Assemblage is a dynamic artistic technique that involves creating three-dimensional compositions by combining various found objects and materials. This method transforms everyday items into expressive artworks full of depth and texture, allowing artists to convey complex narratives and emotions. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how assemblage can inspire your creativity and expand your artistic boundaries.
Table of Comparison
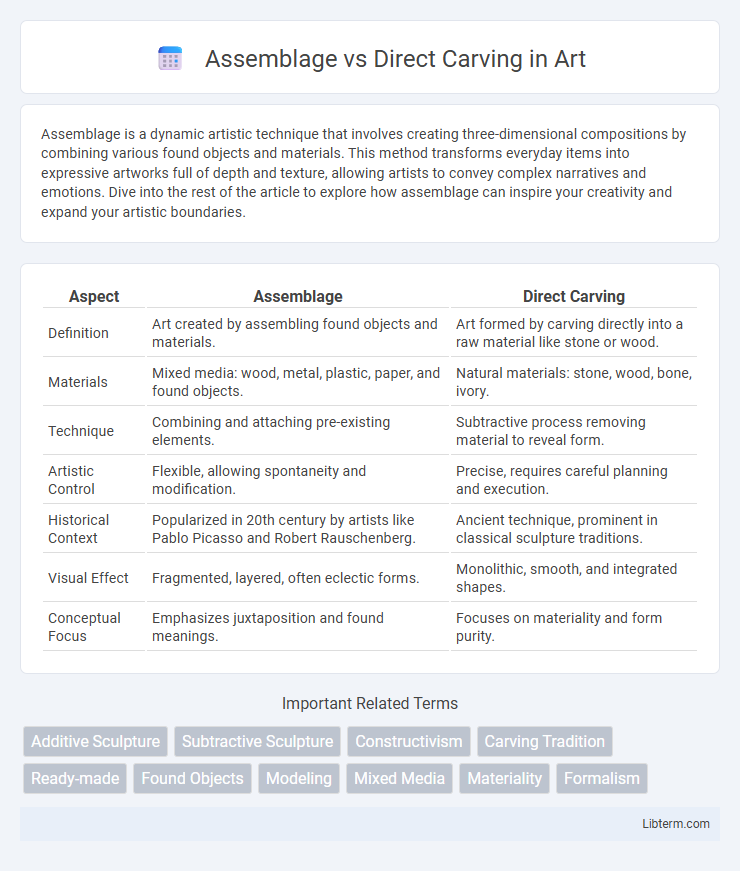
| Aspect | Assemblage | Direct Carving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created by assembling found objects and materials. | Art formed by carving directly into a raw material like stone or wood. |
| Materials | Mixed media: wood, metal, plastic, paper, and found objects. | Natural materials: stone, wood, bone, ivory. |
| Technique | Combining and attaching pre-existing elements. | Subtractive process removing material to reveal form. |
| Artistic Control | Flexible, allowing spontaneity and modification. | Precise, requires careful planning and execution. |
| Historical Context | Popularized in 20th century by artists like Pablo Picasso and Robert Rauschenberg. | Ancient technique, prominent in classical sculpture traditions. |
| Visual Effect | Fragmented, layered, often eclectic forms. | Monolithic, smooth, and integrated shapes. |
| Conceptual Focus | Emphasizes juxtaposition and found meanings. | Focuses on materiality and form purity. |
Introduction to Assemblage and Direct Carving
Assemblage is a sculptural technique that involves creating three-dimensional compositions by combining found objects or disparate materials into a unified artwork, emphasizing conceptual expression and material juxtaposition. Direct carving, or *taille directe*, is a subtractive process where the sculptor carves directly into stone, wood, or other materials without preparatory models, valuing spontaneity and the natural characteristics of the material. Both methods represent distinct approaches to sculpture, with assemblage rooted in construction and assemblage of elements, while direct carving emphasizes material transformation and tactile engagement.
