Cartography is the art and science of creating maps that visually represent geographical information with precision and clarity. Modern cartography integrates geographic information systems (GIS) and digital tools to enhance map accuracy and usability. Explore the rest of this article to discover how cartography continues to shape your understanding of the world.
Table of Comparison
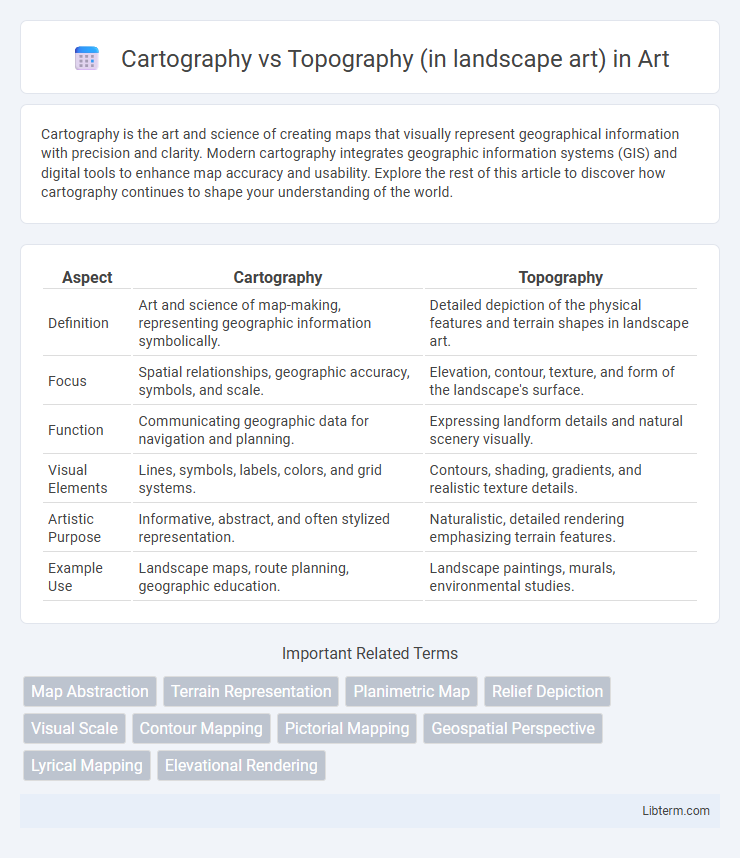
| Aspect | Cartography | Topography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art and science of map-making, representing geographic information symbolically. | Detailed depiction of the physical features and terrain shapes in landscape art. |
| Focus | Spatial relationships, geographic accuracy, symbols, and scale. | Elevation, contour, texture, and form of the landscape's surface. |
| Function | Communicating geographic data for navigation and planning. | Expressing landform details and natural scenery visually. |
| Visual Elements | Lines, symbols, labels, colors, and grid systems. | Contours, shading, gradients, and realistic texture details. |
| Artistic Purpose | Informative, abstract, and often stylized representation. | Naturalistic, detailed rendering emphasizing terrain features. |
| Example Use | Landscape maps, route planning, geographic education. | Landscape paintings, murals, environmental studies. |
Introduction to Cartography and Topography in Landscape Art
Cartography in landscape art involves the creation of detailed maps representing spatial relationships, emphasizing accuracy in depicting geographical features for navigation and interpretation. Topography focuses on the physical characteristics and elevation changes of the land, portraying contours, slopes, and textures to convey the terrain's three-dimensional form visually. Both cartography and topography serve essential roles in landscape art by combining spatial data and physical landforms to enhance geographic understanding and artistic representation.
Defining Cartography: Mapping the Landscape
Cartography in landscape art involves the precise creation of maps that represent geographical features, spatial relationships, and terrain details using symbols and scale. It emphasizes accurate depiction of locations, boundaries, and elevations to guide interpretation and navigation of the physical environment. This contrasts with topography, which focuses more on the surface features and textures of the land for artistic or descriptive purposes.
Topography: Depicting Terrain and Relief
Topography in landscape art emphasizes the detailed depiction of terrain and relief, showcasing hills, valleys, slopes, and elevation changes through techniques such as contour lines, shading, and perspective. This approach provides a three-dimensional understanding of the landform, enhancing the realism and spatial depth in artistic representations. Unlike cartography, which prioritizes accurate map-making and spatial data, topography focuses on conveying the physical character and texture of the landscape.
Historical Evolution of Cartography and Topography in Art
The historical evolution of cartography and topography in landscape art reveals distinct but interconnected developments. Cartography evolved from rudimentary maps in ancient civilizations to detailed thematic representations during the Age of Exploration, emphasizing spatial relationships and geographic accuracy. Topography in art developed through detailed renditions of terrain and elevation, becoming a critical tool for artists to depict realistic landscapes with depth and texture, influenced prominently by advancements in surveying and printing techniques.
Techniques Used in Cartographic Art
Cartographic art employs techniques such as precise line work, gradient shading, and symbolic color coding to represent geographic features accurately and aesthetically. Artists utilize contour lines and elevation markers to convey terrain details while incorporating labels and legends for clarity and context. Advanced tools like GIS software and digital rendering enhance accuracy and allow for dynamic visualization in landscape representation.
Artistic Methods for Topographical Representation
Artistic methods for topographical representation in landscape art utilize techniques such as hachures, contour lines, and graduated shading to convey elevation and terrain features effectively. Artists often employ perspective drawing and color gradation to enhance the sense of depth and highlight variations in landforms, distinguishing topography from the more data-driven precision of cartography. These methods prioritize aesthetic interpretation and visual storytelling over exact spatial measurements, bridging geographic information with creative expression.
Comparing Symbolism: Maps vs Terrain Illustrations
Maps in cartography use standardized symbols and color codes to convey precise geographic information and spatial relationships, facilitating navigation and planning. Terrain illustrations in topography emphasize visual texture and natural forms through shading and contour lines, conveying the physical character and elevation of the landscape. While cartographic symbols prioritize clarity and abstraction, topographic artwork focuses on representing the tangible, sensory experience of the land.
Influence of Cartography and Topography on Artistic Styles
Cartography in landscape art often emphasizes precise spatial representation and structured composition, influencing artistic styles to adopt detailed mapping techniques and geometric forms. Topography contributes to artistic expression by highlighting elevation and natural landforms, encouraging dynamic perspectives and textured brushwork that depict terrain variations. The interplay of cartographic accuracy and topographic realism shapes landscape art through the balance of scientific detail and expressive interpretation.
Contemporary Approaches in Landscape Art
Contemporary approaches in landscape art often merge cartography and topography to enhance spatial understanding and aesthetic expression. Artists incorporate digital mapping technologies and GIS data to create layered representations that reveal both physical terrain and human interactions with the environment. This fusion allows for dynamic visual narratives that challenge traditional perceptions of place and landscape, emphasizing ecological complexity and cultural context.
Conclusion: Integrating Mapping and Terrain in Artistic Expression
Integrating cartography and topography in landscape art enhances spatial understanding by combining precise map features with the detailed representation of terrain forms. This fusion allows artists to convey both geographic accuracy and emotional depth, creating works that resonate with viewers on multiple levels. Emphasizing the interplay of line, texture, and elevation enriches the visual narrative and bridges scientific detail with artistic creativity.
Cartography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com