Minimalist design focuses on simplicity by emphasizing clean lines, open spaces, and essential elements to create a calming and clutter-free environment. This approach enhances functionality while promoting elegance and clarity in both physical spaces and digital interfaces. Discover how incorporating minimalist principles can elevate your lifestyle and productivity by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
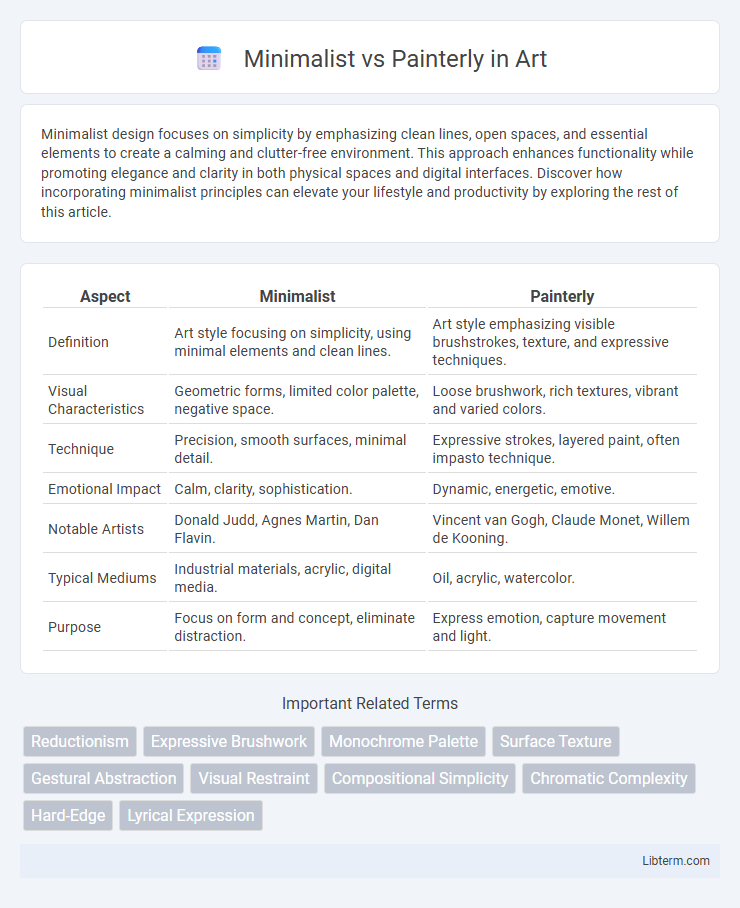
| Aspect | Minimalist | Painterly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style focusing on simplicity, using minimal elements and clean lines. | Art style emphasizing visible brushstrokes, texture, and expressive techniques. |
| Visual Characteristics | Geometric forms, limited color palette, negative space. | Loose brushwork, rich textures, vibrant and varied colors. |
| Technique | Precision, smooth surfaces, minimal detail. | Expressive strokes, layered paint, often impasto technique. |
| Emotional Impact | Calm, clarity, sophistication. | Dynamic, energetic, emotive. |
| Notable Artists | Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, Dan Flavin. | Vincent van Gogh, Claude Monet, Willem de Kooning. |
| Typical Mediums | Industrial materials, acrylic, digital media. | Oil, acrylic, watercolor. |
| Purpose | Focus on form and concept, eliminate distraction. | Express emotion, capture movement and light. |
Understanding Minimalist and Painterly Art Styles
Minimalist art focuses on simplicity, using basic shapes, limited color palettes, and clean lines to emphasize form and space, stripping away unnecessary details to evoke clarity and tranquility. Painterly art embraces visible brushstrokes, texture, and dynamic movement, highlighting the artist's technique and emotional expression through layered, often vibrant, surfaces. Understanding these styles involves recognizing Minimalism's pursuit of purity and restraint contrasted with Painterly art's emphasis on gestural marks and expressive complexity.
