Wax medium offers artists a versatile, durable surface for encaustic painting, blending pigment with heated beeswax to create rich textures and vibrant colors. This medium allows precise layering and manipulation, making it ideal for mixed media projects and preserving artwork longevity. Discover how incorporating wax medium can elevate your creative process in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
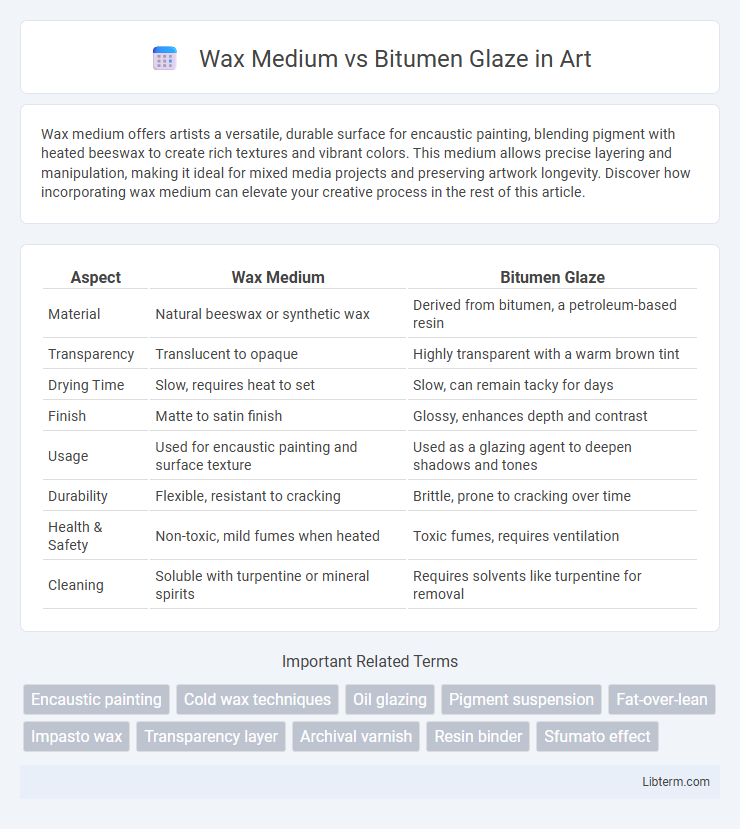
| Aspect | Wax Medium | Bitumen Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural beeswax or synthetic wax | Derived from bitumen, a petroleum-based resin |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | Highly transparent with a warm brown tint |
| Drying Time | Slow, requires heat to set | Slow, can remain tacky for days |
| Finish | Matte to satin finish | Glossy, enhances depth and contrast |
| Usage | Used for encaustic painting and surface texture | Used as a glazing agent to deepen shadows and tones |
| Durability | Flexible, resistant to cracking | Brittle, prone to cracking over time |
| Health & Safety | Non-toxic, mild fumes when heated | Toxic fumes, requires ventilation |
| Cleaning | Soluble with turpentine or mineral spirits | Requires solvents like turpentine for removal |
Understanding Wax Medium: Composition and Uses
Wax medium, primarily composed of beeswax or synthetic waxes blended with oils or solvents, offers artists a versatile binder for encaustic painting and mixed media applications. Its natural translucency and pliability enhance texture and layering, making it ideal for creating depth and luminous effects on various surfaces. Unlike bitumen glaze, which provides a rich, dark patina through fossil-based tar components, wax medium preserves color vibrancy and offers a durable, flexible finish resistant to cracking and yellowing.
What is Bitumen Glaze? Key Properties and Applications
Bitumen glaze is a viscous, black, tar-like coating derived from bitumen, used primarily for waterproofing and protective finishes in industrial and artistic applications. Its key properties include excellent adhesion, water resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it suitable for sealing surfaces against moisture and environmental damage. Common applications of bitumen glaze encompass roofing membranes, corrosion protection on metal surfaces, and finishes in mixed-media art to create deep, glossy textures.
