Still life paintings capture the beauty of inanimate objects through meticulous composition and lighting, emphasizing textures and forms. This art form offers a unique opportunity to observe everyday items from a fresh perspective, revealing hidden details and symbolism. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques and meanings that bring still life to life.
Table of Comparison
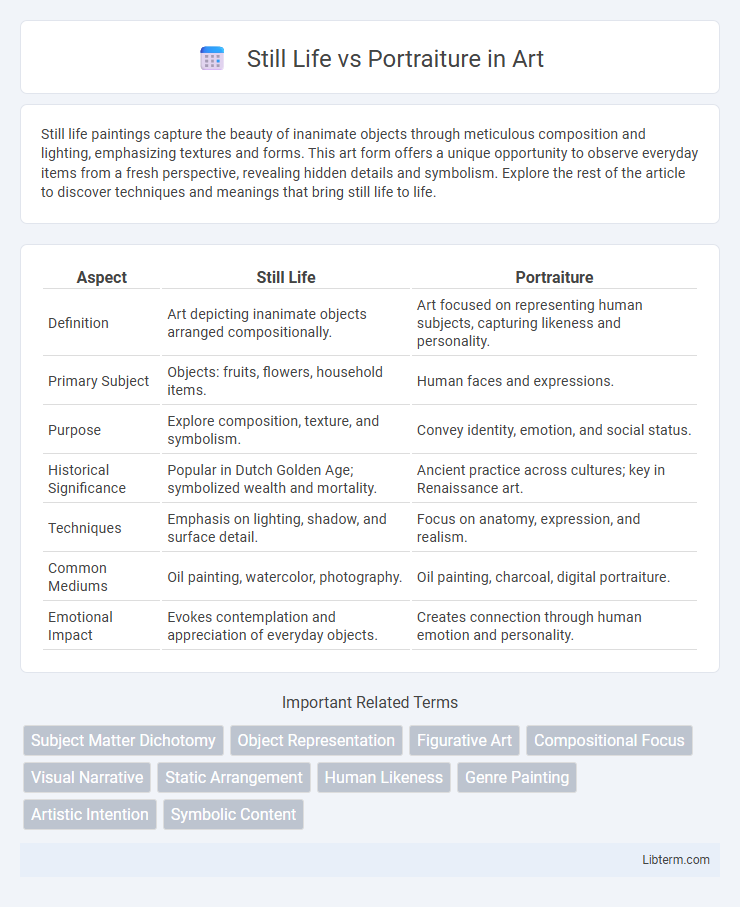
| Aspect | Still Life | Portraiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art depicting inanimate objects arranged compositionally. | Art focused on representing human subjects, capturing likeness and personality. |
| Primary Subject | Objects: fruits, flowers, household items. | Human faces and expressions. |
| Purpose | Explore composition, texture, and symbolism. | Convey identity, emotion, and social status. |
| Historical Significance | Popular in Dutch Golden Age; symbolized wealth and mortality. | Ancient practice across cultures; key in Renaissance art. |
| Techniques | Emphasis on lighting, shadow, and surface detail. | Focus on anatomy, expression, and realism. |
| Common Mediums | Oil painting, watercolor, photography. | Oil painting, charcoal, digital portraiture. |
| Emotional Impact | Evokes contemplation and appreciation of everyday objects. | Creates connection through human emotion and personality. |
Introduction to Still Life and Portraiture
Still life and portraiture are two fundamental genres in visual art, each emphasizing different subjects and techniques. Still life focuses on inanimate objects, carefully arranged to explore composition, texture, and light, often symbolizing deeper themes or everyday life. Portraiture captures the human face and expression, aiming to convey personality, emotion, and identity through pose, lighting, and detail.
Defining Still Life: Key Characteristics
Still life is an art genre emphasizing inanimate objects, such as fruits, flowers, and everyday items, meticulously arranged to highlight texture, form, and composition. Unlike portraiture, which captures human expressions and personality, still life focuses on the symbolic and aesthetic qualities of objects, often conveying deeper meanings through their placement and lighting. Key characteristics include controlled lighting, detailed attention to surface detail, and an emphasis on balance and harmony within the composition.
Understanding Portraiture: Essential Elements
Portraiture centers on capturing the essence and personality of a subject through facial expression, posture, and gaze, emphasizing emotional connection. Key elements include composition, lighting, and background, which work together to highlight the subject's unique traits and mood. Mastery of these components allows artists to convey identity and narrative beyond mere likeness.
Historical Evolution of Still Life and Portraiture
Still life and portraiture have evolved through distinct historical trajectories, with still life emerging prominently during the Renaissance as a means to showcase everyday objects and symbolize themes like mortality and abundance. Portraiture dates back to ancient civilizations, serving primarily as a tool for social status, identity, and political power, with its sophistication increasing during the Renaissance and Baroque periods through enhanced realism and psychological depth. Both genres reflect cultural shifts, technological advancements, and changing artistic priorities from classical antiquity to modern art movements.
Techniques and Artistic Approaches
Still life techniques emphasize meticulous composition, lighting, and texture to capture inanimate objects' details, often using chiaroscuro to create depth. Portraiture techniques focus on capturing the subject's personality and emotion through facial expressions, pose, and eye contact, utilizing brushwork and color to convey mood. Both artistic approaches rely on mastering light manipulation, but still life prioritizes static arrangement while portraiture demands dynamic representation of human features.
Subject Matter and Symbolism
Still life art emphasizes inanimate objects such as fruits, flowers, and household items, often arranged to symbolize themes like mortality, abundance, or beauty. Portraiture centers on human subjects, capturing identity, emotion, and social status through facial expressions, attire, and posture. Symbolism in portraits frequently relates to personality traits or cultural values, while still lifes use iconography to convey deeper philosophical or moral messages.
Composition and Lighting Differences
Still life composition emphasizes arrangement and balance of inanimate objects, often using controlled, directional lighting to highlight textures and shapes. Portraiture focuses on the subject's facial features and expressions, utilizing lighting techniques like Rembrandt or butterfly lighting to create depth and mood. The compositional intent in portraiture centers on capturing personality, whereas still life prioritizes the harmonious interplay of form and shadow.
Emotional Impact and Storytelling
Still life compositions evoke emotional impact by using symbolism, color, and texture to convey moods or themes without human presence, allowing viewers to interpret personal meanings deeply. Portraiture captures the complexity of human emotions through facial expressions, posture, and gaze, directly communicating individual narratives and psychological states. Both genres utilize visual storytelling, with still life emphasizing metaphorical messages and portraiture presenting explicit emotional connections to the subject.
Contemporary Trends in Both Genres
Contemporary still life photography emphasizes minimalism, abstraction, and the interplay of natural light, often incorporating everyday objects to evoke emotional responses and challenge traditional compositions. Portraiture in the modern era trends toward candid, diverse representations, exploring identity, cultural narratives, and incorporating digital manipulation to enhance storytelling. Both genres increasingly utilize mixed media and technology, reflecting a convergence of artistic techniques that push boundaries beyond conventional aesthetics.
Choosing Between Still Life and Portraiture
Choosing between still life and portraiture depends on the artist's intention and subject preference. Still life emphasizes the arrangement of inanimate objects to explore composition, texture, and light, allowing for controlled artistic expression. Portraiture captures human emotion and personality, requiring skill in anatomy and facial expression to create a compelling representation.
Still Life Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com