Lithography crayons offer precise control for creating detailed designs on lithographic plates, making them essential for artists and printmakers. Their waxy texture allows for smooth application and easy manipulation, ensuring sharp lines and varied textures in your prints. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to select and use the perfect lithography crayon for your projects.
Table of Comparison
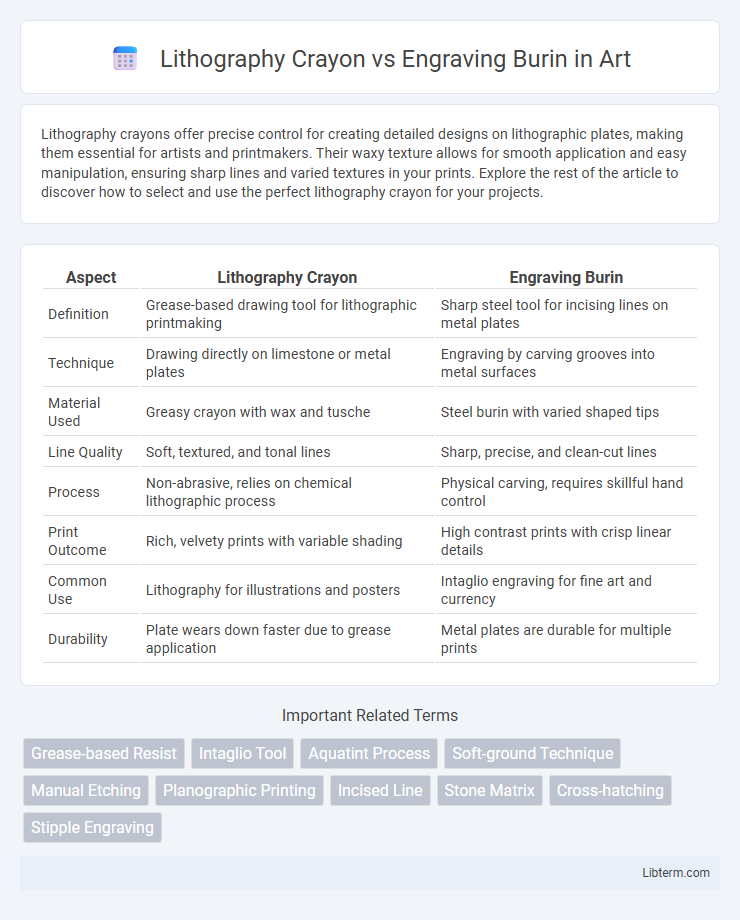
| Aspect | Lithography Crayon | Engraving Burin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grease-based drawing tool for lithographic printmaking | Sharp steel tool for incising lines on metal plates |
| Technique | Drawing directly on limestone or metal plates | Engraving by carving grooves into metal surfaces |
| Material Used | Greasy crayon with wax and tusche | Steel burin with varied shaped tips |
| Line Quality | Soft, textured, and tonal lines | Sharp, precise, and clean-cut lines |
| Process | Non-abrasive, relies on chemical lithographic process | Physical carving, requires skillful hand control |
| Print Outcome | Rich, velvety prints with variable shading | High contrast prints with crisp linear details |
| Common Use | Lithography for illustrations and posters | Intaglio engraving for fine art and currency |
| Durability | Plate wears down faster due to grease application | Metal plates are durable for multiple prints |
Introduction to Lithography Crayon and Engraving Burin
Lithography crayon is a greasy drawing tool used on limestone or aluminum plates to create images for lithographic printing, offering rich tonal variations and smooth application. Engraving burin is a sharp, chisel-like tool used to incise precise lines into metal plates for intaglio printmaking, enabling fine detail and depth control. Both tools serve different printmaking techniques, with lithography crayon suited for tonal, image-based effects and engraving burin ideal for line work and detailed engravings.
