Marquetry is the art of creating decorative patterns by inlaying pieces of wood veneer, often combined with other materials like metal or shell, onto furniture surfaces. This intricate craft enhances the aesthetic appeal and value of wooden objects through detailed and precise designs. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques, history, and tips to master marquetry for your own projects.
Table of Comparison
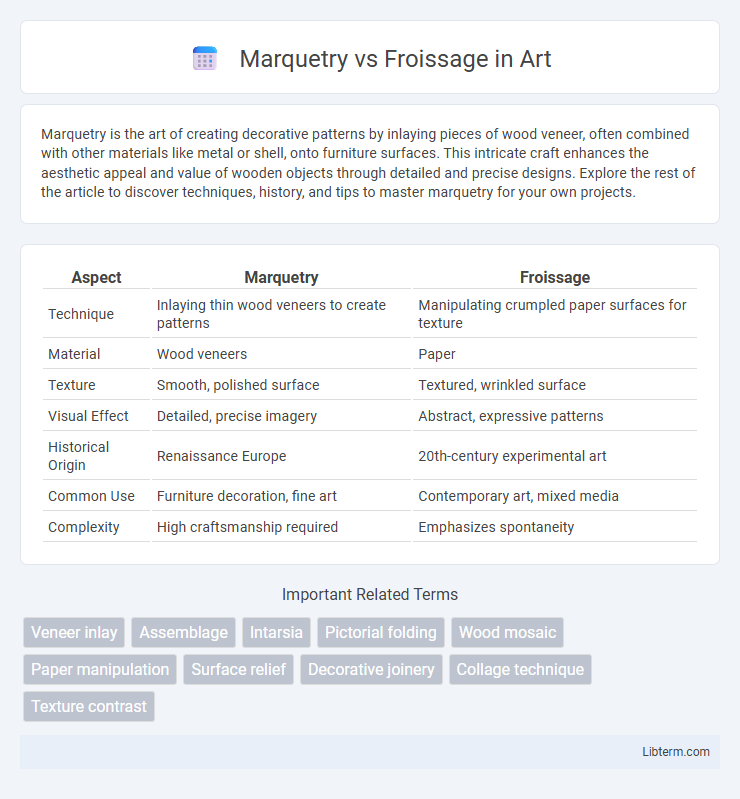
| Aspect | Marquetry | Froissage |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Inlaying thin wood veneers to create patterns | Manipulating crumpled paper surfaces for texture |
| Material | Wood veneers | Paper |
| Texture | Smooth, polished surface | Textured, wrinkled surface |
| Visual Effect | Detailed, precise imagery | Abstract, expressive patterns |
| Historical Origin | Renaissance Europe | 20th-century experimental art |
| Common Use | Furniture decoration, fine art | Contemporary art, mixed media |
| Complexity | High craftsmanship required | Emphasizes spontaneity |
Introduction to Marquetry and Froissage
Marquetry is a decorative art technique involving the application of thin wood veneers to create intricate patterns and images on furniture surfaces, emphasizing precision and craftsmanship. Froissage, in contrast, is an artistic method that manipulates creased paper or fabric to form textured, abstract compositions, highlighting spontaneity and tactile effects. Both techniques showcase unique aesthetic values: marquetry through detailed wood inlay artistry and froissage via expressive surface manipulation.
Historical Origins: Marquetry vs Froissage
Marquetry originated in the 16th century as a decorative woodworking technique popularized in European furniture-making, particularly in France and Italy, involving intricate inlaid designs of wood veneers. Froissage, on the other hand, emerged in the 20th century as an avant-garde art form developed by Czech artist Ladislav Novak, characterized by crumpled paper collages creating textured abstract compositions. The historical origins of marquetry are deeply rooted in traditional craftsmanship and Renaissance artistry, whereas froissage reflects modernist experimentation and the use of unconventional materials.
Materials Used in Marquetry and Froissage
Marquetry primarily utilizes thin veneers of wood, alongside materials like brass, shell, and ivory, to create intricate inlay patterns on furniture and decorative objects. Froissage employs crumpled or textured paper, often translucent or metallic, to produce abstract, layered collage effects that emphasize texture and light. The distinct material choices in marquetry and froissage directly influence their visual impact, with marquetry favoring precise craftsmanship and froissage embracing tactile, experimental surfaces.
Techniques and Processes Compared
Marquetry involves meticulously cutting and fitting thin veneers of wood or other materials to create intricate, flat patterns or images on furniture surfaces. Froissage is a paper art technique where paper is crumpled and manipulated to produce textured, three-dimensional effects, often used in mixed media collages. While marquetry emphasizes precision and smooth surface assemblies, froissage centers on tactile depth and irregular form, reflecting contrasting approaches in material manipulation and artistic expression.
Visual Styles and Artistic Effects
Marquetry involves intricate patterns created by inlaying pieces of wood veneer to form detailed images or geometric designs, offering a smooth, polished surface with rich texture and depth. Froissage uses crumpled or crushed paper techniques to create abstract, tactile effects with dynamic shadows and layered textures that emphasize three-dimensionality. The visual style of marquetry emphasizes precision and clarity, while froissage highlights spontaneity and expressive texture.
Notable Artists and Influencers
Notable marquetry artists include Andre-Jacques and Andre Charles Boulle, renowned for intricate wood veneer designs. Froissage pioneers such as Jules Olitski used textured paper techniques to create dynamic, layered artworks. Contemporary influencers like Emmanuel Viale continue to innovate marquetry, while artists like Claire Morgan explore froissage-inspired textures in mixed media.
Applications in Contemporary Art
Marquetry in contemporary art is often used to create intricate wooden inlays that emphasize texture and pattern, blending traditional craftsmanship with modern design concepts. Froissage, a technique involving the crumpling and manipulating paper or fabric, adds expressive, three-dimensional surfaces that evoke movement and spontaneity in mixed-media artworks. Both methods offer unique tactile qualities, enhancing visual interest and conceptual depth in installations, sculptures, and experimental compositions.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Technique
Marquetry excels in creating detailed, durable wood veneer patterns with precise geometric and floral designs but requires meticulous craftsmanship and is time-consuming. Froissage offers a unique, textured effect by crumpling and manipulating paper or fabric, providing expressive and spontaneous visual appeal, though it lacks fine detail control and permanence. Marquetry's strength lies in its structural integrity and intricate precision, while Froissage's advantage is in its artistic flexibility and tactile dimension.
Marquetry vs Froissage in Interior Design
Marquetry involves inlaying thin wood veneers to create intricate patterns and images on furniture surfaces, adding a luxurious and classic aesthetic to interior design. Froissage, by contrast, uses the artistic technique of crumpling paper to produce textured, tactile surfaces often mimicked in wall coverings and fabric designs for a modern, abstract effect. In interior design, marquetry excels in delivering detailed craftsmanship and timeless elegance, while froissage emphasizes texture and contemporary visual interest.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Marquetry involves creating intricate patterns by inlaying wood veneers, ideal for projects requiring precision and a polished finish, making it perfect for furniture decoration and detailed paneling. Froissage, characterized by its textured, crumpled paper effect, suits artistic, abstract designs where a tactile, expressive surface is desired, commonly used in mixed media and fine art projects. Selecting the right technique depends on the desired visual impact, material compatibility, and project scale, with marquetry emphasizing craftsmanship and froissage highlighting texture and spontaneity.
Marquetry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com