Sculpture transforms raw materials into three-dimensional art that captures emotion, movement, and form. Techniques vary from carving and casting to assembling, offering diverse ways to bring artistic visions to life. Discover how sculpture adds depth and meaning to your surroundings by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
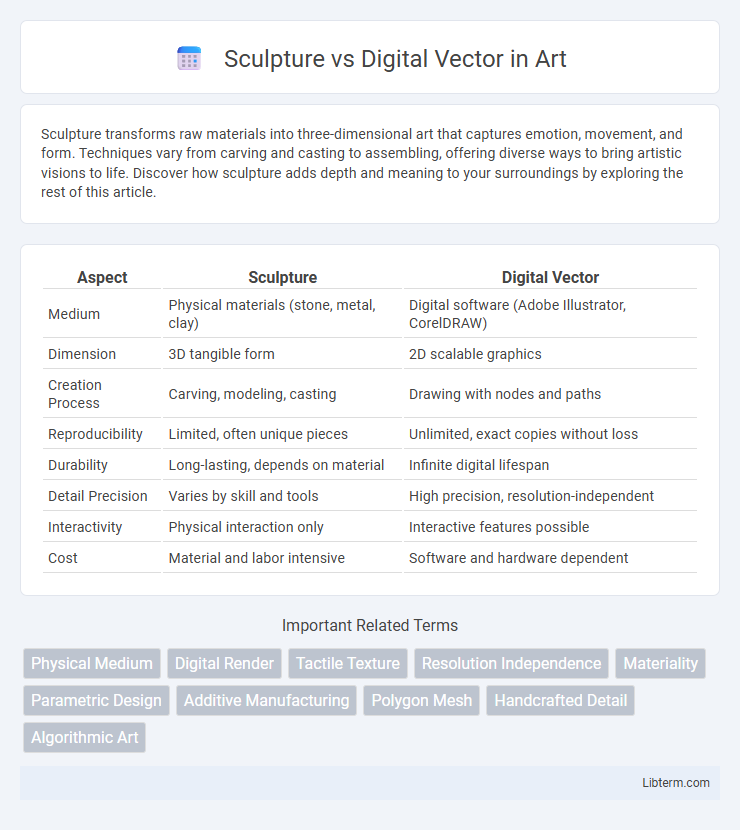
| Aspect | Sculpture | Digital Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials (stone, metal, clay) | Digital software (Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW) |
| Dimension | 3D tangible form | 2D scalable graphics |
| Creation Process | Carving, modeling, casting | Drawing with nodes and paths |
| Reproducibility | Limited, often unique pieces | Unlimited, exact copies without loss |
| Durability | Long-lasting, depends on material | Infinite digital lifespan |
| Detail Precision | Varies by skill and tools | High precision, resolution-independent |
| Interactivity | Physical interaction only | Interactive features possible |
| Cost | Material and labor intensive | Software and hardware dependent |
Introduction to Sculpture and Digital Vector Art
Sculpture involves creating three-dimensional art by shaping materials such as clay, stone, or metal, emphasizing tactile texture and physical form. Digital vector art uses mathematical equations to produce scalable graphics with crisp lines and smooth curves, ideal for logos, illustrations, and digital media. Both mediums offer distinct creative possibilities, with sculpture rooted in physical craftsmanship and digital vector art centered on precision and flexibility in digital design.
Historical Evolution of Sculpture
Sculpture, an ancient art form rooted in materials like stone, clay, and bronze, traces back to prehistoric times with notable advancements during the Renaissance and Classical periods. Its historical evolution emphasizes three-dimensional physicality and tactile craftsmanship, contrasting sharply with the digital vector art that emerged in the late 20th century through computer graphics, prioritizing scalability and precision in two-dimensional design. The transition from traditional sculpting to digital forms reflects broader technological shifts influencing artistic expression, where virtual modeling complements or replaces tangible creation.
The Rise of Digital Vector Art
Digital vector art has surged in popularity due to its scalability, precision, and ease of editing, making it ideal for modern graphic design and branding. Unlike traditional sculpture, which requires physical materials and space, vector art thrives in digital environments, offering unparalleled flexibility for animation, web design, and print media. The rise of powerful software like Adobe Illustrator and CorelDRAW has democratized vector creation, enabling artists to produce intricate designs quickly and efficiently.
Key Differences in Creation Process
Sculpture involves physically shaping materials like clay, stone, or metal using tools and hands, emphasizing tactile manipulation and three-dimensional form development. Digital vector artwork is created using software such as Adobe Illustrator, relying on mathematical equations to produce scalable, two-dimensional images composed of paths and curves. The tactile, subtractive or additive physical approach of sculpture contrasts with the precise, editable, and resolution-independent process of digital vector creation.
Materiality vs. Virtuality
Sculpture emphasizes materiality through tangible substances like stone, metal, or clay, offering a physical presence that engages touch and spatial awareness. Digital vector art exists in virtuality, defined by mathematical equations and scalable without loss of resolution, existing solely in digital environments. This contrast highlights how sculpture anchors art in physical space while digital vectors explore infinite, immaterial dimensions.
Artistic Tools: Traditional vs. Digital
Sculpture as an artistic tool emphasizes tactile interaction with physical materials like clay, stone, or metal, enabling creators to shape three-dimensional forms with hands and traditional tools such as chisels and rasps. In contrast, digital vector art relies on software like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW, where artists manipulate anchor points and paths to create scalable, precise graphics without physical medium limitations. Both approaches offer unique creative processes: sculpture demands spatial awareness and manual dexterity, while digital vector art prioritizes precision, versatility, and ease of editing.
Audience Engagement and Accessibility
Sculpture offers a tactile, three-dimensional experience that engages audiences through physical presence and spatial interaction, often appealing to those who value tangible art forms. Digital vector graphics provide broader accessibility by enabling instant sharing, scaling without quality loss, and interactive online engagement, reaching diverse and global audiences. Combining physical sculptures with digital vector representations can enhance audience interaction by bridging traditional art appreciation with modern digital accessibility.
Preservation and Longevity
Sculptures crafted from durable materials like bronze or stone offer exceptional preservation and longevity, often lasting centuries with minimal degradation. In contrast, digital vectors provide infinite reproducibility and can be preserved indefinitely through cloud storage and backups, though their longevity depends on evolving technology and file format accessibility. Choosing between physical preservation and digital longevity depends on the desired medium's resilience and future-proofing through technological advancements.
Impact on the Art Market
Sculpture maintains a significant physical presence and tactile value, commanding premium prices and attracting collectors who prioritize authenticity and craftsmanship. Digital vector art disrupts the traditional market by enabling limitless reproduction and accessibility, expanding the audience but challenging conventional notions of scarcity. The art market increasingly integrates blockchain technology to authenticate digital works, creating new revenue streams and reshaping investment dynamics.
Future Trends: Merging Sculpture and Digital Vector
The future of art is marked by the seamless integration of sculpture and digital vector techniques, with augmented reality and 3D printing driving innovation in hybrid forms. Artists increasingly use digital vector software to design intricate patterns before translating them into physical sculptures through advanced robotics and additive manufacturing. This convergence enhances creative precision, customization, and scalability, reshaping both traditional sculpture and digital art landscapes.
Sculpture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com