Grayscale plays a crucial role in design and photography, offering a spectrum of shades from black to white that enhances contrast and depth without the distraction of color. Understanding how to effectively use grayscale can improve your visuals by emphasizing texture, form, and composition. Explore the full article to discover techniques and benefits of mastering grayscale in your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
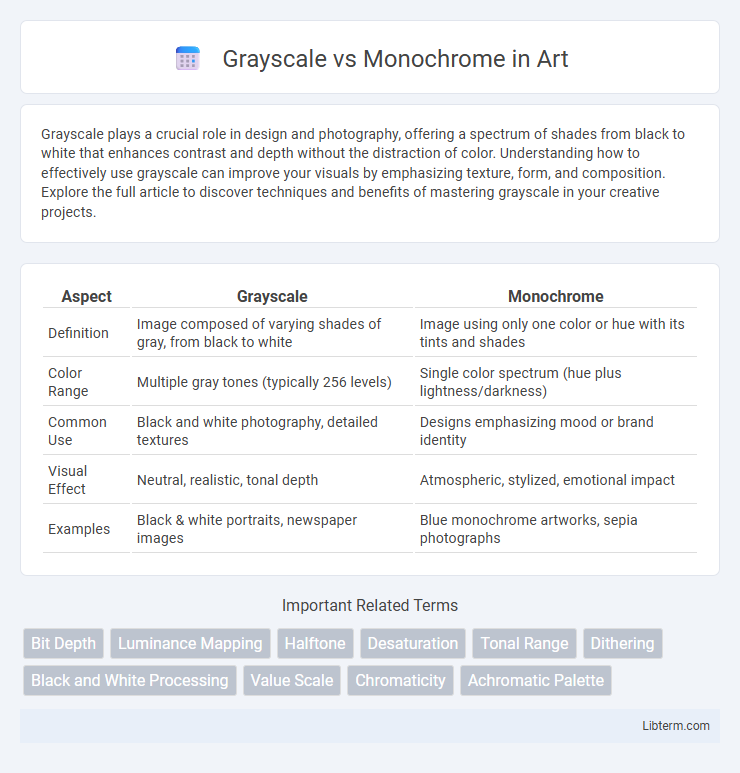
| Aspect | Grayscale | Monochrome |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Image composed of varying shades of gray, from black to white | Image using only one color or hue with its tints and shades |
| Color Range | Multiple gray tones (typically 256 levels) | Single color spectrum (hue plus lightness/darkness) |
| Common Use | Black and white photography, detailed textures | Designs emphasizing mood or brand identity |
| Visual Effect | Neutral, realistic, tonal depth | Atmospheric, stylized, emotional impact |
| Examples | Black & white portraits, newspaper images | Blue monochrome artworks, sepia photographs |
Grayscale vs Monochrome: Key Differences Explained
Grayscale images display a range of gray shades varying from black to white, allowing for subtle detail and depth in visual representation. Monochrome images consist of only two colors, typically black and white, creating a stark contrast without intermediate shades. This fundamental difference impacts image clarity, tonal variation, and application suitability in fields such as printing, photography, and digital design.
What Is Grayscale?
Grayscale represents images composed exclusively of shades of gray, varying from black at the darkest to white at the lightest, without any color hues. Each pixel in a grayscale image carries intensity information, making it ideal for detailed tonal variations in photography, printing, and medical imaging. This format effectively simplifies image data while preserving essential visual details for analysis and display.
What Is Monochrome?
Monochrome refers to images or designs consisting of varying shades of a single color, often black and white or any single hue with its tints and shades. Unlike grayscale, which specifically uses shades of gray to represent images without color, monochrome can include any one color spectrum, offering a broader range of artistic expression. This technique is commonly used in photography, printing, and digital design to emphasize form, texture, and contrast without the distraction of multiple colors.
The Science Behind Grayscale Images
Grayscale images represent varying shades of gray, created by combining red, green, and blue light intensities based on human visual perception sensitivity to each color. The science behind grayscale involves calculating luminance, where green contributes most to brightness, followed by red and blue, reflecting how the human eye detects light. This process results in a single-channel image that preserves brightness information, enabling detailed textures and contrasts essential for image analysis and processing.
How Monochrome Imaging Works
Monochrome imaging captures images using varying intensities of a single color channel, typically black and white, by recording luminance without color information. Unlike grayscale, which represents shades through multiple levels of gray to simulate depth and detail, monochrome focuses on contrast by emphasizing light and dark areas to enhance texture and form. This method relies on varying light absorption and reflection to create distinct, high-contrast images used in applications like art photography, medical imaging, and printing technologies.
Use Cases for Grayscale Photography
Grayscale photography excels in capturing subtle tonal variations and enhancing textures, making it ideal for fine art portraits, architectural studies, and documentary projects where mood and detail are critical. This monochromatic approach emphasizes light and shadow contrasts, which helps to convey emotions and narrative depth more powerfully than color images. In scientific imaging and medical diagnostics, grayscale images provide superior clarity for analyzing structural details and identifying anomalies.
Applications of Monochrome in Design
Monochrome design, using variations of a single color, enhances visual unity and brand consistency across digital and print media. It simplifies user interface elements, improving usability by reducing visual clutter and emphasizing content hierarchy. This approach is widely applied in logo creation, website design, and product packaging to evoke specific moods and reinforce identity through controlled color palettes.
Visual Impact: Grayscale vs Monochrome
Grayscale images display a range of tones from black to white, creating depth and subtle contrast that enhances the perception of texture and detail. Monochrome images use variations of a single color, often creating a heightened emotional or artistic impact by emphasizing color harmony and mood over fine tonal transitions. The visual impact of grayscale lies in its realistic representation of light and shadow, while monochrome offers a more stylized and expressive interpretation.
File Size and Compatibility Considerations
Grayscale images typically use 8 bits per pixel, resulting in larger file sizes compared to monochrome images, which use only 1 bit per pixel and thus offer significant storage savings. Compatibility with grayscale formats is higher across modern software and devices since they preserve varying shades of gray, while monochrome images are mostly supported by specialized applications due to their binary color scheme. Choosing grayscale enhances visual detail at the expense of file size, whereas monochrome ensures maximum compression and simpler compatibility primarily suited for text or simple graphics.
Choosing Between Grayscale and Monochrome
Choosing between grayscale and monochrome depends on the desired image detail and contrast level. Grayscale offers a range of gray shades, providing depth and subtlety in tonal variations, ideal for nuanced photographs and detailed artwork. Monochrome uses a single color or pure black and white, emphasizing stark contrast and simplicity, often preferred for graphic design and bold visual statements.
Grayscale Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com