A burin is a specialized engraving tool featuring a sharp, chisel-like tip used primarily for carving intricate designs into metal or wood surfaces. This precision instrument allows artists and craftsmen to create detailed lines and textures with control and accuracy. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a burin can enhance your artistic projects and techniques.
Table of Comparison
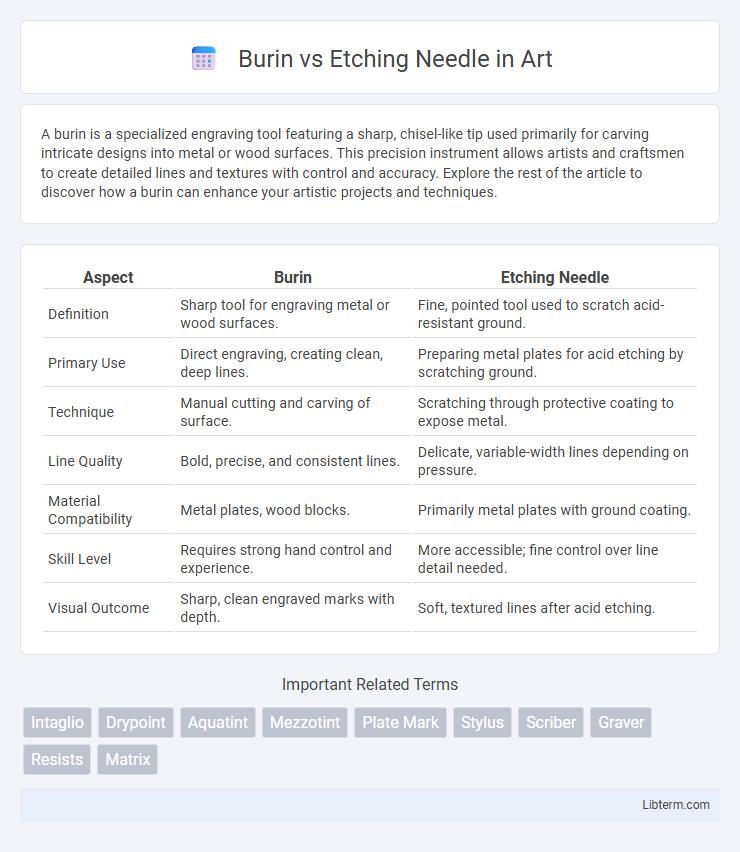
| Aspect | Burin | Etching Needle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sharp tool for engraving metal or wood surfaces. | Fine, pointed tool used to scratch acid-resistant ground. |
| Primary Use | Direct engraving, creating clean, deep lines. | Preparing metal plates for acid etching by scratching ground. |
| Technique | Manual cutting and carving of surface. | Scratching through protective coating to expose metal. |
| Line Quality | Bold, precise, and consistent lines. | Delicate, variable-width lines depending on pressure. |
| Material Compatibility | Metal plates, wood blocks. | Primarily metal plates with ground coating. |
| Skill Level | Requires strong hand control and experience. | More accessible; fine control over line detail needed. |
| Visual Outcome | Sharp, clean engraved marks with depth. | Soft, textured lines after acid etching. |
Introduction to Burin and Etching Needle
A burin is a traditional engraving tool with a sharp, chisel-like tip used primarily for carving precise, fine lines into metal, wood, or other surfaces in intaglio printmaking. An etching needle, on the other hand, is a slender, pointed instrument designed to scratch through a protective ground on a metal plate, exposing the metal beneath for acid etching processes. Both tools are essential in printmaking but serve different roles: the burin for direct engraving and the etching needle for creating acid-exposed designs.
Historical Evolution of Engraving Tools
Burin and etching needles represent key advancements in the historical evolution of engraving tools, with the burin dating back to the Renaissance as a precise metalworking instrument used for intaglio printing. Etching needles emerged in the 17th century, enabling artists to draw through protective ground layers to create lines on metal plates, enhancing detail and versatility in printmaking. The transition from burin to etching needle reflects a significant shift in engraving techniques, facilitating more intricate and expressive artwork while expanding the creative possibilities of early printmakers.
Material Composition of Burin vs Etching Needle
Burins are typically crafted from hardened steel or tool steel, providing exceptional rigidity and durability for precise engraving on metal surfaces. Etching needles commonly feature a fine stainless steel or carbon steel tip, designed for delicate scratching and scribing on coated or metal plates without applying excessive pressure. The distinct material compositions influence their respective applications in printmaking and metalworking, with burins favoring strength and etching needles prioritizing finesse.
Design Differences: Shape and Structure
A burin features a robust, chisel-like shape with a sharply angled tip designed for precise, controlled engraving on metal surfaces. In contrast, an etching needle has a slender, flexible structure with a fine, pointed end, optimized for scratching delicate lines onto coated plates for acid etching. The burin's sturdy build provides depth and consistency, whereas the etching needle allows for intricate, detailed line work through light pressure variations.
Engraving Techniques: Burin vs Etching Needle
Burin and etching needle are distinct engraving tools used in printmaking, each suited to different techniques. The burin carves precise, clean lines directly into metal plates, creating deep grooves for holding ink and producing sharp, detailed images. Etching needles puncture a protective acid-resistant ground on the plate's surface, allowing acid to etch the exposed metal, resulting in softer, more varied line qualities.
Suitable Surfaces for Each Tool
Burins are ideal for engraving on hard surfaces such as metal, wood, and bone due to their sharp, chisel-like tips that create precise lines. Etching needles are best suited for softer, coated surfaces like wax-coated metal plates or resin grounds, where they can easily scratch fine details without damaging the substrate. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the material's hardness and the desired depth and texture of the engraving or etching design.
Artistic Effects Achievable with Burin and Etching Needle
The burin produces sharp, clean lines with a consistent depth, ideal for precise engraving and detailed line work in intaglio printmaking. The etching needle allows for more varied textures and softer, sketch-like effects by scratching through a protective ground to expose the metal plate beneath. Artists often use the burin for controlled, linear designs and the etching needle for expressive, spontaneous marks that enhance tonal variation.
Tool Handling and Maintenance Tips
A burin offers precise control for engraving due to its ergonomic handle and sharp, angled tip, requiring regular sharpening and oiling to maintain performance and prevent rust. An etching needle, with a slender, fine point, demands gentle handling to avoid bending or breaking, and should be cleaned frequently to remove ink residue and ensure clarity in line work. Both tools benefit from storage in a dry, secure case to protect delicate tips and preserve tool longevity.
Common Applications in Printmaking
Burins and etching needles are essential tools in printmaking, each serving distinct functions. Burins, characterized by their sharp, V-shaped steel tips, are primarily used in engraving to carve precise, clean lines into metal plates, enabling detailed intaglio prints. Etching needles, featuring fine, pointed tips, are employed to scratch designs through acid-resistant grounds on metal plates, facilitating the creation of varied line qualities after acid bathing in the etching process.
Choosing Between Burin and Etching Needle
Choosing between a burin and an etching needle depends on the desired artistic effect and technique. A burin, with its sharp, V-shaped steel tip, creates clean, precise lines ideal for intaglio engraving on metal plates, while an etching needle is primarily used to scratch through an acid-resistant ground to expose metal for acid biting in traditional etching processes. For detailed, controlled line work, a burin offers superior accuracy, whereas the etching needle allows more freedom for expressive, varied textures in acid-etched prints.
Burin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com