Expressionism emphasizes emotional experience over physical reality, using bold colors and distorted forms to convey inner feelings and subjective perspectives. This artistic movement profoundly influenced painting, literature, theater, and cinema, reflecting the anxieties and turmoil of early 20th-century life. Discover how expressionism reshaped modern art and culture by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
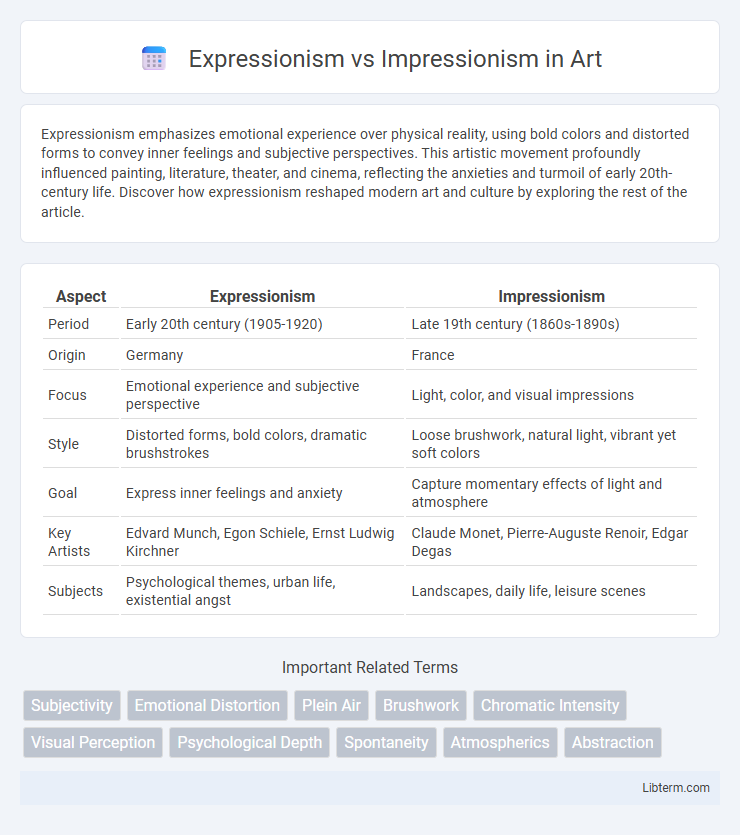
| Aspect | Expressionism | Impressionism |
|---|---|---|
| Period | Early 20th century (1905-1920) | Late 19th century (1860s-1890s) |
| Origin | Germany | France |
| Focus | Emotional experience and subjective perspective | Light, color, and visual impressions |
| Style | Distorted forms, bold colors, dramatic brushstrokes | Loose brushwork, natural light, vibrant yet soft colors |
| Goal | Express inner feelings and anxiety | Capture momentary effects of light and atmosphere |
| Key Artists | Edvard Munch, Egon Schiele, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner | Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Edgar Degas |
| Subjects | Psychological themes, urban life, existential angst | Landscapes, daily life, leisure scenes |
Defining Expressionism and Impressionism
Expressionism emphasizes emotional experience over physical reality, using distorted forms and vivid colors to evoke subjective feelings. Impressionism captures fleeting moments of light and atmosphere, relying on loose brushwork and naturalistic depictions to portray sensory impressions. Both movements revolutionized art by challenging traditional representation, but Expressionism prioritizes inner turmoil while Impressionism focuses on external perception.
Historical Contexts and Origins
Expressionism originated in early 20th-century Germany, reflecting emotional experience through distorted forms and bold colors as a reaction to industrialization and World War I anxieties. Impressionism emerged in 19th-century France, emphasizing light and natural scenery through loose brushwork and vibrant palettes, influenced by modern urban life and advances in optical science. Both movements challenged traditional academic art, but Expressionism focused on inner turmoil while Impressionism captured fleeting moments of external reality.
Key Characteristics and Techniques
Expressionism emphasizes intense emotion and subjective perspective, using bold colors and distorted forms to convey inner experiences. Impressionism captures fleeting moments with loose brushwork, light effects, and vibrant color palettes, focusing on natural scenes and atmospheric conditions. Techniques in Expressionism include exaggerated lines and stark contrasts, whereas Impressionism relies on quick, visible strokes and blending to depict light and movement.
Influential Artists and Their Masterpieces
Expressionism, driven by artists like Edvard Munch with his iconic painting "The Scream" and Egon Schiele known for his raw, emotional portraits, emphasizes subjective experience and emotional intensity through distorted forms and vivid colors. Impressionism features masters such as Claude Monet, celebrated for "Impression, Sunrise," which captures fleeting light effects, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir, renowned for vibrant depictions of social scenes and landscapes. Both movements revolutionized art by focusing on perception and emotion but differ in technique, with Impressionism rooted in light and natural observation, while Expressionism channels inner turmoil and psychological depth.
Use of Color and Brushwork
Expressionism employs bold, often non-representational colors and aggressive brushwork to evoke emotional intensity and subjective experience, creating a dramatic, sometimes distorted visual impact. Impressionism utilizes lighter, more natural color palettes with short, rapid brush strokes that capture the fleeting effects of light and atmosphere, emphasizing realism and momentary impressions. The distinct application of color and brushwork in Expressionism aims to convey inner feelings, whereas Impressionism focuses on representing external visual reality.
Subject Matter and Themes
Expressionism emphasizes emotional experience and often portrays distorted, exaggerated subjects to convey inner feelings, focusing on themes of angst, alienation, and psychological turmoil. Impressionism captures fleeting moments of light and color in everyday scenes, emphasizing natural landscapes, leisure activities, and urban life with themes of beauty and perception. While Impressionism prioritizes visual reality and sensory impressions, Expressionism delves into subjective interpretation and emotional depth.
Emotional Impact vs Visual Experience
Expressionism emphasizes intense emotional impact by using distorted forms and vivid colors to convey inner feelings and subjective experiences. Impressionism prioritizes visual experience through light and color, capturing fleeting moments and the natural environment with soft brushstrokes and subtle tonal variations. While Expressionism engages viewers with psychological depth, Impressionism invites appreciation of atmospheric effects and sensory perception.
Influence on Modern Art Movements
Expressionism, with its emphasis on emotional experience and distortion, profoundly influenced modern movements such as Abstract Expressionism and Surrealism by encouraging artists to explore subjective reality and inner emotions. Impressionism's focus on light, color, and momentary perception paved the way for movements like Fauvism and Cubism, which further deconstructed and reinterpreted visual reality. Both movements challenged traditional techniques and perspectives, laying the groundwork for the diverse experimentation that defines modern art.
Critical Reception and Legacy
Expressionism faced initial criticism for its raw emotion and distortion, yet it profoundly influenced modern art by emphasizing subjective experience and psychological depth. Impressionism, once derided for its loose brushwork and focus on light, gained acclaim for capturing fleeting moments and revolutionizing visual perception. Both movements forged foundational legacies, shaping subsequent artistic developments and expanding the boundaries of visual expression.
Expressionism vs Impressionism: Lasting Impact on Art
Expressionism and Impressionism significantly shaped modern art by challenging traditional perspectives; Expressionism emphasized emotional intensity and subjective experience, while Impressionism focused on capturing light and momentary impressions. Expressionism's lasting impact is evident in its influence on abstract art and modern psychological exploration in painting, whereas Impressionism revolutionized techniques related to color and outdoor scenes. Both movements expanded artistic boundaries, with Expressionism driving emotional depth and Impressionism advancing visual perception realism.
Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com