Mixed media art combines various materials and techniques, creating dynamic and textured visual experiences that challenge traditional art boundaries. This approach allows artists to blend painting, collage, photography, and digital elements, resulting in unique and expressive pieces. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mixed media can transform your artistic practice.
Table of Comparison
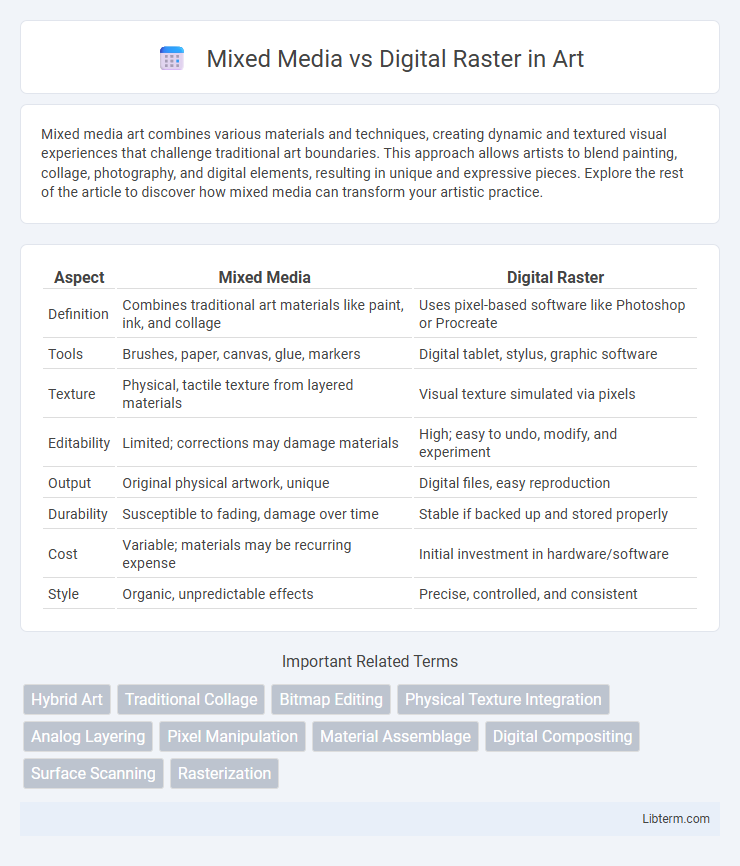
| Aspect | Mixed Media | Digital Raster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines traditional art materials like paint, ink, and collage | Uses pixel-based software like Photoshop or Procreate |
| Tools | Brushes, paper, canvas, glue, markers | Digital tablet, stylus, graphic software |
| Texture | Physical, tactile texture from layered materials | Visual texture simulated via pixels |
| Editability | Limited; corrections may damage materials | High; easy to undo, modify, and experiment |
| Output | Original physical artwork, unique | Digital files, easy reproduction |
| Durability | Susceptible to fading, damage over time | Stable if backed up and stored properly |
| Cost | Variable; materials may be recurring expense | Initial investment in hardware/software |
| Style | Organic, unpredictable effects | Precise, controlled, and consistent |
Understanding Mixed Media Art
Mixed media art combines traditional materials like paint, ink, and paper with digital techniques to create textured, layered compositions that emphasize tactile qualities and physical depth. Unlike digital raster art, which relies solely on pixel-based images generated or manipulated on a computer, mixed media embraces the interplay between analog and digital elements to produce unique, multidimensional artworks. Artists use mixed media to explore material contrasts and enhance visual storytelling, capitalizing on the tangible attributes that digital raster images inherently lack.
What is Digital Raster Art?
Digital raster art is created using pixel-based software such as Adobe Photoshop, where images are composed of a grid of individual pixels that define color and detail. This art form excels at producing rich textures, complex shading, and photo-realistic effects due to its resolution-dependent nature. Unlike mixed media, which combines traditional materials and techniques, digital raster art relies entirely on digital tools to manipulate images with precision and flexibility.
Key Characteristics of Mixed Media
Mixed media art combines traditional materials such as paint, ink, paper, and fabric to create textured, tactile surfaces that engage multiple senses. Its key characteristics include layering diverse elements, the physical manipulation of materials, and the integration of both two-dimensional and three-dimensional components, offering a rich, multisensory experience. Unlike digital raster images that rely on pixels and software manipulation, mixed media emphasizes hands-on techniques and the unique imperfections of handcrafted work.
Core Features of Digital Raster Techniques
Digital raster techniques excel in pixel-based image creation, allowing intricate detail and smooth gradients through high resolution and color depth. Core features include layering for complex compositions, blending modes for varied visual effects, and diverse brush tools that mimic traditional media textures. These tools offer precise control over image editing, enhancing flexibility and creative expression in digital art.
Tools and Materials: Traditional vs Digital
Mixed media art employs traditional tools such as acrylic paints, inks, charcoal, and textured paper, allowing for tactile layering and physical manipulation. Digital raster art relies on software like Adobe Photoshop and Procreate, using digital brushes, layers, and stylus tools to simulate textures and effects. While mixed media emphasizes physical materials and sensory interaction, digital raster prioritizes pixel-based editing, flexibility, and instant modification.
Creative Processes Compared
Mixed media art combines traditional materials like paint, paper, and textiles, allowing tactile experimentation and spontaneous textures that evolve through layering and physical manipulation. Digital raster art relies on pixel-based software tools such as Adobe Photoshop, enabling precise edits, layering, and effects with undo flexibility and infinite color palettes. Creative processes differ as mixed media emphasizes hands-on interaction and material unpredictability, while digital raster prioritizes control, repeatability, and seamless integration of multimedia elements.
Textures and Visual Effects
Mixed media techniques combine traditional textures like paint, fabric, and paper, creating rich tactile surfaces that contribute unique depth and complexity. Digital raster art excels in manipulating textures through software tools, allowing for precise control over layering, blending modes, and effects such as gradients, shadows, and highlights. The visual effects achievable in digital raster are highly versatile and easily editable, whereas mixed media delivers organic, unpredictable textures that add authenticity and physical dimension.
Flexibility and Editing Capabilities
Mixed media art offers unparalleled flexibility by combining traditional materials like paint, ink, and collage, allowing tactile experimentation and spontaneous creativity. Digital raster graphics provide advanced editing capabilities through software tools that enable precise adjustments, layering, and undo functions, enhancing efficiency and control. The blend of mixed media's hands-on adaptability with digital raster's powerful modification features caters to artists seeking both expressive freedom and refined technical manipulation.
Common Uses and Applications
Mixed media art combines traditional materials like paint, ink, and collage with digital techniques, making it popular in fine art, illustration, and experimental design projects. Digital raster images, composed of pixels, are widely used in web design, photo editing, and digital marketing due to their detail and scalability within software like Adobe Photoshop. Both mediums serve distinct purposes: mixed media excels in tactile, textured artworks, while digital raster graphics dominate commercial and digital platforms requiring precise, editable visuals.
Choosing Between Mixed Media and Digital Raster
Choosing between mixed media and digital raster depends on the desired artistic effect and workflow flexibility. Mixed media combines traditional materials like paint, ink, and collage, offering tactile texture and unique depth, ideal for artists seeking physical interaction with their work. Digital raster art, created with pixels in software such as Adobe Photoshop, provides precision, easy revisions, and seamless integration with digital platforms, making it suitable for commercial projects and digital publishing.
Mixed Media Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com