Porcelain is a highly durable and translucent ceramic material prized for its strength and elegance in both artistic and functional applications. Manufacturers achieve its unique properties through a combination of refined clay, kaolin, and high-temperature firing, resulting in a smooth, glass-like surface resistant to chipping and staining. Discover the fascinating history, manufacturing process, and diverse uses of porcelain in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
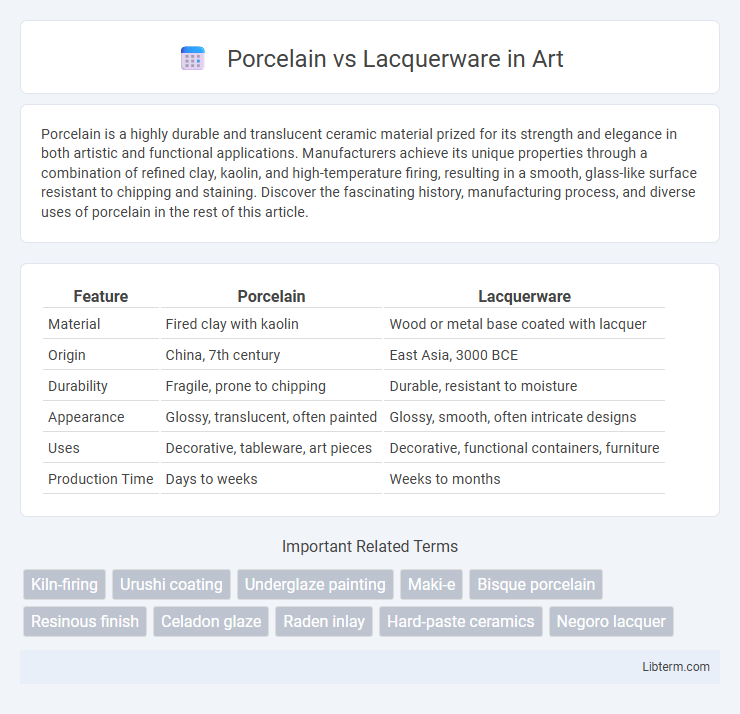
| Feature | Porcelain | Lacquerware |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fired clay with kaolin | Wood or metal base coated with lacquer |
| Origin | China, 7th century | East Asia, 3000 BCE |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Durable, resistant to moisture |
| Appearance | Glossy, translucent, often painted | Glossy, smooth, often intricate designs |
| Uses | Decorative, tableware, art pieces | Decorative, functional containers, furniture |
| Production Time | Days to weeks | Weeks to months |
Introduction to Porcelain and Lacquerware
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating kaolin clay to high temperatures, resulting in a strong, translucent, and white finish valued for its durability and elegance. Lacquerware involves applying multiple layers of natural resin harvested from lacquer trees onto wood or metal surfaces, creating a glossy, protective coating renowned for its vibrant colors and intricate designs. Both techniques represent distinct cultural craftsmanship, with porcelain primarily linked to East Asian ceramics and lacquerware to traditional decorative arts across Asia.
Historical Background of Porcelain
Porcelain originated in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD) and gained prominence in the Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD) due to its refined craftsmanship and translucent quality. This ceramic art form was highly valued for its durability, smooth glaze, and intricate designs, influencing global markets and leading to extensive trade along the Silk Road. European porcelain production began in the early 18th century, inspired by Chinese techniques, marking a significant moment in the history of decorative arts.
Origins and Development of Lacquerware
Lacquerware originated in ancient East Asia, with evidence dating back over 7,000 years, particularly in China, Japan, and Korea, where artisans mastered the application of sap from lacquer trees to create durable, glossy finishes. This technique evolved through centuries, integrating intricate inlay work, metal embellishments, and vibrant pigments, contrasting porcelain's development from refined kaolin clay in China during the Tang and Song dynasties. The cultural significance of lacquerware expanded along trade routes, influencing Southeast Asia and beyond, marking its development as an art form interwoven with regional craftsmanship traditions distinct from the ceramic-focused lineage of porcelain.
Key Differences in Materials and Techniques
Porcelain is crafted from refined clay fired at extremely high temperatures, resulting in a durable, translucent finish prized for its smooth surface and strength. Lacquerware involves applying multiple layers of natural resin, often derived from the sap of the lacquer tree, onto wood or metal surfaces, creating a glossy, protective coating that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. While porcelain emphasizes ceramic art through kiln-firing techniques, lacquerware highlights intricate hand-applied layering and polishing processes unique to traditional craftsmanship.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color, Shine, and Texture
Porcelain exhibits a smooth, glossy finish with a translucent quality that enhances its delicate pastel or vibrant color palette, offering a refined and elegant appearance. Lacquerware features a deep, rich shine with a polished surface, often showcasing intricate designs and bold, saturated colors that create a luxurious and dramatic effect. The texture of porcelain is cool and sleek, while lacquerware provides a slightly tactile, layered surface resulting from multiple lacquer applications.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Porcelain offers exceptional durability due to its dense, non-porous structure, resisting chipping and staining with minimal maintenance requirements. Lacquerware, while aesthetically rich and lightweight, demands careful upkeep to avoid scratches, dents, and damage from heat or moisture exposure. Both materials require distinct care: porcelain withstands dishwasher cleaning and daily use, whereas lacquerware benefits from gentle hand washing and controlled environmental conditions to preserve its finish.
Common Uses and Functional Applications
Porcelain is widely used for dinnerware, decorative items, and bathroom fixtures due to its durability, heat resistance, and non-porous surface, making it ideal for food and liquid containment. Lacquerware serves primarily as ornamental containers, trays, and furniture finishing, prized for its glossy finish and protective coating that resists moisture and insects. Both materials excel in aesthetic appeal, but porcelain is favored for practical absorption resistance and heat endurance, whereas lacquerware is chosen for intricate craftsmanship and surface protection.
Cultural Significance and Symbolism
Porcelain holds deep cultural significance in East Asian societies, symbolizing purity, elegance, and historical refinement, often associated with royal courts and scholarly tradition. Lacquerware, prominent in Southeast Asia and Japan, embodies craftsmanship and spiritual protection, with intricate designs representing prosperity, longevity, and cultural heritage. Both materials serve as vessels for storytelling, embodying centuries of artistic evolution and regional identity.
Collecting and Investment Value
Porcelain offers timeless investment value due to its durability, historical significance, and global demand among collectors, often appreciating steadily over time. Lacquerware, prized for its intricate craftsmanship and cultural uniqueness, appeals to niche collectors seeking rarity and artistic detailing, potentially yielding high returns in specialized markets. Both materials require expert authentication to ensure provenance and maximize their collectible worth.
Choosing Between Porcelain and Lacquerware
Choosing between porcelain and lacquerware depends on intended use and aesthetic preference; porcelain offers durability, heat resistance, and a timeless, glossy finish ideal for everyday dining and formal settings. Lacquerware provides a lightweight, vibrant surface with intricate designs, perfect for decorative pieces or traditional cultural displays. Consider maintenance requirements as porcelain is dishwasher safe while lacquerware requires gentle hand cleaning to preserve its finish.
Porcelain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com