Historical Evolution of Both Techniques
Assemblage and direct carving represent two distinct artistic techniques that have evolved over time with unique historical contexts. Assemblage emerged in the early 20th century, influenced by Cubism and Dada, as artists like Pablo Picasso and Marcel Duchamp repurposed found objects to create new meanings, reflecting modernist challenges to traditional art forms. In contrast, direct carving dates back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece, emphasizing the artist's intimate engagement with raw materials like stone and wood, gaining renewed appreciation during the early 20th century with sculptors like Constantin Brancusi advocating for authenticity and tactile expression.
Defining Assemblage in Sculpture
Assemblage in sculpture refers to the technique of creating three-dimensional works by combining found objects and diverse materials, often repurposed, to form a cohesive artistic expression. Unlike direct carving, which involves shaping a solid material such as stone or wood, assemblage emphasizes construction through assembling pre-existing elements. This method allows artists to explore texture, context, and meaning by integrating everyday items into complex visual narratives.
Understanding Direct Carving
Direct carving emphasizes the artist's intimate engagement with raw materials such as stone, wood, or metal, allowing for spontaneous expressions shaped by the material's natural properties. This technique contrasts with assemblage, where multiple preformed objects are combined into a singular sculpture, often creating a narrative through juxtaposition. Mastery of direct carving demands a deep understanding of the tools, material grain, and structural integrity to reveal form without pre-designed models.
Materials Used in Assemblage and Direct Carving
Assemblage involves combining diverse materials such as found objects, metal, wood, paper, and fabric to create a three-dimensional artwork, often incorporating industrial or everyday items. Direct carving primarily utilizes traditional sculpting materials like stone, wood, and ivory, allowing artists to shape and reveal forms through removal of material. The choice of materials in assemblage offers versatility and mixed media textures, whereas direct carving emphasizes the intrinsic qualities and natural textures of a single medium.
Creative Process Comparison
Assemblage involves combining found objects and materials in a spontaneous, often unpredictable manner, fostering creativity through eclectic juxtaposition and reinterpretation of existing elements. Direct carving requires an intimate engagement with raw material, emphasizing control and intuition as artists reveal forms through subtractive techniques, making the process more meditative and deliberate. Both methods challenge traditional sculptural practices but differ significantly in execution, material interaction, and conceptual development.
Notable Artists and Influential Works
Assemblage, characterized by the combination of found objects into cohesive sculptures, is exemplified by artists like Louise Nevelson, whose monumental wooden wall constructions revolutionized the form. Direct carving, involving the manual shaping of materials such as stone or wood without pre-existing molds, is associated with Constantin Brancusi, whose seminal work "Bird in Space" redefined abstraction in sculpture. Both methods have significantly influenced modern art, with assemblage highlighting the transformation of everyday materials and direct carving emphasizing the artist's intimate engagement with raw media.
Aesthetics and Visual Impact
Assemblage art creates dynamic visual interest through the combination of diverse found objects, resulting in textured surfaces and layered meanings that provoke curiosity and interaction. Direct carving emphasizes the artist's intimate connection with the raw material, producing refined forms that highlight natural textures and reveal the inherent beauty of stone or wood. The aesthetics of assemblage rely on complexity and contrast, while direct carving offers a unified, often more organic visual impact rooted in craftsmanship.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Method
Assemblage offers versatility by combining diverse materials and found objects, enabling intricate compositions and conceptual depth, but it challenges artists with potential structural instability and material compatibility issues. Direct carving provides a tactile, immediate connection to the medium, resulting in unique, expressive works through subtractive techniques, yet it demands precision and limits error correction due to its irreversible nature. Both methods require distinct skill sets, with assemblage excelling in mixed-media creativity while direct carving emphasizes craftsmanship and material mastery.
Contemporary Trends and Future Perspectives
Assemblage and direct carving showcase contrasting techniques in contemporary sculpture, with assemblage emphasizing mixed media and found objects, fostering ecological awareness and sustainability in art practices. Direct carving experiences a resurgence through its tactile engagement and authenticity, appealing to artists prioritizing materiality and craftsmanship amid digital proliferation. Future perspectives suggest a hybrid approach blending assemblage's conceptual layering with the physical immediacy of direct carving, reflecting evolving cultural narratives and technological integration.
Assemblage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com