Painting transforms blank spaces into vivid expressions of creativity and emotion, using colors and techniques that captivate the viewer's imagination. Mastering various painting styles enhances your ability to convey stories and evoke powerful feelings through visual art. Explore the nuances of painting techniques and find inspiration to elevate your artistic journey in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
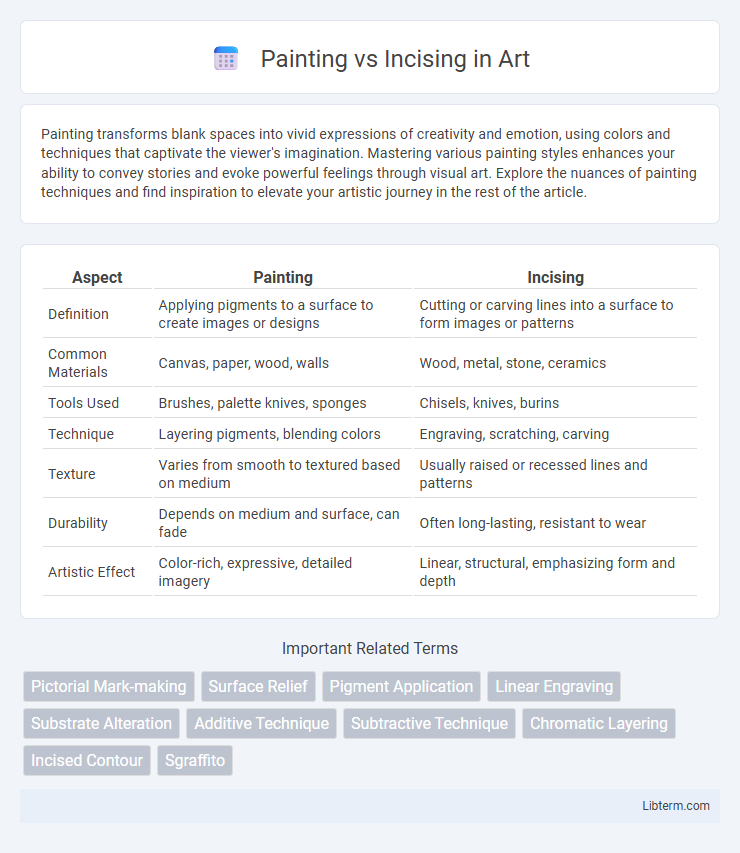
| Aspect | Painting | Incising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying pigments to a surface to create images or designs | Cutting or carving lines into a surface to form images or patterns |
| Common Materials | Canvas, paper, wood, walls | Wood, metal, stone, ceramics |
| Tools Used | Brushes, palette knives, sponges | Chisels, knives, burins |
| Technique | Layering pigments, blending colors | Engraving, scratching, carving |
| Texture | Varies from smooth to textured based on medium | Usually raised or recessed lines and patterns |
| Durability | Depends on medium and surface, can fade | Often long-lasting, resistant to wear |
| Artistic Effect | Color-rich, expressive, detailed imagery | Linear, structural, emphasizing form and depth |
Understanding Painting and Incising
Painting involves applying pigments to a surface to create images or patterns, emphasizing color, texture, and visual expression. Incising refers to carving or engraving lines into a material, such as clay, stone, or metal, to form designs or inscriptions that rely on depth and contrast. Understanding the techniques and tools used in both painting and incising reveals their distinct roles in art history and cultural communication.
Historical Evolution of Techniques
Painting and incising illustrate distinct historical evolutions in artistic techniques, with painting dating back to prehistoric cave art where pigments were applied to surfaces to create imagery. Incising emerged as a method in ancient cultures, involving carving or engraving lines into materials such as bone, stone, or ceramics to produce decorative or symbolic designs. Over time, painting evolved with the development of various media and brushes, while incising techniques advanced through improved tools and materials, reflecting changes in technology and cultural expression.
Materials and Tools Comparison
Painting involves applying pigments suspended in a liquid medium such as oil, acrylic, or watercolor, using brushes, sponges, or palette knives to create colors and textures on surfaces like canvas, paper, or wood. Incising requires tools like burins, gravers, or knives to carve or cut into materials such as metal plates, stone, or wood, producing grooves that hold ink or create detailed designs. While painting focuses on adding color layers for visual effects, incising emphasizes precision and depth through physical removal or displacement of surface material.
Methods and Process Differences
Painting involves applying pigments mixed with a binder onto a surface, allowing for color blending and layering techniques to create visual effects, while incising entails carving or cutting into a substrate to produce lines or patterns without adding color. Painting's process relies on the manipulation of liquid media such as oils, acrylics, or watercolors, enabling a fluid and expressive outcome, whereas incising requires tools like chisels, knives, or styluses to physically remove material, resulting in textured and often permanent marks. The fundamental distinction lies in painting as an additive and surface-based method, contrasting with incising as a subtractive technique that alters the surface structure itself.
Aesthetic Outcomes and Visual Effects
Painting produces vibrant color layers with rich textures and depth, enhancing visual dynamism through varied brush strokes and pigment opacity. Incising creates intricate linear patterns and tactile surface contrasts by carving into materials, offering a subtle interplay of light and shadow. The choice between painting and incising significantly influences the artwork's aesthetic outcome, with painting emphasizing color vibrancy and incising highlighting form and texture.
Durability and Longevity
Painting on surfaces relies on pigments applied to a substrate, which can fade or peel over time due to environmental exposure, reducing its durability and longevity. Incising, the technique of carving or engraving designs directly into materials like stone, ceramic, or metal, typically offers greater resistance to wear and environmental damage. The physical depth of incisions protects the artwork from superficial abrasion and weathering, making incised pieces more enduring across centuries compared to painted surfaces.
Popular Artistic Styles and Movements
Painting dominates popular artistic styles such as Impressionism, Abstract Expressionism, and Surrealism, emphasizing color, texture, and brushwork to evoke emotion and atmosphere. Incising is prominent in movements like Cubism and early modern ceramics, where artists carve or engrave surfaces to create geometric forms and tactile patterns that highlight structure and form. Techniques in painting and incising have evolved to reflect cultural shifts, with painting favoring fluidity and expression, while incising accentuates precision and dimensionality.
Applications in Modern Art and Design
Painting offers expansive possibilities in modern art and design through versatile color blending and texture creation, enabling artists to convey emotion and atmosphere on diverse surfaces. Incising, involving precise cutting or engraving into materials such as metal, wood, or ceramics, emphasizes texture and dimensionality, often used in contemporary sculpture and textile design for intricate patterns or tactile effects. Both techniques play crucial roles in multimedia installations and experimental art forms, where the interplay of painted surfaces and incised details enhances visual depth and conceptual impact.
Pros and Cons of Painting vs Incising
Painting offers vibrant color variation and surface decoration, making it ideal for detailed and expressive artwork, but it risks fading and chipping over time. Incising provides durability through carved or etched patterns, ensuring longevity and textural depth, yet it lacks the color diversity and visual softness painting can achieve. While painting allows for easy alterations and bold contrasts, incising demands precision and is less adaptable to changes once completed.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Selecting between painting and incising depends on your project's surface material and desired texture; painting offers vibrant color application suitable for smooth or porous surfaces, while incising creates detailed, tactile patterns by cutting into materials like clay or wood. Consider the durability needed--incising provides long-lasting designs often resistant to fading, whereas paint may require sealing or touch-ups over time. Evaluate your project's artistic vision and functional requirements to determine the best technique for achieving depth, detail, and aesthetic impact.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com