Traditional painting techniques offer timeless methods for creating expressive and textured artwork using materials like oil, acrylic, and watercolor. Mastering brush strokes, color mixing, and composition enhances your ability to convey emotion and bring subjects to life on canvas. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of traditional painting practices and elevate your artistic skills.
Table of Comparison
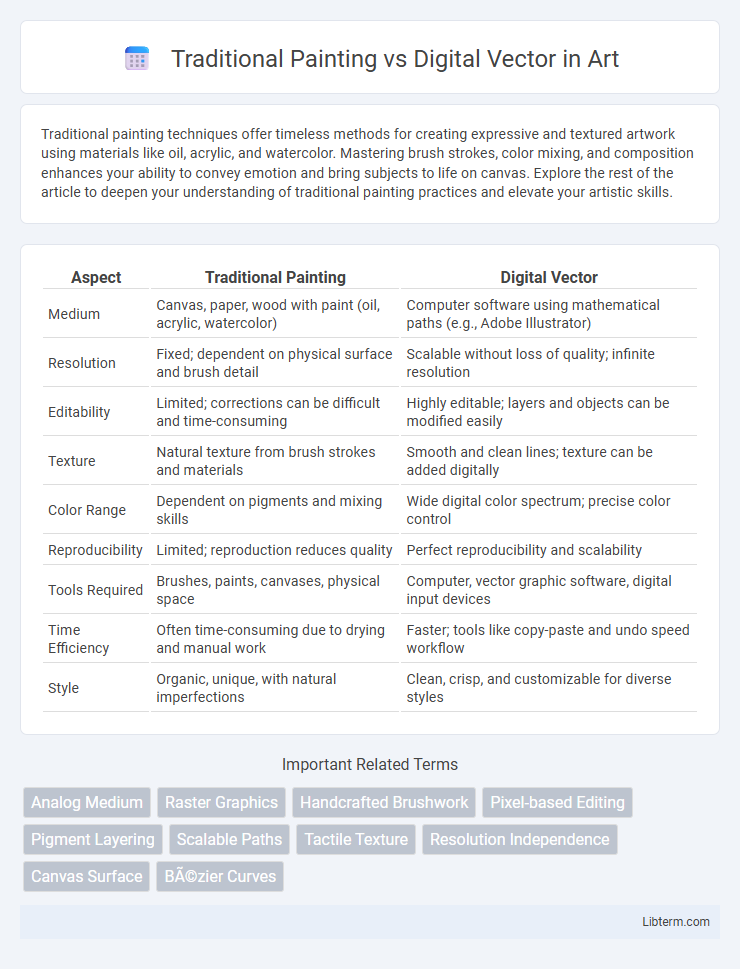
| Aspect | Traditional Painting | Digital Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Canvas, paper, wood with paint (oil, acrylic, watercolor) | Computer software using mathematical paths (e.g., Adobe Illustrator) |
| Resolution | Fixed; dependent on physical surface and brush detail | Scalable without loss of quality; infinite resolution |
| Editability | Limited; corrections can be difficult and time-consuming | Highly editable; layers and objects can be modified easily |
| Texture | Natural texture from brush strokes and materials | Smooth and clean lines; texture can be added digitally |
| Color Range | Dependent on pigments and mixing skills | Wide digital color spectrum; precise color control |
| Reproducibility | Limited; reproduction reduces quality | Perfect reproducibility and scalability |
| Tools Required | Brushes, paints, canvases, physical space | Computer, vector graphic software, digital input devices |
| Time Efficiency | Often time-consuming due to drying and manual work | Faster; tools like copy-paste and undo speed workflow |
| Style | Organic, unique, with natural imperfections | Clean, crisp, and customizable for diverse styles |
Introduction to Traditional Painting and Digital Vector
Traditional painting involves applying pigments on surfaces like canvas or paper using brushes, characterized by tactile textures and unique strokes that reflect the artist's hand. Digital vector art utilizes mathematical equations to create scalable, resolution-independent graphics ideal for logos, illustrations, and animations. Both mediums offer distinct advantages: traditional painting emphasizes organic aesthetics and physical presence, while digital vector art excels in precision, versatility, and ease of editing.
