Casein and acrylic are two distinct types of paint mediums used by artists, each offering unique properties and effects. Casein, made from milk protein, provides a matte finish and fast drying time, ideal for creating rich textures and layering, while acrylic paint, a synthetic polymer, is known for its versatility, vibrant colors, and water-resistant qualities once dry. Explore the article to discover how choosing between casein and acrylic can enhance Your artistic projects.
Table of Comparison
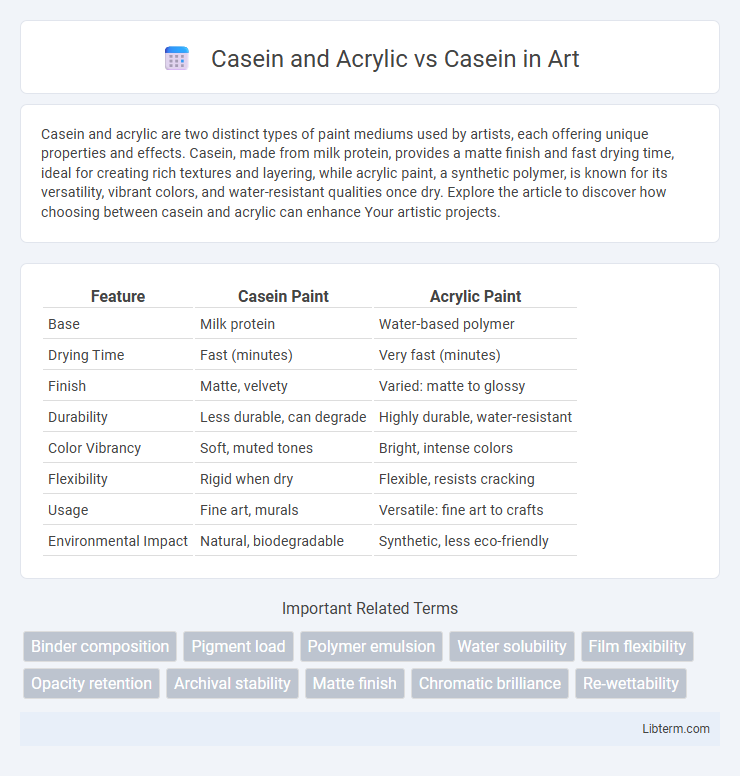
| Feature | Casein Paint | Acrylic Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Milk protein | Water-based polymer |
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes) | Very fast (minutes) |
| Finish | Matte, velvety | Varied: matte to glossy |
| Durability | Less durable, can degrade | Highly durable, water-resistant |
| Color Vibrancy | Soft, muted tones | Bright, intense colors |
| Flexibility | Rigid when dry | Flexible, resists cracking |
| Usage | Fine art, murals | Versatile: fine art to crafts |
| Environmental Impact | Natural, biodegradable | Synthetic, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Casein and Acrylic Paints
Casein paint, derived from milk protein, offers a durable, fast-drying, and water-soluble medium favored for its matte finish and excellent pigment retention. Acrylic paint, composed of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, dries quickly to a flexible, water-resistant surface suitable for diverse techniques and supports. Both mediums provide versatility in artistic expression, with casein excelling in traditional applications and acrylic prized for its adaptability and vibrant color retention.
What is Casein Paint?
Casein paint is a traditional, water-soluble medium made from milk protein, known for its fast-drying and durable properties. Unlike acrylic paint, casein offers a matte finish with excellent adhesion to various surfaces, making it ideal for fine art and decorative painting. Its natural composition allows for rich pigmentation while being environmentally friendly and non-toxic compared to synthetic acrylics.
Understanding Acrylic Paint
Acrylic paint is a fast-drying medium composed of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, offering superior water resistance and flexibility compared to traditional casein paint, which is derived from milk protein and is more fragile when dry. While casein paint allows for smooth blending and a matte finish favored in classical art techniques, acrylics provide vibrant colors, durability, and versatility suitable for a wide range of surfaces including canvas, wood, and fabric. Understanding acrylic paint's polymer-based formulation highlights its advantages in longevity and adaptability, making it a preferred choice for contemporary artists seeking both intensity and resilience in their work.