Origins and Historical Context
Minimalist art emerged in the 1960s as a reaction against the emotional intensity of Abstract Expressionism, emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and industrial materials to celebrate purity and objectivity. Painterly style dates back to the Renaissance but gained prominence in the 19th century, characterized by loose brushwork, visible strokes, and a focus on texture and light to capture emotion and spontaneity. Both movements reflect distinct philosophical approaches: Minimalism rooted in modernist ideals of reduction and clarity, and Painterly grounded in expressive, tactile engagement with the medium.
Key Characteristics of Minimalism
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity through clean lines, geometric shapes, and a limited color palette, often using monochromatic schemes to create a sense of calm and order. It prioritizes negative space and eliminates unnecessary details, highlighting functionality and form over decoration. The style uses industrial materials like steel, glass, and concrete, showcasing an uncluttered and streamlined aesthetic.
Defining Features of Painterly Techniques
Painterly techniques emphasize visible brushstrokes, texture, and a dynamic use of color that conveys movement and emotion rather than precise detail. Unlike minimalist art, which relies on simplicity, clean lines, and reduction of form, painterly works celebrate the physicality of paint and the artist's hand. This approach often results in layered, expressive surfaces that engage viewers through rich visual complexity and spontaneity.
Color Use in Minimalism vs Painterly Art
Minimalist art emphasizes the use of a limited color palette, often focusing on monochromatic schemes or primary colors to create simplicity and clarity. Painterly art features rich, varied colors with complex layering and blending, highlighting texture and brushwork to evoke emotion and depth. The contrast between Minimalism's controlled color restraint and Painterly's vibrant, dynamic color application defines their distinct visual and emotional impact.
Emotional Impact and Viewer Response
Minimalist art evokes emotional impact through simplicity, using clean lines and limited color palettes to create a sense of calm, clarity, and introspection. Painterly styles engage viewers with expressive brushstrokes, textured surfaces, and dynamic compositions that convey intense feelings and emotional depth. The viewer response in minimalist works often leans toward contemplation and tranquility, while painterly art stimulates emotional intensity and visceral reactions.
Materials and Methods in Each Style
Minimalist art emphasizes simplicity through the use of basic materials such as industrial paint, canvas, and geometric shapes applied with precision and uniform techniques to eliminate emotional expression. Painterly style utilizes rich textures, varied brushstrokes, and thicker application of oil or acrylic paints to convey emotion and movement, often highlighting the artist's hand in the work. Methods in minimalist art prioritize uniformity and repetition, while painterly techniques focus on spontaneity and expressive layering of colors.
Notable Artists and Influential Works
Minimalist art, exemplified by artists like Donald Judd and Agnes Martin, emphasizes simplicity, geometric forms, and monochromatic palettes, with notable works such as Judd's "Untitled" (1969) and Martin's "Untitled #3" (1974) defining the movement. Painterly art, characterized by expressive brushstrokes and vibrant colors, is represented by figures like Willem de Kooning and Francis Bacon, whose influential works include de Kooning's "Woman I" (1950-52) and Bacon's "Study after Velazquez's Portrait of Pope Innocent X" (1953). These distinct styles highlight Minimalism's focus on form and austerity versus Painterly art's dynamic texture and emotional intensity.
Minimalist vs Painterly in Contemporary Art
Minimalist art emphasizes simplicity, geometric forms, and limited color palettes, focusing on purity of form and space to evoke clarity and order in contemporary art. Painterly art in contrast showcases expressive brushwork, texture, and dynamic movement, highlighting emotional intensity and the artist's hand. Contemporary art often juxtaposes Minimalist precision against Painterly expressiveness to explore the tension between structure and spontaneity.
Choosing Between Minimalist and Painterly Approaches
Choosing between minimalist and painterly approaches depends on the desired emotional impact and visual complexity; minimalist designs emphasize simplicity, clarity, and space, making them suitable for conveying straightforward messages and modern aesthetics. Painterly styles, characterized by textured brushwork and rich color layers, evoke emotion and depth, ideal for storytelling and expressive artwork. Evaluating project goals and audience perception helps determine whether the clean, structured look of minimalism or the dynamic, textured feel of painterly techniques will resonate best.
Minimalist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com