Historical Evolution of Art Mediums
Traditional painting, rooted in ancient techniques such as frescoes and oil on canvas, has evolved over millennia through cultural and technological shifts, shaping the foundation of visual art. The emergence of digital vector art in the late 20th century revolutionized artistic expression by enabling scalable, editable graphics through software like Adobe Illustrator, drastically altering design workflows. This transition reflects the broader historical evolution of art mediums from tactile, manual methods to precision-driven, computer-based technologies, highlighting ongoing innovation in visual communication.
Material and Tools Comparison
Traditional painting relies on physical materials such as canvas, brushes, and acrylic or oil paints, offering tactile texture and organic variation with each stroke. Digital vector art utilizes software like Adobe Illustrator, employing mathematical algorithms to create scalable graphics with tools such as the pen tool, anchor points, and layers. The contrast in mediums highlights the physicality and unpredictability of traditional tools against the precision, editability, and infinite scalability of digital vector techniques.
Learning Curve and Accessibility
Traditional painting demands mastering tactile skills such as brushwork, color mixing, and layering techniques, which often require extended practice and hands-on experimentation. Digital vector art utilizes software like Adobe Illustrator, offering intuitive tools, customizable brushes, and undo functionality that significantly reduce trial-and-error, making the learning curve more accessible for beginners. Access to digital vector tools is facilitated by affordable software subscriptions and abundant online tutorials, whereas traditional painting requires investment in physical materials and studio space.
Creative Process Differences
Traditional painting involves tactile materials like brushes and canvases, promoting texture and spontaneous brushstrokes that influence creative expression. Digital vector art relies on precise, scalable paths and anchor points within software like Adobe Illustrator, enabling easy modifications and consistent line quality. The creative process in traditional painting is often more intuitive and unpredictable, whereas digital vector design emphasizes planning, editing flexibility, and reproducibility.
Aesthetic Qualities and Visual Styles
Traditional painting showcases rich textures, organic brushstrokes, and subtle color variations that convey depth and emotional warmth. Digital vector art excels in crisp lines, scalable shapes, and vibrant, uniform colors, offering a clean and modern aesthetic ideal for logos and illustrations. The tactile imperfections of traditional media contrast with the precision and smoothness of vector graphics, each appealing to different artistic preferences and visual communication needs.
Flexibility and Editing Capabilities
Traditional painting offers tactile texture and rich color blending but lacks the ease of precise editing and scalability found in digital vector art. Digital vector graphics provide unparalleled flexibility with infinite resizing without loss of quality and seamless modifications through anchor points and paths. This makes vector art ideal for projects requiring frequent revisions and multi-platform adaptability.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Traditional painting often involves recurring expenses for canvases, brushes, paints, and studio space, which can accumulate significantly over time, whereas digital vector art requires upfront investment in software and hardware but minimal ongoing material costs. From a sustainability perspective, digital vector art has a lower environmental impact by reducing physical waste and resource consumption associated with paints and canvases. The choice between traditional and digital mediums affects both financial outlay and ecological footprint, prompting artists to weigh cost efficiency against sustainable practices.
Professional Applications and Industries
Traditional painting remains essential in fine arts, galleries, and heritage restorations, offering unique textures and tactile depth that digital methods often lack. Digital vector graphics dominate industries like advertising, branding, and animation due to scalability, precision, and ease of editing across multiple platforms. Professionals in product design, UX/UI, and web development prefer vector tools for creating clean, adaptable visuals that maintain quality at any size.
Future Trends in Artistic Expression
Future trends in artistic expression reveal a growing integration of traditional painting techniques with digital vector technology, enhancing creative possibilities through hybrid workflows. Advances in vector-based software enable precision and scalability, while traditional mediums continue to offer tactile, unique textures sought after by collectors and artists. Emerging tools like AI-assisted design and augmented reality promise to further blur the boundaries between analog and digital art, shaping new paradigms in visual storytelling.
Traditional Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com