Baroque art and architecture are characterized by dramatic expressions, intricate details, and grandeur that reflect the cultural shifts of the 17th century. This style combines bold contrasts of light and shadow with dynamic movement to evoke emotional intensity and spiritual awe. Explore the article to discover how Baroque influences continue to shape modern aesthetics and enrich your appreciation of art history.
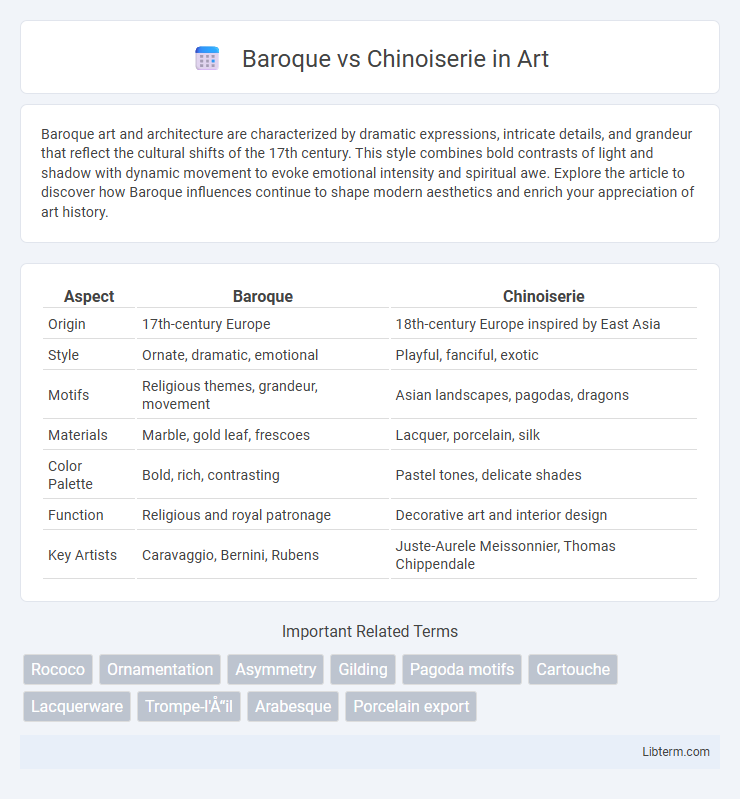
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Baroque | Chinoiserie |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 17th-century Europe | 18th-century Europe inspired by East Asia |
| Style | Ornate, dramatic, emotional | Playful, fanciful, exotic |
| Motifs | Religious themes, grandeur, movement | Asian landscapes, pagodas, dragons |
| Materials | Marble, gold leaf, frescoes | Lacquer, porcelain, silk |
| Color Palette | Bold, rich, contrasting | Pastel tones, delicate shades |
| Function | Religious and royal patronage | Decorative art and interior design |
| Key Artists | Caravaggio, Bernini, Rubens | Juste-Aurele Meissonnier, Thomas Chippendale |
Origins and Historical Context
Baroque style originated in early 17th-century Europe, characterized by dramatic expression, grandeur, and intricate details, influenced by the Catholic Church's desire to evoke emotional involvement during the Counter-Reformation. Chinoiserie emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries as a European interpretation of Chinese and East Asian artistic motifs, driven by expanding trade and fascination with Asian culture. The Baroque period reflects European power and religious themes, while Chinoiserie represents cross-cultural exchange and exoticism in decorative arts.
Key Characteristics of Baroque
Baroque art and architecture are characterized by dramatic expressions, bold ornamentation, and a strong sense of movement, with elaborate details and grandeur often emphasized through intricate carvings and dynamic contrasts of light and shadow. This style commonly incorporates large-scale ceiling frescoes, rich textures, and a lavish use of gold and marble to convey power and opulence. Baroque's emotional intensity and intricate designs distinguish it from the more delicate, decorative nature of Chinoiserie, which draws inspiration from East Asian motifs.
