Proper installation ensures optimal performance and longevity of your equipment by following precise manufacturer guidelines and using the right tools. Skipping essential steps during the setup can lead to malfunctions, safety hazards, and costly repairs. Explore the complete article to master the installation process and secure your device's reliability.
Table of Comparison
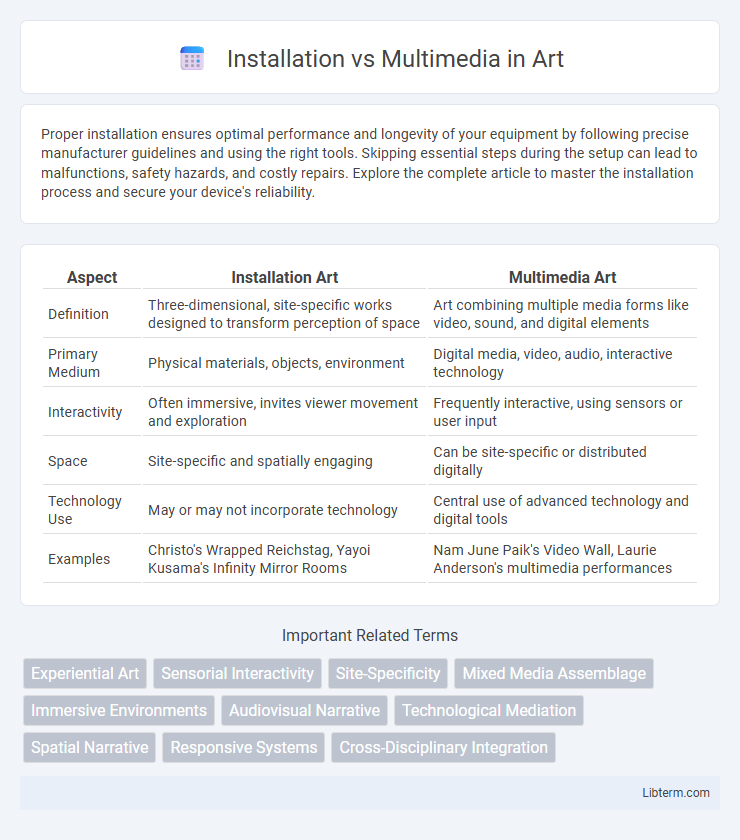
| Aspect | Installation Art | Multimedia Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional, site-specific works designed to transform perception of space | Art combining multiple media forms like video, sound, and digital elements |
| Primary Medium | Physical materials, objects, environment | Digital media, video, audio, interactive technology |
| Interactivity | Often immersive, invites viewer movement and exploration | Frequently interactive, using sensors or user input |
| Space | Site-specific and spatially engaging | Can be site-specific or distributed digitally |
| Technology Use | May or may not incorporate technology | Central use of advanced technology and digital tools |
| Examples | Christo's Wrapped Reichstag, Yayoi Kusama's Infinity Mirror Rooms | Nam June Paik's Video Wall, Laurie Anderson's multimedia performances |
Introduction to Installation and Multimedia Art
Installation art transforms space by immersing viewers in three-dimensional environments that engage multiple senses. Multimedia art integrates various forms of media, such as video, sound, and digital technologies, to create interactive and dynamic experiences. Both art forms challenge traditional boundaries by emphasizing viewer interaction and blending physical and digital elements.
Defining Installation Art
Installation art is a three-dimensional, site-specific work designed to transform the perception of a space by engaging viewers in an immersive experience. It differs from traditional multimedia by emphasizing physical interaction and spatial presence rather than combining various digital or audiovisual elements alone. Installation art often incorporates diverse materials and sensory stimuli to create a cohesive environment that challenges conventional art boundaries.
Understanding Multimedia Art
Multimedia art integrates diverse digital mediums such as video, sound, and interactive elements to create immersive experiences that challenge traditional artistic boundaries. Installation art often occupies physical space, inviting viewers to engage spatially and sensorially, whereas multimedia art emphasizes the convergence of technology and narrative to evoke dynamic responses. Understanding multimedia art requires analyzing how digital interfaces and multi-sensory stimuli transform audience interaction and redefine the artwork's meaning.
Historical Evolution of Both Mediums
Installation art emerged in the early 20th century, evolving from traditional sculpture to immersive environments that engage multiple senses and spatial awareness. Multimedia art developed alongside technological advancements in the late 20th century, integrating digital video, audio, and interactive components to create dynamic experiences. Both mediums reflect a shift from static forms to experiential narratives, influenced by innovations in technology and changing cultural contexts.
Key Differences Between Installation and Multimedia
Installation art is a three-dimensional, site-specific work designed to transform the viewer's perception of a space, often incorporating physical materials and environmental interaction. Multimedia art combines various digital and analog media such as video, sound, text, and graphics to create an integrated sensory experience, typically presented on screens or through electronic devices. The key difference lies in installation's spatial and physical engagement versus multimedia's emphasis on digital and audiovisual integration.
The Role of Technology in Art Forms
Technology plays a pivotal role in both installation and multimedia art by enabling artists to create immersive and interactive experiences that engage multiple senses. Installation art often incorporates digital sensors, projection mapping, and augmented reality to transform physical spaces into dynamic environments. Multimedia art leverages software, video, sound design, and virtual reality to merge various forms of media, enhancing storytelling and emotional impact through technological innovation.
Audience Interaction and Experience
Installation art creates immersive environments that engage audiences through physical presence and spatial interaction, encouraging active exploration and personal interpretation. Multimedia art integrates various digital elements such as video, sound, and interactive technology, offering dynamic sensory experiences that adapt to audience input in real time. Both forms prioritize audience participation but differ in their approach: installations emphasize tangible, environmental immersion while multimedia focuses on interactive digital engagement.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Installation art features immersive environments by artists like Yayoi Kusama with her "Infinity Mirror Rooms" and James Turrell's light-based works, transforming space and perception. Multimedia art blends various mediums, exemplified by Nam June Paik's pioneering video installations and Bill Viola's profound video art exploring human experience. Both genres push boundaries, with installations emphasizing spatial interaction and multimedia focusing on integrating sound, video, and technology.
Challenges and Opportunities in Creation
Installation art faces challenges in spatial constraints, requiring artists to adapt their multimedia elements to physical environments while ensuring audience interaction remains immersive. Multimedia creation offers opportunities through evolving digital technologies, enabling dynamic content integration, but demands expertise in various software and hardware to maintain seamless execution. Balancing the tactile nature of installation with the versatility of multimedia fosters innovative expressions that expand artistic boundaries.
Future Trends in Installation and Multimedia Art
Future trends in installation and multimedia art emphasize immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and interactive digital interfaces that enhance audience engagement. Artists increasingly integrate AI-driven algorithms and real-time data processing to create dynamic, evolving installations. Sustainable materials and eco-conscious design also shape the development of multimedia art, reflecting growing environmental awareness within the creative industry.
Installation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com