Non-representational art focuses on shapes, colors, and forms without depicting recognizable objects or scenes, emphasizing emotion and abstraction. This style challenges traditional artistic conventions by inviting viewers to interpret meaning through personal perception rather than literal representation. Explore the rest of the article to discover how non-representational art can transform your understanding of creativity and expression.
Table of Comparison
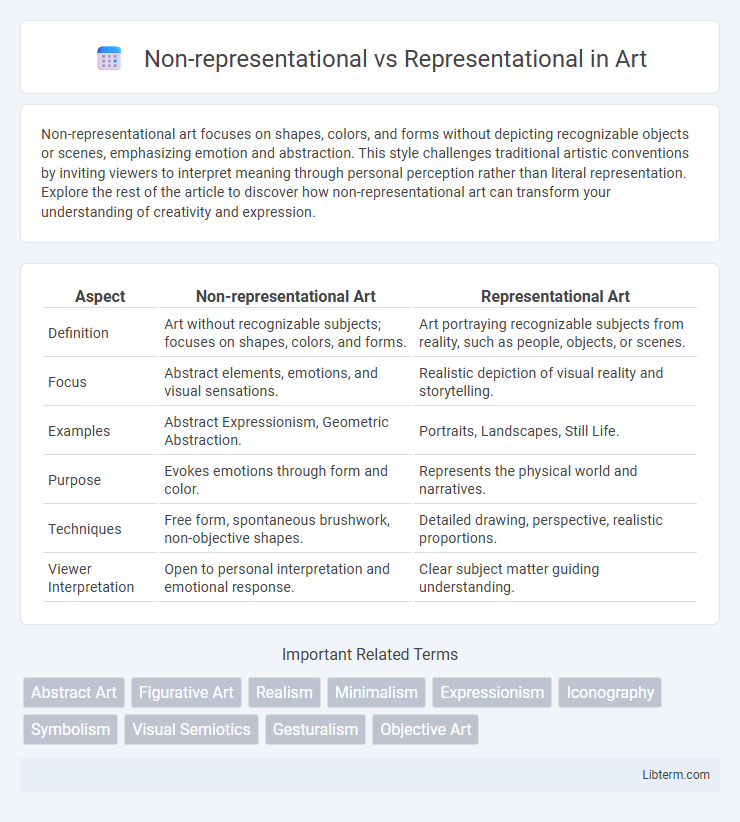
| Aspect | Non-representational Art | Representational Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art without recognizable subjects; focuses on shapes, colors, and forms. | Art portraying recognizable subjects from reality, such as people, objects, or scenes. |
| Focus | Abstract elements, emotions, and visual sensations. | Realistic depiction of visual reality and storytelling. |
| Examples | Abstract Expressionism, Geometric Abstraction. | Portraits, Landscapes, Still Life. |
| Purpose | Evokes emotions through form and color. | Represents the physical world and narratives. |
| Techniques | Free form, spontaneous brushwork, non-objective shapes. | Detailed drawing, perspective, realistic proportions. |
| Viewer Interpretation | Open to personal interpretation and emotional response. | Clear subject matter guiding understanding. |
Understanding Representational Art
Representational art depicts recognizable subjects from the real world, allowing viewers to identify people, objects, or scenes with clarity and intention. This form emphasizes accuracy, detail, and perspective to convey meaning through familiar visual references. Understanding representational art involves analyzing how artists use these elements to evoke emotion and communicate narratives effectively.
Defining Non-Representational Art
Non-representational art, also known as abstract art, rejects the depiction of recognizable objects or subjects and instead emphasizes shapes, colors, and forms for their own intrinsic value. This artistic approach prioritizes emotional expression, sensory experience, and conceptual ideas over realistic visual representation. Non-representational art includes movements such as Abstract Expressionism and Color Field painting, where meaning derives from visual elements rather than figurative content.
