Titanium White is a highly opaque, bright white pigment commonly used in painting for its excellent coverage and durability. Its strong tinting strength and non-toxic nature make it a favorite among artists for creating vibrant highlights and mixing with other colors. Discover how Titanium White can enhance Your artwork by exploring the full range of its properties and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
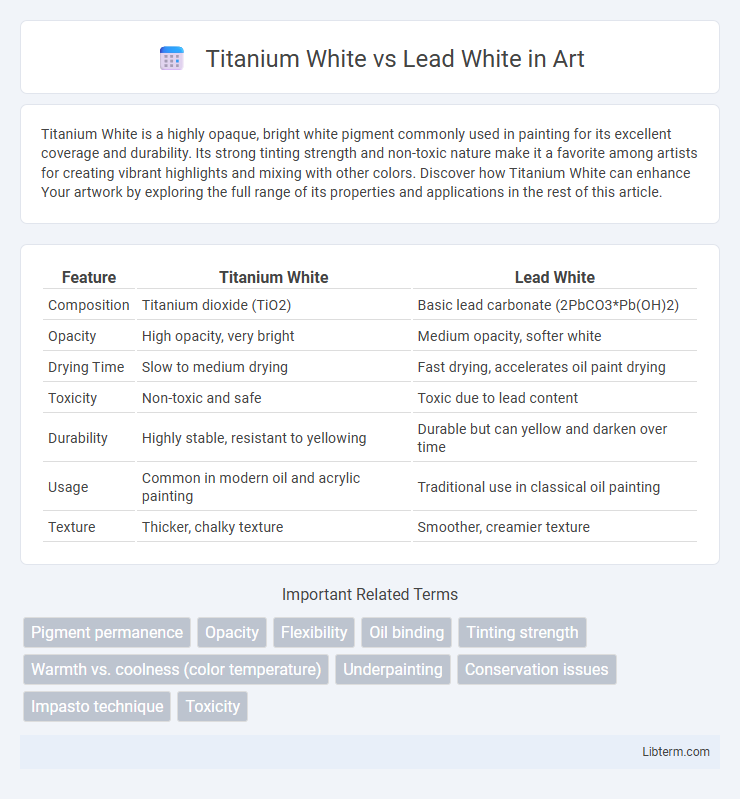
| Feature | Titanium White | Lead White |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Titanium dioxide (TiO2) | Basic lead carbonate (2PbCO3*Pb(OH)2) |
| Opacity | High opacity, very bright | Medium opacity, softer white |
| Drying Time | Slow to medium drying | Fast drying, accelerates oil paint drying |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic and safe | Toxic due to lead content |
| Durability | Highly stable, resistant to yellowing | Durable but can yellow and darken over time |
| Usage | Common in modern oil and acrylic painting | Traditional use in classical oil painting |
| Texture | Thicker, chalky texture | Smoother, creamier texture |
Introduction to Titanium White and Lead White
Titanium White, primarily composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), offers superior opacity, brightness, and non-toxic qualities compared to traditional Lead White, which consists of basic lead carbonate. Lead White has been widely used historically for its warm undertones and strong adhesive properties but poses significant toxicity risks due to lead content. Artists favor Titanium White for its durability and high covering power, making it the preferred choice in modern painting.
Historical Use of White Pigments in Art
Titanium White, chemically titanium dioxide, revolutionized the art world in the 20th century by offering a brighter, more opaque alternative to Lead White, which dominated from antiquity through the 19th century. Lead White, composed of basic lead carbonate, provided warm undertones and excellent blending properties but posed significant toxicity risks to artists. The transition to Titanium White marked a pivotal shift in white pigment use, enhancing durability and safety while preserving the essential visual qualities required in fine art applications.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Titanium White, composed primarily of titanium dioxide (TiO2), offers high opacity, strong covering power, and excellent non-toxicity, making it a popular modern pigment. Lead White, chemically basic lead carbonate (2PbCO3*Pb(OH)2), is known for its warm tone, durability, and fast drying properties but exhibits toxicity concerns due to lead content. Titanium White provides superior lightfastness and chemical stability compared to Lead White, which can darken over time from sulfur exposure and environmental factors.
Color and Opacity Differences
Titanium White offers a brilliant, cool-toned white with exceptionally high opacity, making it ideal for strong coverage and bright highlights in painting. In contrast, Lead White provides a warmer, slightly yellowish hue with moderate opacity, favored for its subtle blending and traditional use in underpainting. The distinct color temperatures and opacity levels of Titanium White and Lead White significantly influence texture, layering, and luminosity in artwork.
Mixing Behavior and Tint Strength
Titanium White exhibits a higher tinting strength compared to Lead White, allowing it to dominate mixtures with vibrant opacity. Its mixing behavior results in cooler, more opaque blends, while Lead White offers a warmer, more translucent quality that gently modifies colors without overpowering them. Artists favor Titanium White for bold coverage and Lead White for subtle color shifts and glazing effects.
Drying Time and Handling Characteristics
Titanium White offers slower drying times compared to Lead White, which dries relatively fast due to its lead content enhancing oxidation. Handling characteristics of Titanium White include a stiffer consistency and greater opacity, making it ideal for thick applications and impasto techniques, whereas Lead White provides a smoother, creamier texture favored for detailed blending. Artists often choose Lead White for fast-drying layers and Titanium White for its non-toxic composition and superior lightfastness.
Archival Quality and Longevity
Titanium White offers superior archival quality compared to Lead White due to its high opacity and non-toxic properties, ensuring artworks remain vibrant without yellowing over time. Lead White, while historically favored for its warm tone and smooth blending, tends to darken and develop cracks because of its chemical instability and toxicity. Modern conservators prefer Titanium White for its durability and safety, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting, archival-quality paintings.
Toxicity and Health Considerations
Titanium White is considered non-toxic and safe for use in art, making it suitable for artists concerned about health risks, whereas Lead White contains lead, a highly toxic heavy metal linked to severe health hazards including neurological damage and poisoning. Prolonged exposure to Lead White, especially through inhalation or ingestion of paint dust or chips, poses significant risks, necessitating strict safety measures such as proper ventilation and protective equipment. Titanium White's inert chemical properties minimize health concerns, making it a preferred choice for artists seeking a safer alternative without compromising on opacity and brightness.
Cost and Availability
Titanium white is generally more affordable and widely available than lead white, which has become scarce due to health regulations restricting lead-based pigments. Artists often choose titanium white for its cost-effectiveness and ease of purchase from most art supply stores worldwide. Lead white remains more expensive and harder to find, primarily used by professionals who prioritize its unique opacity and drying qualities despite its limited availability.
Choosing the Right White for Your Painting Style
Titanium White offers superior opacity and brightness, making it ideal for artists who prefer bold, vibrant highlights and faster drying times. Lead White, known for its warm undertone and smooth, buttery texture, is favored in classical techniques for subtle blending and longer working times. Selecting the right white depends on your painting style: Titanium White suits modern, expressive artworks, while Lead White enhances traditional, detailed oil paintings.
Titanium White Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com