Sculpture transforms raw materials like stone, metal, and clay into expressive three-dimensional art that captures movement, emotion, and form. This timeless art form has evolved through various cultures and historical periods, reflecting societal values and artistic innovation. Discover how sculpture influences your appreciation of art by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
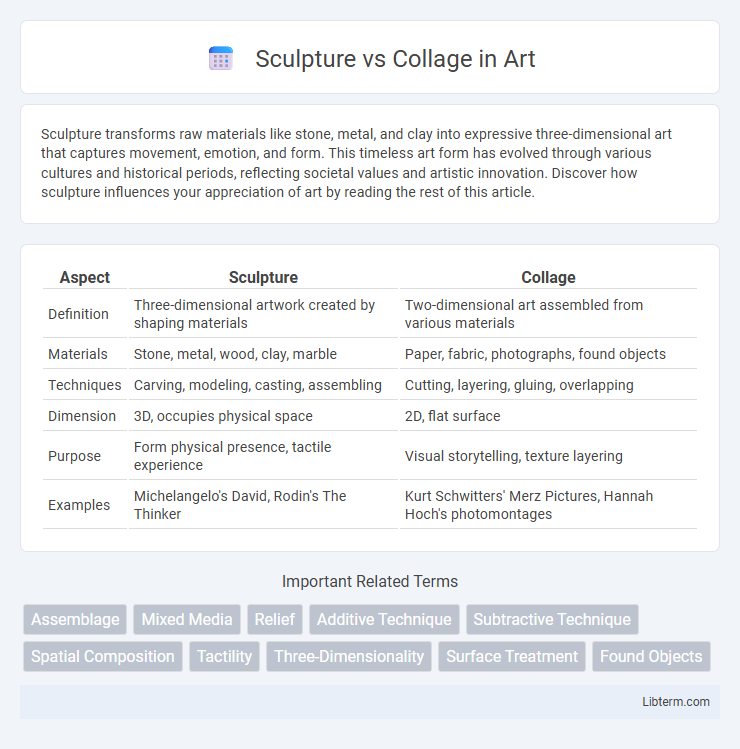
| Aspect | Sculpture | Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional artwork created by shaping materials | Two-dimensional art assembled from various materials |
| Materials | Stone, metal, wood, clay, marble | Paper, fabric, photographs, found objects |
| Techniques | Carving, modeling, casting, assembling | Cutting, layering, gluing, overlapping |
| Dimension | 3D, occupies physical space | 2D, flat surface |
| Purpose | Form physical presence, tactile experience | Visual storytelling, texture layering |
| Examples | Michelangelo's David, Rodin's The Thinker | Kurt Schwitters' Merz Pictures, Hannah Hoch's photomontages |
Understanding Sculpture and Collage
Sculpture involves creating three-dimensional art by shaping materials such as clay, stone, metal, or wood, emphasizing form, volume, and space. Collage is a technique that assembles various two-dimensional materials like paper, photographs, and fabric onto a surface to create a unified composition. Understanding sculpture requires an appreciation of its tactile, spatial qualities, while collage relies on layering and juxtaposition of textures and imagery.
Historical Origins of Sculpture and Collage
Sculpture originated in prehistoric times with carved stone and clay figures, evolving through ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman civilizations as a prominent form of three-dimensional art. Collage emerged in the early 20th century, pioneered by Cubist artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, combining paper, fabric, and found objects to create layered, two-dimensional compositions. The historical development of sculpture emphasizes durability and form, while collage highlights fragmentation and assemblage in modern artistic exploration.
Materials and Techniques Used
Sculpture primarily utilizes materials such as stone, metal, clay, and wood, shaped through carving, modeling, casting, or assembling to create three-dimensional forms. Collage involves adhering various materials like paper, fabric, photographs, and found objects onto a flat surface, employing techniques such as cutting, layering, and gluing. The tactile manipulation in sculpture contrasts with the compositional layering central to collage, highlighting different artistic approaches to texture and form.
Key Differences in Artistic Process
Sculpture involves shaping three-dimensional materials such as clay, metal, or stone through carving, modeling, or assembling to create a singular, tactile form. Collage focuses on assembling various two-dimensional materials like paper, photographs, and fabric onto a flat surface, emphasizing layering and juxtaposition. The artistic process in sculpture prioritizes volume, mass, and spatial interaction, while collage centers on composition, texture, and visual narrative through diverse elements.
Iconic Examples of Sculpture and Collage
Michelangelo's David exemplifies iconic sculpture through its masterful marble craftsmanship and human anatomical precision, symbolizing Renaissance artistic triumph. Pablo Picasso's "Still Life with Chair Caning" revolutionizes collage by integrating oil, paper, and rope to challenge traditional art boundaries and pioneer Cubist aesthetics. Both forms emphasize distinct creative processes: sculpture offers three-dimensional realism, while collage leverages mixed media to construct fragmented, conceptual narratives.
Expressive Potential: 3D vs 2D Art
Sculpture offers unparalleled expressive potential through its three-dimensional form, allowing artists to manipulate space, volume, and texture for immersive sensory experiences. Collage, confined to two dimensions, excels in layering diverse materials and images to create complex visual narratives and symbolic juxtapositions. The tactile depth of sculpture contrasts with the conceptual richness of collage, each medium harnessing unique spatial dynamics to evoke emotional resonance.
Popular Movements and Influential Artists
Sculpture and collage have each played pivotal roles in modern and contemporary art movements, with sculpture prominently featured in Cubism and Abstract Expressionism through artists like Pablo Picasso and Henry Moore. Collage gained prominence in Dada and Surrealism, championed by pioneers such as Hannah Hoch and Kurt Schwitters, who utilized found materials to challenge traditional aesthetics. Both mediums continue to inspire innovative practices in assemblage and mixed media, reflecting evolving artistic explorations.
Display and Interpretation in Galleries
Sculpture in galleries offers a three-dimensional experience, allowing viewers to engage with form, texture, and spatial relationships from multiple angles, enhancing tactile interpretation. Collage presents layered imagery and mixed media on a typically two-dimensional plane, encouraging viewers to decode visual narratives and symbolic juxtapositions closely. The display of sculpture often involves strategic lighting and placement to emphasize volume and shadow, while collage relies on framing and positioning to highlight intricate details and thematic complexity.
Contemporary Trends in Sculpture and Collage
Contemporary sculpture increasingly incorporates mixed media, digital technology, and interactive elements, pushing boundaries beyond traditional materials like stone or bronze. Collage evolves through layering diverse physical and digital imagery, reflecting themes of fragmentation and hybridity in modern visual culture. Both practices engage with spatial dynamics and viewer interaction, emphasizing conceptual depth and multidisciplinary approaches.
Choosing Between Sculpture and Collage for Creative Expression
Sculpture offers a three-dimensional medium that emphasizes form, space, and tactile interaction, making it ideal for artists seeking to explore volume and physical presence. Collage provides a versatile, two-dimensional platform that combines various materials and images, allowing for dynamic layering and conceptual depth in visual storytelling. Selecting between sculpture and collage depends on the desired sensory engagement and narrative complexity an artist aims to achieve in their creative expression.
Sculpture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com