Structural lines are essential design elements that define and organize the form of a building or object, providing clarity and stability to the overall composition. They guide the viewer's eye and emphasize important features, helping to create a balanced and cohesive visual experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how structural lines transform your design projects.
Table of Comparison
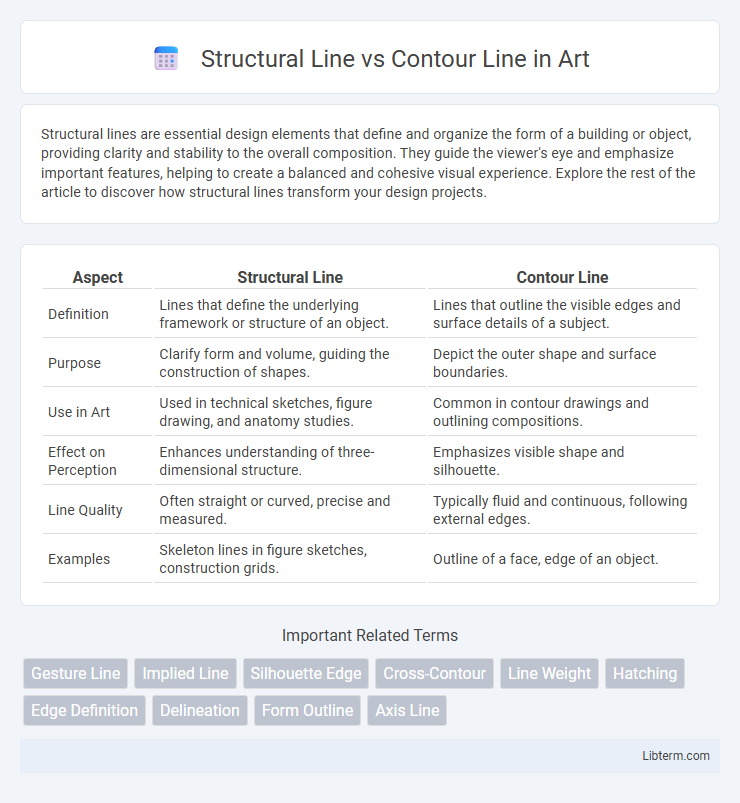
| Aspect | Structural Line | Contour Line |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lines that define the underlying framework or structure of an object. | Lines that outline the visible edges and surface details of a subject. |
| Purpose | Clarify form and volume, guiding the construction of shapes. | Depict the outer shape and surface boundaries. |
| Use in Art | Used in technical sketches, figure drawing, and anatomy studies. | Common in contour drawings and outlining compositions. |
| Effect on Perception | Enhances understanding of three-dimensional structure. | Emphasizes visible shape and silhouette. |
| Line Quality | Often straight or curved, precise and measured. | Typically fluid and continuous, following external edges. |
| Examples | Skeleton lines in figure sketches, construction grids. | Outline of a face, edge of an object. |
Introduction to Structural and Contour Lines
Structural lines represent the underlying framework or skeleton of an object, highlighting its essential form and spatial orientation. Contour lines, on the other hand, depict the surface edges and shapes, capturing the visible boundaries and curves that define the object's silhouette. Together, these lines provide a comprehensive understanding of both the internal structure and external appearance.
Defining Structural Lines in Art
Structural lines in art define the underlying framework of a composition by outlining the basic shapes and forms that organize spatial relationships and guide the viewer's eye. Unlike contour lines, which trace the external edges and surface details of objects, structural lines establish the foundational geometry, volume, and perspective critical for accurately representing three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional plane. Artists use structural lines to construct the proportional layout and ensure balance within the artwork before refining details with contour lines.
What are Contour Lines?
Contour lines represent lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation, illustrating the shape and elevation of the terrain. These lines help visualize landforms like hills, valleys, and slopes by indicating height differences and terrain steepness. Unlike structural lines, which show the orientation of geological features, contour lines specifically facilitate understanding topographical variations.
Key Differences Between Structural and Contour Lines
Structural lines represent the underlying framework or skeleton of a design, emphasizing the fundamental geometry and form, while contour lines depict the surface shape and elevation, outlining the object's external boundaries and curves. Structural lines often convey the object's essential construction elements, such as beams or supports, whereas contour lines provide detailed topographical or surface information that reflects the object's shape in three dimensions. Understanding the key differences between these lines is crucial for effectively interpreting architectural drawings, engineering blueprints, and topographic maps.
Functions and Uses of Structural Lines
Structural lines reveal the underlying framework and form of objects, essential in architectural and engineering drawings to define edges, corners, and joints that inform construction processes. These lines guide the interpretation of spatial relationships and load-bearing elements, ensuring accurate assembly and structural integrity. Unlike contour lines that represent surface elevation changes, structural lines emphasize the object's core geometry and support functions in design and fabrication.
The Role of Contour Lines in Drawing
Contour lines play a crucial role in drawing by representing the edges and surface boundaries of objects, thereby conveying volume and three-dimensional form on a two-dimensional plane. Unlike structural lines, which emphasize the underlying framework and proportions, contour lines define the precise shapes and curves that outline an object's visible features. These lines help artists create depth, enhance realism, and provide spatial context, making them essential for lifelike and detailed illustrations.
Visual Examples: Structural vs Contour Lines
Structural lines emphasize the underlying form and geometry of objects, highlighting edges and intersections that define shape and volume, such as the framework of a building or the skeleton of a figure. Contour lines follow the outer boundaries and surface edges, capturing the visible silhouette and subtle surface details, as seen in the outline of a human profile or the curves of a vase. Visual examples illustrate structural lines with angular, precise strokes reflecting construction, while contour lines use smooth, flowing lines to represent the object's shape and depth.
Techniques for Drawing Structural Lines
Techniques for drawing structural lines emphasize capturing the underlying form and volume of objects through lines that follow the object's three-dimensional structure, often using curved or parallel lines to indicate planes and surface direction. Artists use contour wrapping methods, cross-contour lines, and gesture drawing to build an accurate skeletal framework, aiding in realistic depth and proportion representation. Mastery of pressure control and line weight variation enhances the perception of dimensionality and solidity in structural line work.
Techniques for Drawing Contour Lines
Techniques for drawing contour lines include using smooth, continuous strokes to accurately depict the edges and surfaces of objects, emphasizing volume and depth without shading. Employing varying line weight enhances the perception of form, with thicker lines indicating prominent edges and thinner lines used for intricate details. Unlike structural lines that map the underlying framework or skeleton of a form, contour lines focus on outlining the visible boundaries, requiring careful observation to capture the subtle curves and shapes defining the subject's exterior.
When to Use Structural Line or Contour Line
Use structural lines when emphasizing the underlying framework or form of an object, highlighting edges, folds, and important shape-defining elements. Choose contour lines to depict the outer boundary or silhouette, capturing the object's overall shape and volume without internal detail. Structural lines are ideal for technical drawings or architectural plans, while contour lines suit sketches and illustrations emphasizing shape clarity.
Structural Line Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com