Historical Development of Lithography and Engraving
Lithography, invented by Alois Senefelder in 1796, revolutionized image reproduction by using a grease-based crayon on limestone to create prints, enabling artists to achieve a wide range of tonal effects. In contrast, engraving, with origins dating back to the 15th century, utilized the burin-- a precise steel cutting tool-- to incise images onto metal plates, facilitating detailed and durable prints. The historical development of lithography introduced a chemical printing process that expanded artistic possibilities beyond the intricate line work characteristic of the burin engraving technique.
Tools and Materials Used in Lithography Crayon
Lithography crayon is composed of a waxy, greasy substance that adheres to flat limestone or metal plates, enabling artists to draw directly onto the surface for printmaking. These crayons are formulated with a blend of waxes, soap, and pigments, allowing for precise control over texture and line quality in lithography. Unlike the engraving burin, which is a sharpened steel tool used to incise lines into metal plates, lithography crayons do not physically cut the surface but rely on the chemical repellent properties of grease to transfer images onto paper.
Tools and Materials Used in Engraving Burin
Engraving burins are steel tools with sharpened, diamond-shaped tips used to incise precise lines into metal plates, typically copper or zinc, for intaglio printmaking. These burins require a solid, smooth surface to effectively carve detailed grooves, making metals the preferred material for this technique. Unlike lithography crayons that work on limestone or aluminum plates, engraving burins deliver crisp, controlled cuts essential for producing fine-line engravings with deep, textured impressions.
Artistic Processes: Lithography Crayon Techniques
Lithography crayon techniques involve drawing directly onto a limestone or metal plate using a greasy, wax-based crayon that repels water and attracts ink, enabling artists to create rich textures and gradients. The crayon's variable softness allows for nuanced shading and expressive line work, which is essential for producing detailed lithographic prints. This contrasts with engraving burins, which carve precise, linear grooves into metal plates, offering different artistic effects and requiring distinct technical skills.
Artistic Processes: Engraving Burin Techniques
Engraving burin techniques involve using a sharp, steel tool to incise fine lines directly into metal plates, enabling detailed and precise artwork with varying line thickness and depth. This method allows artists to achieve rich textures and intricate designs, essential for intaglio printmaking processes such as copperplate and steel engraving. The control and pressure applied with the burin influence the quality of the lines, making it a traditional yet highly skilled tool for creating durable and high-resolution prints.
Visual Differences in Finished Prints
Lithography crayon prints exhibit soft, textured lines with subtle tonal variations due to the greasy composition that interacts with the stone surface, producing a more painterly effect. In contrast, engraving burin prints display sharp, precise lines with consistent depth and strong contrast, as the burin cuts clean grooves into the metal plate that hold the ink. The visual distinction in finished prints lies in the lithograph's rich, velvety shading versus the burin engraving's crisp, linear clarity and detailed cross-hatching.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Method
Lithography crayon offers versatility in creating detailed textures and tonal variations, making it ideal for expressive and experimental artwork, but it is limited by its dependence on greasy substances that require specific chemical processes to transfer images. Engraving burin excels in producing precise, sharp lines and fine details ideal for intaglio printmaking, yet it demands significant skill and manual effort, and corrections are difficult once the metal plate is incised. Each method's strengths cater to different artistic needs: lithography crayon supports rich tonal gradations and easier revisions, while engraving burin provides superior line clarity and durability in prints.
Notable Artists and Works Using Each Technique
Notable artists who extensively used lithography crayons include Toulouse-Lautrec, whose vibrant posters like "Moulin Rouge: La Goulue" exemplify the technique's ability to produce rich textures and expressive lines. Engraving burins were masterfully employed by Albrecht Durer, whose detailed works such as "Melencolia I" showcase the precision and depth achievable through this method. Each technique's distinct impact is reflected in these artists' seminal works, highlighting the crayon's fluid, bold marks versus the burin's intricate, finely incised detail.
Choosing Between Lithography Crayon and Engraving Burin
Choosing between lithography crayon and engraving burin depends on the desired artistic effect and technique. Lithography crayon allows for softer, more textured lines ideal for dynamic and expressive artwork, while engraving burin delivers precise, clean lines suited for detailed and highly controlled engravings. Artists prioritize lithography for printmaking versatility and burin for traditional metal engraving precision.
Lithography Crayon Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com