Printmaking involves transferring images from a matrix onto paper or fabric using techniques such as etching, lithography, and screen printing. This art form allows artists to create multiple copies of a work while exploring textures, lines, and contrasts in unique ways. Discover how mastering printmaking can elevate your artistic expression by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
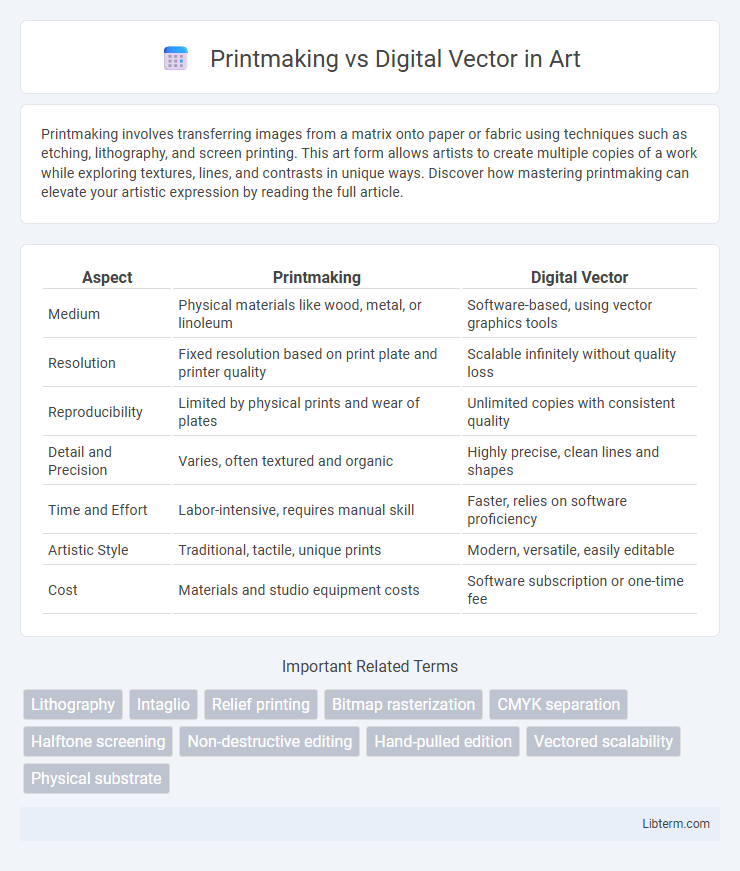
| Aspect | Printmaking | Digital Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials like wood, metal, or linoleum | Software-based, using vector graphics tools |
| Resolution | Fixed resolution based on print plate and printer quality | Scalable infinitely without quality loss |
| Reproducibility | Limited by physical prints and wear of plates | Unlimited copies with consistent quality |
| Detail and Precision | Varies, often textured and organic | Highly precise, clean lines and shapes |
| Time and Effort | Labor-intensive, requires manual skill | Faster, relies on software proficiency |
| Artistic Style | Traditional, tactile, unique prints | Modern, versatile, easily editable |
| Cost | Materials and studio equipment costs | Software subscription or one-time fee |
Introduction to Printmaking and Digital Vector Art
Printmaking involves creating images through physical processes such as engraving, etching, or screen printing, resulting in tactile artworks with unique textures and ink variations. Digital vector art relies on mathematical algorithms to generate scalable images composed of points, lines, and shapes, enabling precise, clean, and easily editable designs for various media. Both methods serve distinct artistic purposes, with printmaking emphasizing traditional craftsmanship and digital vector art offering flexibility and resolution-independent graphics.
Historical Evolution of Printmaking
Printmaking, rooted in ancient techniques like woodblock printing from 9th-century China, evolved through innovations such as Johannes Gutenberg's 15th-century movable type press and 18th-century lithography by Alois Senefelder; these methods laid the foundation for mass-produced texts and artwork. Digital vector technology emerged in the late 20th century, revolutionizing graphic design by enabling scalable, resolution-independent images through mathematical path definitions. This shift from traditional printmaking to digital vector formats reflects a broader transition from analog reproduction methods to versatile, computer-based design tools.
Rise of Digital Vector Techniques
The rise of digital vector techniques revolutionized printmaking by enabling precise, scalable artwork that maintains quality across various sizes and mediums. Vector graphics software such as Adobe Illustrator allows artists to create intricate designs with editable paths and anchor points, facilitating efficient modifications and color adjustments. This advancement has significantly expanded creative possibilities and streamlined production processes in contemporary printmaking.
Material and Tool Differences
Printmaking relies on traditional materials like woodblocks, linoleum, or metal plates and tools such as carving knives, brushes, and ink rollers to create tactile, textured prints. Digital vector design uses software like Adobe Illustrator and tools such as graphic tablets or mouse input to produce scalable, editable artwork composed of mathematically defined shapes and lines. The physicality of printmaking contrasts sharply with the virtual precision and flexibility inherent in digital vector workflows.
Creative Processes Compared
Printmaking emphasizes hands-on techniques like etching, screen printing, and lithography, allowing artists to manipulate textures and colors physically, fostering unique variations with each print. Digital vector art relies on software tools such as Adobe Illustrator, enabling precise control over shapes, scalability without loss of quality, and easy adjustments, streamlining the creative workflow. Both processes offer distinct advantages: printmaking provides tactile, organic results, while digital vectors deliver consistency and versatility for modern design applications.
Visual Qualities: Texture and Precision
Printmaking offers rich texture and organic imperfections that create a tactile, handcrafted feel, highlighting the unique variations in each print. Digital vector graphics provide exceptional precision and clean lines, enabling scalable images without loss of quality or detail. The choice depends on the desired visual outcome: textured, expressive aesthetics versus sharp, flawless accuracy.
Practical Applications in Modern Art
Printmaking offers tactile qualities and unique textures prized in contemporary fine art and limited edition prints, while digital vector graphics excel in scalability and precision, making them ideal for commercial design, branding, and digital media. Artists leverage printmaking for expressive, handcrafted effects that emphasize materiality, whereas vector tools allow for crisp lines and easy modifications suited to interactive and multimedia projects. The integration of both methods enhances creative possibilities, blending traditional craftsmanship with modern technological efficiency in artistic production.
Environmental and Economic Factors
Printmaking relies heavily on physical materials such as paper, inks, and chemicals, which can generate significant waste and environmental pollution. Digital vector art significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for physical supplies, lowering carbon footprints associated with production and distribution. Economically, printmaking incurs ongoing costs for materials and equipment, while digital vector work offers cost efficiency through reusable files and scalable reproduction without additional material expenses.
Flexibility and Reproducibility
Printmaking offers unique textures and organic variations that digital vector art cannot replicate, making each print one-of-a-kind despite limited flexibility in editing. Digital vector graphics provide unparalleled flexibility with scalable designs and precise modifications, ensuring exact reproducibility across multiple platforms and sizes. The reproducibility of digital vectors surpasses printmaking by enabling consistent output without degradation, crucial for branding and mass production.
Choosing the Right Medium: Printmaking or Digital Vector
Choosing between printmaking and digital vector depends on your project's goals, desired aesthetics, and reproduction needs. Printmaking offers unique textures, rich tactile qualities, and limited edition appeal, while digital vector excels in scalability, easy editing, and crisp, clean lines suitable for logos and digital media. Prioritize printmaking for handcrafted authenticity and digital vector for precise, flexible designs optimized for multiple platforms.
Printmaking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com