Sgraffito is an ancient decorative technique where layers of plaster or ceramic slip are scratched to reveal underlying colors, creating intricate designs. This method enhances architectural details and pottery with textured, visually striking patterns. Discover how mastering sgraffito can transform your artistic projects in the full article.
Table of Comparison
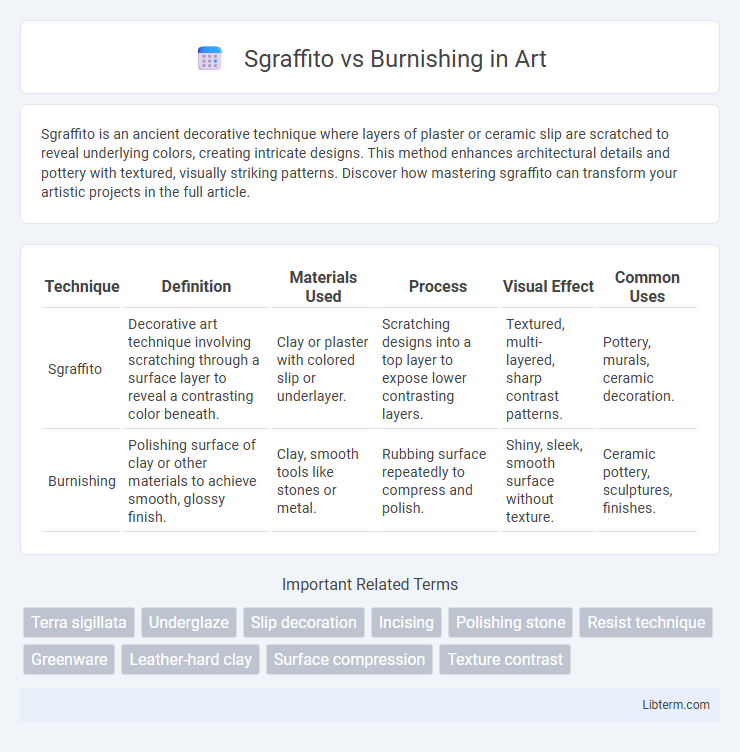
| Technique | Definition | Materials Used | Process | Visual Effect | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sgraffito | Decorative art technique involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath. | Clay or plaster with colored slip or underlayer. | Scratching designs into a top layer to expose lower contrasting layers. | Textured, multi-layered, sharp contrast patterns. | Pottery, murals, ceramic decoration. |
| Burnishing | Polishing surface of clay or other materials to achieve smooth, glossy finish. | Clay, smooth tools like stones or metal. | Rubbing surface repeatedly to compress and polish. | Shiny, sleek, smooth surface without texture. | Ceramic pottery, sculptures, finishes. |
Introduction to Sgraffito and Burnishing
Sgraffito is a decorative pottery technique involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, often used to create intricate patterns or textures. Burnishing, by contrast, is a polishing method that compacts the clay surface with a smooth tool, producing a shiny, reflective finish without the use of glaze. Both techniques enhance the visual appeal and tactile experience of ceramic pieces through different surface treatments.
Historical Origins and Development
Sgraffito, with origins tracing back to Ancient Greece and Etruscan pottery, developed further during the Renaissance in Italy as artisans scratched through layers of colored slip to reveal contrasting surfaces beneath. Burnishing, a technique dating to prehistoric times and widely used in Neolithic pottery, involves polishing the clay surface with a smooth tool to create a shiny finish before firing. Both methods showcase historical advancements in ceramic art, reflecting cultural preferences in texture and decoration across different civilizations.
Core Techniques Explained
Sgraffito involves scratching through a top layer of slip or glaze to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating intricate, textured patterns on ceramics. Burnishing is the technique of polishing the surface of a clay object with a smooth tool to achieve a glossy, smooth finish before firing. Both methods enhance the visual and tactile qualities of pottery but use fundamentally different approaches: sgraffito relies on incision and layering, while burnishing focuses on surface compression and shine.
Tools and Materials Used
Sgraffito involves using sharp tools such as needles, knives, or styluses to scratch through a surface layer of slip or glaze to reveal the clay body beneath, often applied on leather-hard pottery for precise designs. Burnishing requires smooth tools like polished stones, spoons, or wooden paddles to rub the surface of leather-hard clay, creating a shiny, compressed finish without additional materials. Both techniques rely on the state of the clay--leather-hard for sgraffito and usually leather-hard to bone dry for burnishing--and are enhanced by choosing compatible slips or clay bodies for optimal texture and visual contrast.
Visual and Textural Differences
Sgraffito reveals intricate patterns by scratching through a surface layer to expose a contrasting color underneath, creating a tactile, layered texture often found in pottery and wall art. Burnishing produces a smooth, glossy finish by polishing the surface with a hard tool, enhancing the material's natural sheen and resulting in a sleek, reflective appearance. The key visual difference lies in sgraffito's detailed, rough texture versus burnishing's uniform, shiny surface.
Ideal Applications for Each Technique
Sgraffito is ideal for creating intricate, textured designs on pottery or walls by scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, making it perfect for decorative ceramics and murals. Burnishing suits smooth, glossy finishes on leather or clay, achieved by polishing the surface to a shine without glaze, which enhances durability and aesthetics in leather goods and polished ceramic vessels. Each technique excels in distinct applications where texture or sheen is the primary artistic or functional goal.
Strengths and Limitations
Sgraffito offers precise texture and intricate designs by carving through layers of contrasting clay, but it can be fragile and prone to chipping if not properly sealed. Burnishing compacts the clay surface to create a smooth, glossy finish that enhances durability and water resistance, though it limits decorative detail compared to sgraffito. Both techniques require careful technique; sgraffito demands steady carving skills while burnishing needs smooth, plastic clay and timely application before firing.
Artistic Styles and Influences
Sgraffito involves layering contrasting slips or glazes and scratching through to reveal underlying colors, reflecting influences from Renaissance ceramics and folk art traditions. Burnishing produces a smooth, polished surface by rubbing clay before firing, originating from ancient Native American and African pottery techniques that emphasize tactile elegance. Both styles convey distinct artistic expressions--Sgraffito through intricate patterns and texture; Burnishing through glossy minimalism and refined form.
Contemporary Uses in Ceramics and Art
Sgraffito and burnishing are prominent techniques in contemporary ceramics and art, each offering unique textural and visual effects. Sgraffito involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, widely used for intricate designs on pottery and tiles that enhance tactile and aesthetic appeal. Burnishing creates a polished, smooth surface by rubbing clay with a hard tool, favored in modern sculptures and functional wares for its glossy finish and durability without glaze.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Choosing between sgraffito and burnishing depends on the desired texture and visual effect of your ceramic project. Sgraffito involves carving through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, ideal for intricate designs and detailed patterns. Burnishing creates a smooth, glossy finish by polishing the clay surface before firing, suitable for minimalistic and elegant styles.
Sgraffito Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com