Intaglio is a printing technique where an image is incised into a surface, and the recessed areas hold the ink to create detailed, high-quality prints. This method is widely used for security printing, such as banknotes and passports, due to its precision and resistance to counterfeiting. Discover more about how intaglio enhances the quality and security of your printed materials in the rest of this article.
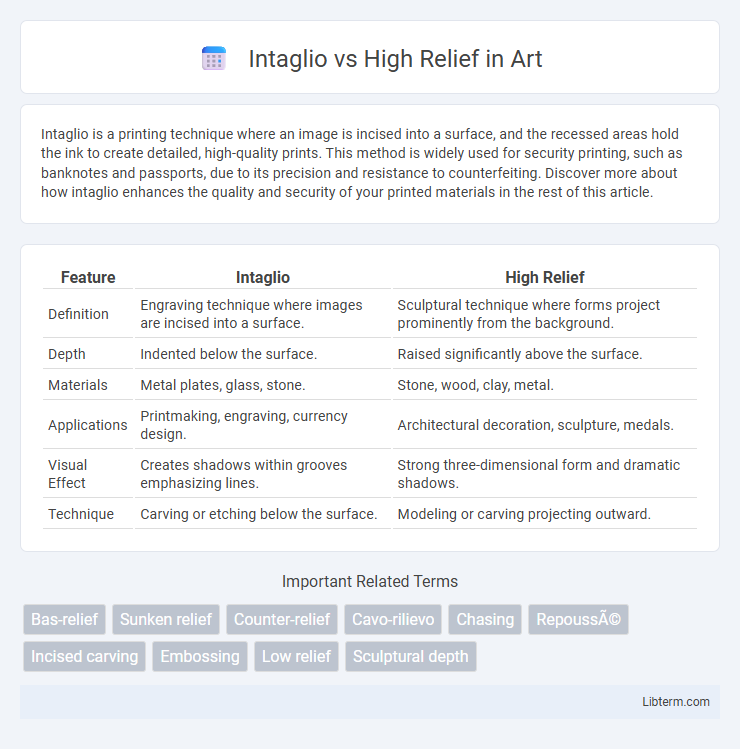
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Intaglio | High Relief |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engraving technique where images are incised into a surface. | Sculptural technique where forms project prominently from the background. |
| Depth | Indented below the surface. | Raised significantly above the surface. |
| Materials | Metal plates, glass, stone. | Stone, wood, clay, metal. |
| Applications | Printmaking, engraving, currency design. | Architectural decoration, sculpture, medals. |
| Visual Effect | Creates shadows within grooves emphasizing lines. | Strong three-dimensional form and dramatic shadows. |
| Technique | Carving or etching below the surface. | Modeling or carving projecting outward. |
Introduction to Intaglio and High Relief
Intaglio is a printmaking technique where designs are incised into a surface, with ink held in the recesses to create detailed, precise images, commonly used in metal engraving and etching. High relief, also known as alto-relievo, is a sculptural method where elements are carved deeply to project significantly from the background, creating strong shadows and a dramatic three-dimensional effect. Both techniques emphasize depth and texture but differ fundamentally in process and visual impact: intaglio relies on recessed lines for printing, while high relief focuses on raised forms for sculptural prominence.
Defining Intaglio: Technique and Features
Intaglio is a printmaking technique where designs are engraved or incised into a surface, allowing ink to settle into the recessed areas for detailed image transfer. This method contrasts with high relief, where elements project prominently from the background, creating a raised, three-dimensional effect. The precision and depth of intaglio produce fine lines and intricate textures, essential for artworks requiring high definition and tonal variation.
Understanding High Relief: Characteristics and Process
High relief sculpture, characterized by figures projecting significantly from the background, creates a dramatic sense of depth and dimension compared to intaglio, where designs are incised into the surface. The high relief process often involves carving deeply into materials like stone or wood, allowing the forms to stand out prominently and cast dynamic shadows. This technique enhances visual impact, making it ideal for architectural decoration and monumental art.
Historical Origins of Intaglio and High Relief
Intaglio originated in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, where artists engraved designs into surfaces for seals and jewelry, emphasizing recessed patterns. High relief, or alto-relievo, emerged prominently in classical Greek and Roman sculpture, characterized by deeply carved figures projecting boldly from the background. Both techniques reflect significant cultural developments in artistic expression and craftsmanship across different civilizations.
Artistic Applications in Sculpture and Coinage
Intaglio and high relief serve distinct artistic applications in sculpture and coinage, with intaglio featuring engraved or incised designs that create recessed images widely used in detailed coinage and gemstone carving. High relief involves projecting forms significantly raised from the background, offering dynamic depth ideal for architectural sculptures and commemorative coins that emphasize dramatic imagery. The choice between intaglio and high relief depends on desired visual impact, durability, and intended tactile experience in artistic and numismatic works.
Visual Differences: Depth and Perspective
Intaglio engraving features designs carved into the surface, creating recessed lines that produce shadows and subtle depth, enhancing detailed contrast through negative space. High relief sculpture projects prominently from the background, with elements raised more than 50% of their depth, offering dramatic shadows and a strong sense of three-dimensionality and perspective. The key visual difference lies in intaglio's incised depth versus high relief's pronounced outward projection, influencing how light interacts with each form and enhancing their spatial perception.
Material Choices for Intaglio and High Relief
Intaglio typically uses softer materials like metal plates, especially copper or zinc, to allow for precise engraving and ink retention in recessed areas. High relief sculptures favor durable and robust materials such as marble, bronze, or wood to support their pronounced three-dimensional forms. Material selection impacts the depth and detail achievable, with intaglio requiring materials conducive to fine incisions and high relief demanding substances capable of sustaining raised, intricate carvings.
Durability and Preservation Considerations
Intaglio engraving involves carving into a surface, creating recessed designs that are less prone to wear and erosion, enhancing durability and long-term preservation even in high-contact environments. High relief sculptures, with their pronounced protrusions, are more susceptible to physical damage and environmental factors, requiring careful maintenance to prevent chipping or breaking. Materials commonly used for intaglio, such as metal or stone, further improve preservation prospects, while high relief often demands sturdier substrates or protective measures to ensure longevity.
Notable Examples in Art History
Intaglio art, characterized by engraving or carving into a surface, finds notable examples in the intricate gems of the Renaissance and ancient Roman engraved gemstones like the Gemma Augustea. High relief, where figures project prominently from the background, is exemplified by the dramatic depth in the Parthenon sculptures and Gian Lorenzo Bernini's Baroque masterpieces, such as "The Ecstasy of Saint Teresa." These techniques distinctly demonstrate the artists' mastery in manipulating depth to enhance visual impact in historical art.
Choosing Between Intaglio and High Relief Techniques
Choosing between intaglio and high relief techniques depends on the desired depth and texture of the artwork; intaglio involves engraving below the surface for fine, detailed lines, while high relief creates dramatic, raised forms that project significantly from the background. Intaglio is ideal for intricate, precise prints and allows ink to settle in recessed areas, enabling subtle shading effects. High relief suits sculptures requiring pronounced three-dimensional impact and strong visual contrasts, making it effective for dynamic, tactile designs.
Intaglio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com