders are substances that hold materials together, providing cohesion and structural integrity, commonly used in construction, adhesives, and composites. Mediums act as carriers or solvents in formulations, influencing the texture, application, and drying properties without necessarily contributing to the binding strength. Understanding the distinct roles of binders and mediums clarifies their impact on product performance, durability, and functionality in various industrial and artistic applications.
What is a Medium? Key Differences from a Binder
A medium is a substance used to disperse pigments and binders, facilitating application and ensuring consistent texture, while a binder acts primarily as the adhesive agent that holds pigment particles together and to the painting surface. Unlike binders, which form the paint film itself, mediums modify the paint's viscosity, drying time, and finish without necessarily contributing to film formation. Key differences include the medium's role in adjusting physical properties and the binder's function in creating a durable, cohesive paint layer.
Binder vs Binder and Medium: Core Distinctions
Binder vs Binder involves comparing different types of binding agents used in various applications, emphasizing their chemical composition and performance characteristics. Binder and Medium vs Binder highlights the combined role of a binding agent and a medium, where the medium influences the texture, drying time, and overall stability of the mixture. Core distinctions focus on the specific functions: binders primarily provide adhesion and cohesion, while mediums modify flow properties, gloss, and flexibility.
The Functionality of Binders in Artistic Processes
Binders play a crucial role in artistic processes by binding pigment particles together to form a cohesive paint film, directly impacting the paint's adhesion, durability, and texture. Mediums, often composed of binders mixed with solvents or oils, modify the consistency, drying time, and finish of the paint, allowing artists to manipulate the workability and visual effects. Understanding the specific properties of different binders, such as acrylic or oil-based, enhances control over the medium's performance and the longevity of the artwork.
How Mediums Influence Material Properties
Mediums significantly influence the mechanical and chemical properties of binder-based materials by altering their viscosity, drying time, and adhesion characteristics. The choice of medium affects polymer chain interactions within the binder, impacting flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. In applications such as paints and composites, the medium modifies pigment dispersion and film formation, directly shaping the final product's performance and appearance.
Common Types of Binders Used in Art and Industry
Common types of binders used in art and industry include acrylic, epoxy, and latex, each selected for their adhesive properties and durability. Acrylic binders are prevalent in paints for their flexibility and UV resistance, while epoxy binders offer exceptional strength for industrial coatings and adhesives. Latex binders provide water resistance and elasticity, making them popular in both artistic mediums and construction materials.
Binder and Medium Combinations: Practical Applications
Binder and medium combinations play a crucial role in optimizing the performance of paints, adhesives, and coatings by enhancing adhesion, flexibility, and durability. Common practical applications include paint formulations where acrylic binders are mixed with water-based mediums to improve drying time and environmental resistance. This synergy allows manufacturers to create products tailored for automotive, construction, and art industries, balancing cost-efficiency with high-quality finish and longevity.
Choosing the Right Binder or Medium for Your Project
Selecting the right binder or medium is crucial for achieving desired texture and adhesion in your project. Binders such as acrylic or gum arabic provide strong cohesion and flexibility for different paint types, while mediums modify consistency, drying time, and finish without compromising stability. Understanding the chemical properties and compatibility of each binder or medium with your materials ensures optimal durability and visual effects.
Impact on Durability and Appearance: Binder vs Binder and Medium
Binder combined with a medium enhances paint durability by improving flexibility and adhesion, reducing cracking and peeling compared to binder alone. The medium also influences the drying time and finish, often resulting in a smoother, more even appearance with better resistance to environmental factors. In contrast, using binder alone may lead to a stiffer paint film that is more prone to brittleness and surface imperfections over time.
Future Trends in Binder and Medium Technologies
Emerging trends in binder and medium technologies emphasize eco-friendly, bio-based materials that enhance sustainability and reduce environmental impact in various applications. Advanced nanotechnology integration improves adhesion, mechanical strength, and functionality, driving innovations in coatings, batteries, and composite materials. The future landscape prioritizes smart binders with self-healing and responsive properties, tailored for next-generation industrial and consumer products.
Binder and Medium Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com