Historical Evolution of Art Styles
Non-representational art, emerging prominently in the early 20th century with movements like Abstract Expressionism, breaks away from depicting recognizable subjects, focusing instead on colors, shapes, and forms to evoke emotions and ideas. Representational art, with roots tracing back to prehistoric cave paintings and flourishing through the Renaissance and Baroque periods, emphasizes realistic depiction of figures and scenes to convey narratives and capture the visible world. The historical evolution from representational to non-representational art marks a shift in artistic priorities, reflecting changing cultural attitudes towards interpretation, abstraction, and the role of the artist's subjective vision.
Key Differences Between Representational and Non-Representational Art
Representational art depicts recognizable subjects from the physical world, emphasizing accurate and detailed portrayal, while non-representational art focuses on abstract elements such as shapes, colors, and textures without referencing real-world objects. Key differences include the reliance on visual realism in representational art versus the emphasis on emotional expression or concept in non-representational pieces. Representational works often communicate narratives or straightforward interpretations, whereas non-representational art invites subjective interpretation and prioritizes formal qualities over literal depiction.
Famous Artists and Their Works
Non-representational art, exemplified by Wassily Kandinsky and Mark Rothko, emphasizes abstract forms and colors that evoke emotions without depicting recognizable objects. Representational art, seen in the works of Leonardo da Vinci and Johannes Vermeer, focuses on accurately portraying subjects from reality, highlighting detailed human figures and landscapes. Both styles have shaped art history, influencing modern and contemporary artists across various mediums.
Interpretation and Viewer Engagement
Non-representational art relies on abstract forms and colors, inviting viewers to interpret meaning through personal emotions and subjective experiences, fostering a diverse range of emotional responses. Representational art depicts recognizable subjects and narratives, guiding the viewer toward a shared understanding and specific cultural or historical contexts. Viewer engagement in representational works often involves identification and storytelling, while non-representational art encourages introspection and imaginative exploration.
Techniques and Materials Used
Non-representational art employs techniques such as abstract expressionism, color field painting, and geometric abstraction, using materials like acrylics, mixed media, and unconventional textures to explore form and emotion without depicting recognizable subjects. Representational art utilizes classical methods including oil painting, detailed sketching, and realistic shading, emphasizing lifelike portrayals through materials like canvas, charcoal, and natural pigments. Both approaches integrate innovative tools, but non-representational art prioritizes experimental media to evoke subjective experience, while representational art focuses on precision to convey realistic imagery.
Cultural and Philosophical Influences
Non-representational art emphasizes abstraction and sensory experience, influenced by early 20th-century avant-garde movements like Fauvism and Abstract Expressionism, which sought to break from traditional depiction and explore subjective realities. Representational art, deeply rooted in Renaissance humanism and Enlightenment ideals, aims to depict recognizable subjects, reflecting cultural narratives and philosophical inquiries into nature, identity, and society. The divergence between these styles reflects broader philosophical debates between realism and abstraction, objectivity and personal interpretation, shaping cultural perceptions of meaning and artistic value.
Contemporary Relevance and Trends
Non-representational art emphasizes abstract forms, emotions, and concepts, reflecting contemporary trends in digital media and immersive experiences that prioritize sensory engagement over literal interpretation. Representational art remains relevant by adapting to modern contexts through hyperrealism and mixed media, merging traditional techniques with technological innovations to communicate detailed narratives. Current trends show a fluid boundary between these approaches, with artists increasingly blending abstraction and representation to challenge perceptions and address socio-political themes.
Choosing Between Non-Representational and Representational Approaches
Choosing between non-representational and representational approaches depends on the desired outcome and context; representational methods provide clear, concrete depictions that communicate specific ideas or objects, ideal for instructional or illustrative purposes. Non-representational approaches emphasize abstract forms and emotions, fostering interpretative engagement and creative exploration, making them suitable for experimental art and conceptual frameworks. Evaluating the target audience, purpose, and communicative clarity guides the selection process toward the most effective visual strategy.
Non-representational Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com