Screen printing offers vibrant, durable designs ideal for custom apparel and promotional products. This technique uses a mesh screen to transfer ink, ensuring sharp and long-lasting prints on various materials. Discover how screen printing can elevate your creative projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
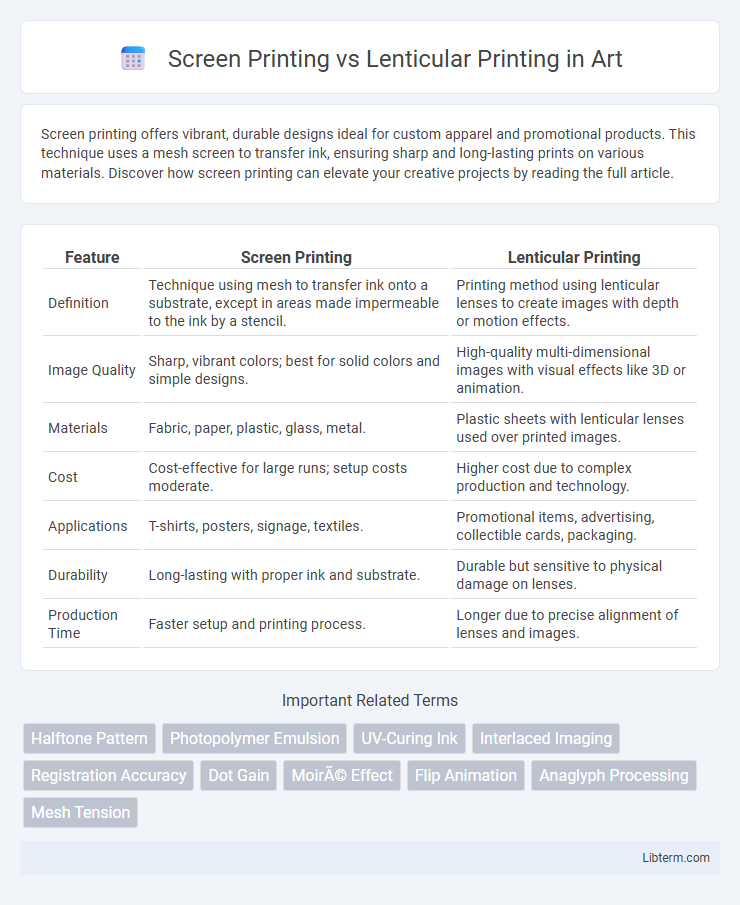
| Feature | Screen Printing | Lenticular Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique using mesh to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a stencil. | Printing method using lenticular lenses to create images with depth or motion effects. |
| Image Quality | Sharp, vibrant colors; best for solid colors and simple designs. | High-quality multi-dimensional images with visual effects like 3D or animation. |
| Materials | Fabric, paper, plastic, glass, metal. | Plastic sheets with lenticular lenses used over printed images. |
| Cost | Cost-effective for large runs; setup costs moderate. | Higher cost due to complex production and technology. |
| Applications | T-shirts, posters, signage, textiles. | Promotional items, advertising, collectible cards, packaging. |
| Durability | Long-lasting with proper ink and substrate. | Durable but sensitive to physical damage on lenses. |
| Production Time | Faster setup and printing process. | Longer due to precise alignment of lenses and images. |
Introduction to Screen Printing and Lenticular Printing
Screen printing uses a mesh stencil to transfer ink onto materials like fabric or paper, creating vibrant, durable designs ideal for apparel and signage. Lenticular printing produces images with depth and motion effects by layering lenses over interlaced images, commonly used in advertising and novelty items. Both techniques serve distinct purposes: screen printing excels in solid-color graphics, while lenticular printing offers dynamic visual experiences.
