Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on essential features while hiding unnecessary details, enhancing clarity and efficiency in design and communication. This principle is widely applied in software development, art, and philosophy to create manageable models that address specific problems or ideas. Explore the rest of this article to understand how abstraction can improve your approach to problem-solving.
Table of Comparison
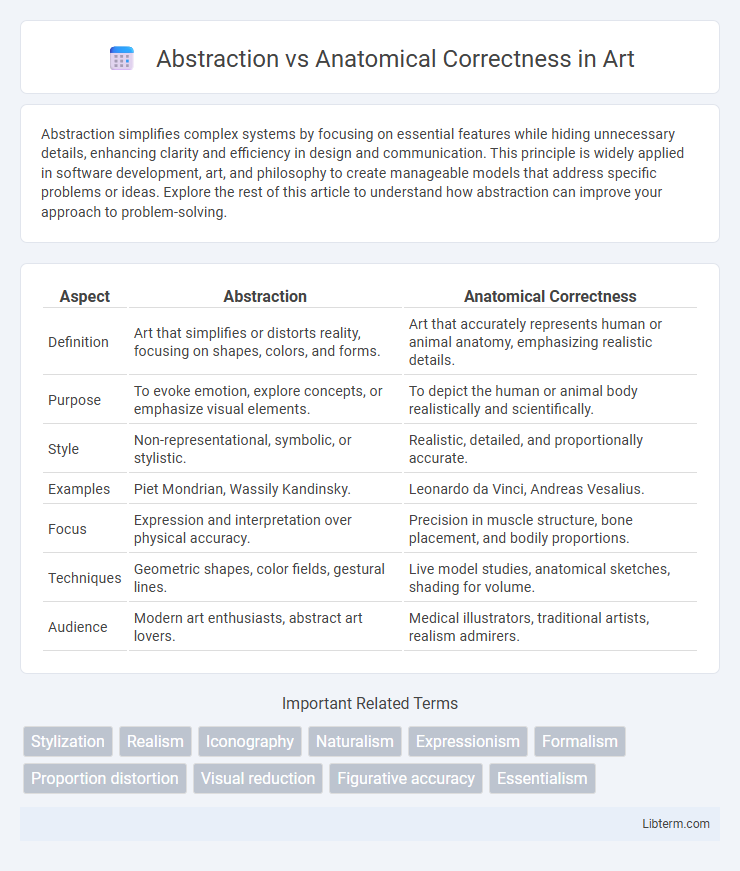
| Aspect | Abstraction | Anatomical Correctness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art that simplifies or distorts reality, focusing on shapes, colors, and forms. | Art that accurately represents human or animal anatomy, emphasizing realistic details. |
| Purpose | To evoke emotion, explore concepts, or emphasize visual elements. | To depict the human or animal body realistically and scientifically. |
| Style | Non-representational, symbolic, or stylistic. | Realistic, detailed, and proportionally accurate. |
| Examples | Piet Mondrian, Wassily Kandinsky. | Leonardo da Vinci, Andreas Vesalius. |
| Focus | Expression and interpretation over physical accuracy. | Precision in muscle structure, bone placement, and bodily proportions. |
| Techniques | Geometric shapes, color fields, gestural lines. | Live model studies, anatomical sketches, shading for volume. |
| Audience | Modern art enthusiasts, abstract art lovers. | Medical illustrators, traditional artists, realism admirers. |
Understanding Abstraction in Art
Understanding abstraction in art involves recognizing how artists simplify or distort forms to convey emotions, ideas, or concepts rather than replicating anatomical accuracy. Abstraction prioritizes expressive qualities, color, and composition, allowing for subjective interpretation beyond literal representation. This approach contrasts with anatomical correctness, which demands precise, realistic depictions of human or animal anatomy, emphasizing proportion and structure.
Defining Anatomical Correctness
Anatomical correctness refers to the accurate representation of the human body's structure based on real anatomical features such as muscle placement, bone alignment, and proportions. This precision is essential in fields like medical illustration, realistic character modeling, and scientific visualization where exact details impact understanding and functionality. In contrast to abstraction, anatomical correctness prioritizes fidelity to real-world anatomy over stylization or simplification.
Historical Perspectives: Abstraction vs Anatomical Accuracy
Historical perspectives on abstraction versus anatomical correctness reveal evolving artistic priorities where Renaissance artists emphasized anatomical accuracy through detailed human anatomy studies, exemplified by Leonardo da Vinci's sketches. In contrast, modernist movements like Cubism and Expressionism embraced abstraction, prioritizing emotional expression and conceptual representation over precise anatomical form. This shift reflects broader cultural and philosophical changes influencing the interpretation of the human body in art across different eras.
The Role of Anatomy in Traditional Art
The role of anatomy in traditional art is crucial for achieving anatomical correctness, which ensures lifelike representation of human figures through accurate depiction of muscles, bones, and proportions. While abstraction emphasizes stylization and emotional expression, traditional artists rely on anatomical knowledge to create realistic and believable forms that adhere to natural human structures. Mastery of anatomy enhances the precision and depth in artwork, providing a solid foundation for both realistic and stylized interpretations.
Why Artists Choose Abstraction
Artists choose abstraction to convey emotions and ideas beyond the limitations of anatomical correctness, allowing for more personal and subjective interpretations. Abstraction enables the exploration of form, color, and composition without strict adherence to realistic details, fostering creativity and innovation. This approach often creates a stronger emotional impact by emphasizing symbolic meaning over precise anatomical representation.
Balancing Expressiveness and Realism
Balancing expressiveness and realism involves navigating the spectrum between abstraction and anatomical correctness in art and design. Abstraction prioritizes emotional impact and stylistic freedom, allowing exaggerated forms and simplified shapes that convey mood and concept effectively. Anatomical correctness emphasizes precise human or animal structures, enhancing believability and naturalism but potentially limiting creative expression by adhering strictly to physical accuracy.
Artistic Techniques: From Reference to Reinvention
Artistic techniques evolve by balancing abstraction with anatomical correctness, allowing creators to move from precise references to imaginative reinvention. Mastery of foundational anatomy provides a realistic framework that artists can selectively distort or simplify to evoke emotion and emphasize conceptual themes. This dynamic interplay fosters unique visual languages, blending factual structure with expressive abstraction for compelling art.
The Impact of Style on Viewer Perception
Abstraction in art emphasizes emotional expression and conceptual interpretation by simplifying or distorting forms, influencing viewers to engage with the artwork on a subjective and imaginative level. Anatomical correctness focuses on precise, realistic representation of the human body, guiding viewers toward appreciating technical skill and lifelike detail. The contrast between these styles shapes viewer perception by either evoking personal feelings and symbolic meaning or reinforcing recognition and cognitive understanding of physical form.
Contemporary Trends in Figure Representation
Contemporary trends in figure representation increasingly blur the lines between abstraction and anatomical correctness, prioritizing expressive forms over realistic precision. Artists integrate exaggerated proportions, simplified shapes, and fragmented anatomy to evoke emotional responses and challenge traditional depictions. This movement reflects a shift towards conceptual interpretation, emphasizing personal and cultural narratives rather than strict adherence to classical anatomical rules.
Choosing Your Path: Finding Your Artistic Voice
Choosing between abstraction and anatomical correctness shapes an artist's unique style and expression. Embracing abstraction allows for emotional interpretation and creative freedom, while anatomical correctness demands precision and detailed knowledge of human form. Balancing these approaches helps artists discover their authentic voice and communicate their vision effectively.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com