Color blocking uses bold, contrasting blocks of color to create striking visual effects in fashion and design. This technique emphasizes your individuality by combining vibrant hues that highlight shapes and enhance style. Discover how color blocking can transform your wardrobe and living spaces in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
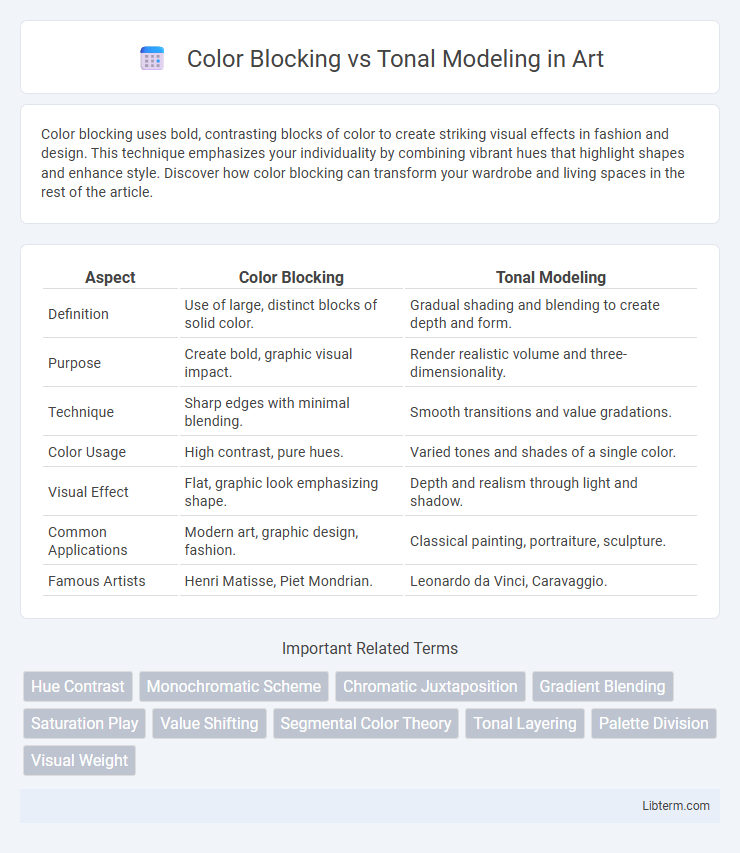
| Aspect | Color Blocking | Tonal Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of large, distinct blocks of solid color. | Gradual shading and blending to create depth and form. |
| Purpose | Create bold, graphic visual impact. | Render realistic volume and three-dimensionality. |
| Technique | Sharp edges with minimal blending. | Smooth transitions and value gradations. |
| Color Usage | High contrast, pure hues. | Varied tones and shades of a single color. |
| Visual Effect | Flat, graphic look emphasizing shape. | Depth and realism through light and shadow. |
| Common Applications | Modern art, graphic design, fashion. | Classical painting, portraiture, sculpture. |
| Famous Artists | Henri Matisse, Piet Mondrian. | Leonardo da Vinci, Caravaggio. |
Introduction to Color Blocking and Tonal Modeling
Color blocking involves using bold, contrasting blocks of color to create visually striking designs, emphasizing distinct areas with solid hues. Tonal modeling employs subtle gradations of a single color or closely related shades to build depth, form, and dimension in artwork or fashion. Both techniques enhance visual interest, with color blocking prioritizing contrast and tonal modeling focusing on harmony and shading.
Defining Color Blocking in Fashion
Color blocking in fashion is the technique of combining large, solid blocks of contrasting colors within a single outfit to create bold visual impact and dynamic style. This approach emphasizes geometric shapes and sharp color divisions, often using unblended hues like red, blue, or yellow to enhance vibrancy and structure. Unlike tonal modeling, which relies on gradients and shades of a single color to produce depth, color blocking prioritizes stark color contrasts to define silhouette and energy.
What is Tonal Modeling?
Tonal modeling is a makeup technique that emphasizes the use of varying shades and tones of the same color to sculpt and define facial features, creating a natural and seamless contour. Unlike color blocking, which uses contrasting blocks of color for a bold, graphic effect, tonal modeling relies on subtle gradients and blending to enhance the face's structure. This approach highlights depth and dimension by strategically placing lighter and darker tones to mimic natural shading.
Key Differences Between Color Blocking and Tonal Modeling
Color blocking emphasizes using contrasting, solid color sections to create bold, graphic designs, while tonal modeling relies on subtle variations within a single color family to achieve depth and realism. Color blocking simplifies visual elements, prioritizing shape and structure over texture, whereas tonal modeling enhances form through gradual shading and highlights. The key difference lies in color application: color blocking uses stark contrasts, and tonal modeling employs nuanced gradients to convey dimensionality.
Visual Impact: Boldness vs. Subtlety
Color blocking creates a bold visual impact by juxtaposing contrasting, vibrant colors that draw immediate attention and energize a composition. Tonal modeling emphasizes subtlety through gradual shifts in hue and value within a color family, enhancing depth and form without overwhelming the viewer. The choice between color blocking and tonal modeling ultimately shapes the artwork's emotional intensity and narrative clarity.
Color Theory Behind Each Technique
Color blocking relies on high-contrast, distinct hues placed side by side to create bold visual impact, emphasizing complementary or analogous color schemes for maximum vibrancy. Tonal modeling uses gradual transitions of shades and tints within a single hue to build depth, volume, and realism by manipulating light and shadow through value variation. Both techniques apply foundational color theory principles--color blocking accentuates hue contrast, while tonal modeling exploits value gradation to influence perception.
Styling Tips for Color Blocking
For effective color blocking, select bold, contrasting colors such as red and navy or emerald and mustard to create striking visual impact. Balance the outfit by limiting patterns and keeping accessories minimal to let the color blocks stand out prominently. Incorporate neutral bases like black or white to anchor vibrant hues and maintain cohesion in your overall look.
How to Achieve the Tonal Modeling Look
To achieve the tonal modeling look, focus on layering multiple shades of the same color family to create depth and dimension. Use gradients and subtle transitions between light and dark tones to enhance the natural contours of the face or objects, emphasizing shadow and highlight interplay. Avoid harsh contrasts typical of color blocking and instead blend colors smoothly to maintain a cohesive and sophisticated appearance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Both Approaches
Color blocking often suffers from harsh contrasts that overwhelm the composition, while tonal modeling mistakes frequently involve insufficient value variation leading to flatness. Avoid using clashing hues without a unifying color scheme in color blocking and neglecting light source consistency in tonal modeling. Proper balance in saturation and intentional gradient transitions are essential to prevent visual discord and maintain depth in both techniques.
Choosing Between Color Blocking and Tonal Modeling
Choosing between color blocking and tonal modeling depends on the desired visual impact and context of the design. Color blocking emphasizes bold, contrasting colors for a striking, modern aesthetic, ideal for making elements stand out, while tonal modeling uses subtle shades and gradients within a single color family to create depth and dimension, enhancing realism and sophistication. Consider the project's goals--whether you want vivid contrast or smooth transitions--to select the technique that best enhances user engagement and visual hierarchy.
Color Blocking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com