Historical Context: Wax Medium and Bitumen Glaze in Art
Wax medium, used since ancient Egypt, was a crucial element in encaustic painting, valued for its durability and luminous finish, while bitumen glaze, derived from natural asphalt, gained prominence in the 19th century for its rich, dark tones and ability to create depth in oil paintings. Artists like Fayum portrait painters exploited wax's malleability and preservation qualities, whereas Romantic painters employed bitumen glaze to achieve dramatic shadow effects and atmospheric intensity. Both substances shaped artistic techniques by enhancing texture and color richness, reflecting evolving material technologies and aesthetic preferences throughout art history.
Visual Effects: Surface Texture and Finish Comparison
Wax medium imparts a smooth, subtle sheen with a soft, tactile surface that enhances depth and color richness, creating a delicate, natural finish often favored in fine art painting. Bitumen glaze produces a darker, more transparent layer with a glossy, glass-like surface that emphasizes shadow and contrast, resulting in a dramatic, aged, or antique effect. The wax medium maintains a matte to satin finish, while bitumen glaze offers a pronounced reflective quality, affecting the overall luminosity and texture perception of the artwork.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Wax medium provides a durable finish but is prone to wear and may require reapplication within a year or two, especially in high-traffic or humid environments. Bitumen glaze offers superior longevity due to its water-resistant properties and robust barrier against environmental factors, often lasting several years without significant degradation. Artists seeking long-lasting protection typically favor bitumen glaze for its enhanced durability and resistance to cracking or fading over time.
Application Techniques: Step-by-Step for Each Medium
Wax medium application begins by evenly heating the wax to a workable temperature, then applying thin, consistent layers with a soft brush or cloth to build depth and texture. Bitumen glaze requires mixing bitumen with a transparent medium, glazing over dry paint layers with a soft brush, allowing each coat to fully dry to achieve rich, luminous shadows. Both techniques demand patience and precision, using multiple thin layers to enhance transparency and surface quality without compromising the underlying paint.
Color Interaction: Wax Medium vs Bitumen Glaze
Wax medium enhances color depth by creating a translucent, luminous finish that allows underlying hues to shine through with clarity, intensifying vibrancy and subtle tonal variations. Bitumen glaze produces a rich, darkened effect by adding a warm, amber-brown tint that modifies color saturation and contrast, creating a more muted, aged appearance. The interaction of wax medium maintains color brilliance while bitumen glaze alters color warmth and opacity, influencing the painting's overall mood and visual texture.
Studio Safety: Handling Wax Medium and Bitumen Glaze
Wax medium and bitumen glaze require careful handling in the studio due to their distinct safety profiles; wax medium is generally non-toxic but can pose a fire hazard when heated, necessitating proper ventilation and flame precautions. Bitumen glaze contains harmful hydrocarbons that emit toxic fumes, demanding the use of gloves, adequate ventilation, and avoidance of inhaling vapors. Studio safety protocols must include secure storage, protective equipment, and awareness of each material's specific risks to prevent health issues and accidents.
Artistic Styles Best Suited for Each Medium
Wax medium excels in encaustic painting, favored for its rich texture and vibrant color retention, making it ideal for abstract and mixed-media art. Bitumen glaze, known for its slow drying and deep, luminous quality, suits classical realism and detailed portraiture by enhancing shadow depth and subtle tonal variations. Artists seeking expressive brushwork and layered surfaces often prefer wax, while those aiming for precise tonal gradation and smooth finishes typically choose bitumen glaze.
Choosing the Right Option: Wax Medium or Bitumen Glaze?
Choosing the right option between wax medium and bitumen glaze depends on the desired finish and durability of the artwork. Wax medium offers a smooth, matte finish with excellent flexibility and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for fine detail work and layering. Bitumen glaze provides a rich, dark tint that enhances depth and texture but can become brittle over time, suitable for achieving aged or antique effects.
Wax Medium Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com