Key Differences Between Casein and Acrylic
Casein paint is a natural, water-soluble medium derived from milk protein, offering a matte finish and excellent adhesion on porous surfaces, whereas acrylic paint is a synthetic polymer that dries quickly to a durable, flexible, and water-resistant finish. Casein is valued for its ability to create rich, velvety textures and slow drying times that allow blending, but it is less flexible and can crack over time compared to acrylic. Acrylic excels in versatility, longevity, and vibrant color retention, making it ideal for outdoor and mixed-media applications.
Casein vs Casein: Varieties and Uses
Casein varieties include acid casein, rennet casein, and caseinates, each distinguished by their production methods and solubility, influencing their applications in food, adhesives, and cosmetics. Acid casein is typically used in cheese making and adhesives, while rennet casein is favored for its smooth texture in dairy products and specialized adhesives. Caseinates, such as sodium or calcium caseinate, offer enhanced solubility and nutritional benefits, making them popular in protein supplements and processed foods.
Performance and Application: Casein vs Acrylic
Casein paint offers excellent adhesion, durability, and matte finish, making it ideal for fine art and traditional applications, while acrylic paint excels in versatility, fast drying time, and water resistance, preferred for modern and outdoor projects. Performance-wise, acrylics provide better flexibility and are less prone to cracking over time compared to casein, which can be reactivated with water even after drying. For application, casein requires a porous surface and is often favored for detailed work and layering, whereas acrylic works effectively on various surfaces, including canvas, wood, and plastic, supporting a broader range of artistic techniques.
Durability and Longevity: Which Paint Lasts Longer?
Casein paint, made from milk protein, offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and sunlight compared to acrylic paint. Acrylic paint, composed of synthetic polymers, provides superior longevity and resistance to environmental factors like UV rays and humidity, making it ideal for outdoor and long-term applications. Artists seeking lasting vibrancy and durability typically prefer acrylics due to their enhanced weatherproof qualities and flexibility on various surfaces.
Surface Compatibility: Casein and Acrylic Compared
Casein paint adheres effectively to porous surfaces such as wood, paper, and canvas, offering a matte finish with good breathability, while acrylic paint provides strong adhesion on a wider range of surfaces, including metal, glass, and plastic, due to its synthetic polymer base. The flexibility and water resistance of acrylic make it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications, unlike casein which can deteriorate when exposed to moisture. Surface preparation for casein requires more absorbent substrates, whereas acrylic's versatile bonding properties allow it to be applied on primed or unprimed surfaces without extensive treatment.
Artistic Effects and Finishes
Casein and Acrylic both offer unique artistic effects, with Casein providing a matte, velvety finish ideal for blending and layering subtle textures, while Acrylic dries quickly to a vibrant, glossy surface that enhances color intensity. Casein's natural protein base allows for smooth brushstrokes and soft transitions, favored in traditional and portrait painting, whereas Acrylic's synthetic composition supports versatility in creating sharp edges, impasto, and mixed-media applications. The finish of Casein remains more delicate and matte, making it suitable for works requiring fine detail, compared to the durable, water-resistant finish of Acrylic that preserves vividness on various substrates.
Choosing the Right Paint for Your Project
Casein paint, derived from milk protein, offers excellent adhesion and a matte finish ideal for fine art and traditional projects, while acrylic paint provides durability, vibrant colors, and fast drying suitable for versatile uses and outdoor applications. When choosing between casein and acrylic, consider the project's surface, desired texture, and longevity requirements since casein excels on porous surfaces but is less water-resistant. Acrylic's synthetic composition ensures greater flexibility and permanence, making it the preferred choice for commercial or long-lasting artworks.
Casein and Acrylic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com