Key Differences Between Screen Printing and Lenticular Printing
Screen printing uses a mesh stencil to apply layers of ink directly onto a surface, offering vibrant colors and durability ideal for textiles and posters, while lenticular printing employs lenses to create images with depth or motion effects, perfect for promotional materials requiring 3D or animated visuals. Screen printing delivers solid, opaque colors with a tactile texture, whereas lenticular printing produces dynamic visuals that change with the viewing angle but relies on precise image alignment and specialized materials. The choice depends on desired visual impact, cost, and application, with screen printing excelling in bold, static designs and lenticular printing suited for eye-catching, interactive graphics.
How Screen Printing Works: Process Overview
Screen printing involves creating a stencil, or screen, where ink is pushed through mesh openings onto a substrate, such as fabric or paper. The process begins by coating a fine mesh screen with a light-sensitive emulsion, which hardens after exposure to UV light through a film positive, leaving open areas where ink passes through. Each color requires a separate screen, and multiple layers of ink are applied sequentially, resulting in vibrant and durable prints ideal for textiles and promotional materials.
Understanding Lenticular Printing Technology
Lenticular printing technology uses lenses to create images with an illusion of depth or motion, achieved by interlacing multiple images and aligning them with a lenticular lens sheet. This method differs from traditional screen printing by delivering dynamic visual effects such as 3D depth, flip, or animation, enhancing viewer engagement. Precision in lens alignment and image interlacing is critical for optimal lenticular image clarity and effect performance.
Material Compatibility for Both Printing Methods
Screen printing is highly compatible with a wide range of materials, including textiles, plastics, glass, metal, and wood, due to its ability to use various ink types like plastisol and water-based inks. Lenticular printing requires specialized lenticular lenses made from plastic substrates such as PET or acrylic, which must be precisely aligned with the printed interlaced images on compatible films or paper to achieve desired 3D or animated effects. The fundamental difference lies in substrate flexibility, as screen printing supports diverse material surfaces while lenticular printing is limited to transparent, rigid plastic sheets and certain coated papers for optimal visual performance.
Visual Effects and Image Quality Comparison
Screen printing delivers vibrant, solid colors with high opacity, making it ideal for bold graphic designs and sharp contrast images. Lenticular printing offers dynamic visual effects like 3D depth, motion, or morphing images by using lenticular lenses to manipulate light, creating unique interactive viewing experiences. While lenticular printing excels in visual engagement and motion simulation, screen printing maintains superior color saturation and detail precision for static images.
Cost Analysis: Screen Printing vs Lenticular Printing
Screen printing offers lower setup costs and is cost-effective for large volume orders due to its streamlined process and reusable screens. Lenticular printing involves higher initial expenses driven by specialized lenses and precise alignment, making it more suitable for smaller, premium runs. Businesses should weigh long-term print volume and desired visual effects against these cost factors to determine the most economical choice.
Ideal Applications for Screen Printing
Screen printing excels in producing durable, vibrant designs on textiles, posters, and promotional products, making it ideal for bulk apparel manufacturing and branded merchandise. Its ability to apply thick layers of ink ensures high opacity and color consistency, especially on dark or uneven surfaces. Screen printing is preferred for simple, bold graphics with limited colors, suited for t-shirts, banners, and packaging where longevity and cost-effectiveness are crucial.
Best Use Cases for Lenticular Printing
Lenticular printing excels in applications requiring dynamic visual effects such as 3D depth, flip images, or animation, making it ideal for promotional displays, packaging, and interactive marketing materials. Unlike screen printing, which is suited for solid colors and durable prints on textiles or posters, lenticular printing offers eye-catching motion and transformation effects that enhance consumer engagement. Best use cases include advertising campaigns, product labels that stand out on shelves, and collectible cards that leverage visual interactivity.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Screen printing excels in producing vibrant, durable designs on fabrics and flat surfaces, ideal for bulk orders requiring consistent quality and bold colors. Lenticular printing offers dynamic, eye-catching visuals with 3D effects or motion illusions, best suited for promotional materials and packaging that aim to capture attention with unique visual impact. Selecting the right method depends on project goals, budget constraints, and desired visual effects, balancing cost-efficiency with the need for innovative presentation.
Screen Printing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com