Defining Features of Chinoiserie
Chinoiserie is characterized by intricate motifs inspired by East Asian art, including pagodas, dragons, and delicate floral patterns, often rendered in vibrant colors and gilded details. The style emphasizes asymmetry, fanciful landscapes, and a playful combination of exotic elements, contrasting with the grandeur and symmetry of Baroque design. Unlike Baroque's heavy ornamentation and dramatic intensity, Chinoiserie evokes a light, whimsical aesthetic reflecting Western fascination with Asian culture during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Influences and Inspirations
Baroque art draws heavily from classical antiquity and the Renaissance, characterized by dramatic expressions, ornate details, and grandeur inspired by religious themes and European aristocracy. Chinoiserie, emerging in the 17th and 18th centuries, is influenced primarily by East Asian aesthetics, integrating Chinese motifs, lacquerwork, pagodas, and exotic flora into European decorative arts. Both styles reflect cultural exchanges: Baroque emphasizes Western religious and royal power, while Chinoiserie showcases Western fascination with Eastern craftsmanship and imaginative interpretations of Asian culture.
Color Palettes and Materials
Baroque designs feature rich, deep color palettes such as gold, burgundy, and emerald, emphasizing opulence through materials like gilded wood, marble, and heavy velvet. Chinoiserie contrasts with lighter, pastel colors including soft blues, pinks, and greens, often incorporating lacquer, porcelain, and delicate silk fabrics. The Baroque's dramatic textures and weighty materials reflect grandeur, while Chinoiserie embraces airy, intricate details with a focus on exotic Asian-inspired motifs.
Architectural Expressions
Baroque architecture is characterized by dramatic curves, grand staircases, and elaborate ornamentation, often emphasizing bold forms and dynamic movement to convey power and grandeur. Chinoiserie, in contrast, incorporates delicate motifs inspired by Chinese art, such as pagoda-style roofs, intricate latticework, and asymmetrical designs, reflecting a European interpretation of East Asian aesthetics. While Baroque architecture focuses on opulence and theatricality, Chinoiserie introduces exotic, playful elements that blend ornamental lightness with cultural symbolism.
Decorative Arts and Furniture
Baroque decorative arts feature intricate carvings, gilded finishes, and dramatic, bold forms emphasizing grandeur and movement, often seen in sumptuous furniture with curvaceous legs and ornate motifs. Chinoiserie, inspired by East Asian aesthetics, incorporates delicate lacquer work, asymmetrical designs, and fanciful motifs such as pagodas, dragons, and floral patterns, often applied to cabinets, screens, and porcelain. Both styles reflect cultural exchange and evolving tastes in European furniture, with Baroque emphasizing opulence and Chinoiserie highlighting exotic elegance.
Cultural Symbolism and Meanings
Baroque art, originating in 17th-century Europe, symbolizes power, grandeur, and religious intensity through its dramatic use of light, intricate details, and emotional depth. Chinoiserie reflects Western fascination with East Asian aesthetics, representing exoticism, elegance, and cultural exchange, often characterized by stylized motifs, pagodas, and delicate porcelain designs. The cultural symbolism in Baroque emphasizes divine authority and European aristocracy, while Chinoiserie conveys a romanticized, idealized vision of Asian culture that influenced decorative arts and architecture.
Baroque vs Chinoiserie in Modern Design
Baroque in modern design emphasizes opulence and intricate detailing with bold curves and lavish ornamentation, creating a dramatic and luxurious atmosphere. Chinoiserie incorporates Asian-inspired motifs, delicate patterns, and a lighter color palette, offering an exotic, whimsical contrast to Baroque's grandeur. The fusion of Baroque's richness with Chinoiserie's playful elegance results in eclectic interiors that balance Western excess with Eastern refinement.
Lasting Legacy and Global Impact
Baroque art, characterized by dramatic intensity, grandeur, and intricate detail, has influenced European architecture, music, and visual arts, leaving a lasting legacy seen in iconic landmarks such as St. Peter's Basilica and Versailles. Chinoiserie, reflecting Western interpretations of East Asian aesthetics during the 17th and 18th centuries, introduced exotic motifs and decorative styles that permeated European design, fashion, and interior decor. Both movements facilitated cross-cultural exchange, embedding Oriental elements into Western art while Baroque's dramatic style shaped global artistic trends and religious architecture.
Baroque Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com