Effective image compression reduces file size while preserving quality, enabling faster loading times and saving storage space. Techniques like lossless and lossy compression balance clarity and efficiency depending on your needs. Discover how these methods can enhance your digital experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
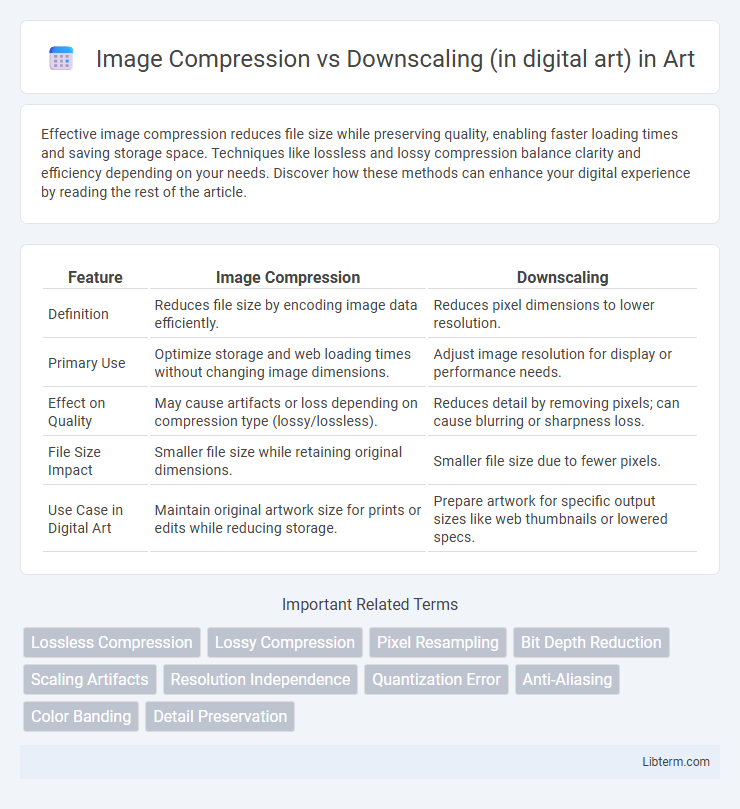
| Feature | Image Compression | Downscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduces file size by encoding image data efficiently. | Reduces pixel dimensions to lower resolution. |
| Primary Use | Optimize storage and web loading times without changing image dimensions. | Adjust image resolution for display or performance needs. |
| Effect on Quality | May cause artifacts or loss depending on compression type (lossy/lossless). | Reduces detail by removing pixels; can cause blurring or sharpness loss. |
| File Size Impact | Smaller file size while retaining original dimensions. | Smaller file size due to fewer pixels. |
| Use Case in Digital Art | Maintain original artwork size for prints or edits while reducing storage. | Prepare artwork for specific output sizes like web thumbnails or lowered specs. |
Introduction to Image Compression and Downscaling
Image compression reduces file size by encoding image data more efficiently, preserving essential details while eliminating redundancies to optimize storage and transmission. Downscaling decreases image resolution by resampling pixels, which simplifies the visual information and reduces dimensions for easier display or faster loading. Both methods impact image quality differently: compression retains overall resolution with potential artifacts, while downscaling directly lowers pixel count, affecting sharpness and detail.
Key Differences Between Compression and Downscaling
Image compression in digital art reduces file size by encoding data more efficiently without altering the image's original dimensions, often through lossy or lossless methods. Downscaling decreases the resolution and pixel count of an artwork, resulting in a smaller image that may lose detail and sharpness but reduces display or storage requirements. The key difference lies in compression maintaining dimension fidelity through data optimization, while downscaling changes the image's physical size and pixel density.
Technical Overview: How Image Compression Works
Image compression reduces file size by encoding pixel data more efficiently using algorithms like JPEG, PNG, or WebP, which apply techniques such as transform coding, quantization, and entropy coding to minimize redundant information. Unlike downscaling that decreases image resolution by resampling fewer pixels, compression preserves original dimensions while optimizing storage through lossless or lossy methods. Lossy compression algorithms analyze image frequency components to discard imperceptible details, significantly reducing file size without visually degrading the artwork.
Technical Overview: How Downscaling Modifies Images
Downscaling in digital art reduces the pixel dimensions of an image, effectively decreasing its resolution while preserving essential visual information. This process involves resampling techniques such as bilinear or bicubic interpolation, which blend pixel values to maintain image clarity and minimize artifacts. Unlike image compression that primarily reduces file size by encoding data efficiently, downscaling modifies the image structure itself, altering detail levels and potentially enhancing performance in display or transmission scenarios.
Impacts on Image Quality: Compression vs Downscaling
Image compression reduces file size by encoding image data more efficiently, often causing artifacts like blurring or banding that degrade perceived image quality. Downscaling decreases image resolution by reducing pixel dimensions, resulting in the loss of fine details but maintaining overall sharpness and fewer compression artifacts. Digital artists must balance compression's potential for faster loading times against downscaling's preservation of visual fidelity when optimizing images for web or print.
File Size Considerations in Digital Art
Image compression reduces file size by encoding digital art with algorithms that eliminate redundant data while preserving visual quality, making it ideal for maintaining resolution and detail in large artworks. Downscaling decreases file dimensions, effectively lowering pixel count and drastically reducing file size, but this often results in loss of fine details and sharpness. Choosing between compression and downscaling depends on balancing storage efficiency with the desired quality and resolution for digital art projects.
Use Cases: When to Compress vs When to Downscale
Image compression is ideal for reducing file size while maintaining original dimensions, making it suitable for web use where bandwidth optimization and fast loading times are critical. Downscaling is preferred when changing the image's physical resolution to fit specific display requirements or to create lower-resolution previews, often used in mobile apps and thumbnails. For digital art showcasing, compression preserves detail, whereas downscaling optimizes display size without retaining full detail.
Common Tools and Software for Each Process
Common tools for image compression in digital art include Adobe Photoshop, TinyPNG, and ImageOptim, which reduce file size while preserving visual quality through algorithms like JPEG and PNG optimization. Downscaling is often performed using software such as GIMP, Affinity Photo, and Paint.NET, focusing on resizing images by reducing pixel dimensions to fit specific resolutions without significant loss of detail. Both processes are essential for optimizing digital artwork, balancing quality and file size to enhance web performance and storage efficiency.
Best Practices for Preserving Artwork Details
Preserving artwork details in digital art requires choosing between image compression and downscaling techniques based on project goals and output quality. Lossless compression formats such as PNG maintain original pixel data, ensuring intricate details remain intact without visual artifacts, while downscaling must be executed using high-quality algorithms like bicubic or Lanczos to minimize detail loss and edge smoothing. Optimizing resolution by balancing file size and visual fidelity preserves texture, fine lines, and color gradients, crucial for professional digital art reproduction and display across different devices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Artwork
Selecting the appropriate technique between image compression and downscaling depends on the specific needs of your digital artwork, such as preserving detail versus reducing file size. Compression algorithms like JPEG or PNG optimize storage with minimal quality loss, while downscaling physically reduces image dimensions, which can impact visual clarity. Prioritize maintaining the artistic integrity of your work by balancing resolution needs and file efficiency based on the intended display platform or usage.
Image Compression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com