Additive painting builds up layers of color and texture to create depth and complexity in artwork. This technique contrasts with subtractive methods by continuously adding materials rather than removing them. Discover how additive painting can transform your creative process by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
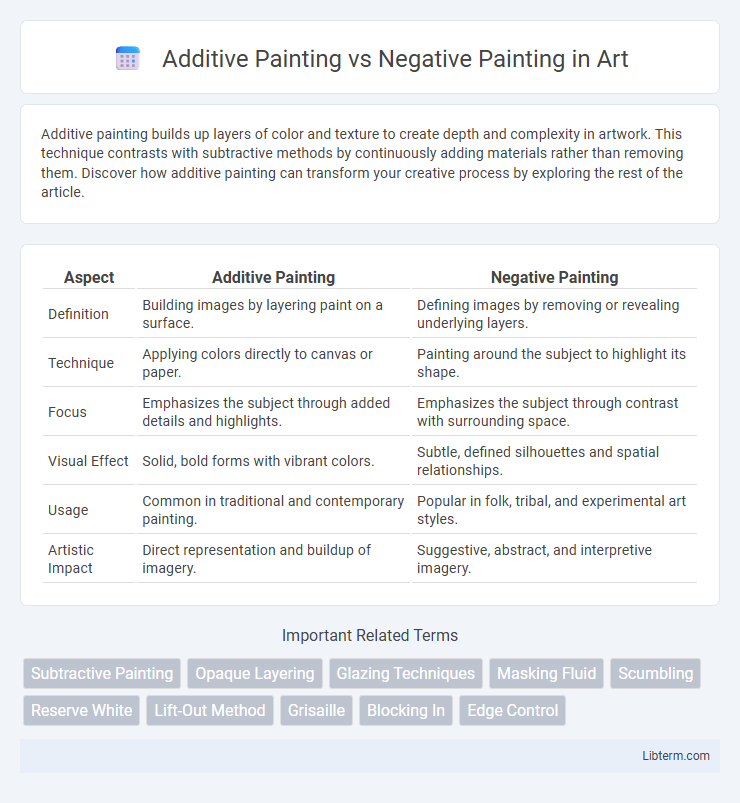
| Aspect | Additive Painting | Negative Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building images by layering paint on a surface. | Defining images by removing or revealing underlying layers. |
| Technique | Applying colors directly to canvas or paper. | Painting around the subject to highlight its shape. |
| Focus | Emphasizes the subject through added details and highlights. | Emphasizes the subject through contrast with surrounding space. |
| Visual Effect | Solid, bold forms with vibrant colors. | Subtle, defined silhouettes and spatial relationships. |
| Usage | Common in traditional and contemporary painting. | Popular in folk, tribal, and experimental art styles. |
| Artistic Impact | Direct representation and buildup of imagery. | Suggestive, abstract, and interpretive imagery. |
Introduction to Additive and Negative Painting
Additive painting involves layering colors and shapes to build images, emphasizing the gradual construction of forms by applying pigments onto a surface. Negative painting creates images by painting around the subject, using the background to define shapes and contours through the absence of color. Both techniques manipulate figure-ground relationships but differ in their approach to defining visual elements, with additive focusing on positive space and negative on negative space.
Defining Additive Painting Techniques
Additive painting techniques involve building up layers of paint to create images by gradually adding color and texture, enhancing depth and dimension. This method emphasizes positive shapes formed by applying pigment directly onto the canvas, contrasting with negative painting, which defines forms by painting around the subject. Mastery of additive painting requires understanding color blending, layering effects, and brushstroke control to achieve vibrant, detailed compositions.
Exploring Negative Painting Methods
Negative painting methods emphasize the deliberate removal or masking of paint to reveal underlying layers, creating shapes and forms through contrast rather than direct application. This technique contrasts with additive painting, where color and texture are built up by layering paint onto the canvas. Exploring negative painting allows artists to manipulate space and depth uniquely, often enhancing visual interest and composition through subtle, intentional hollows in the pigmentation.
Key Differences Between Additive and Negative Painting
Additive painting builds an image by layering colors and shapes onto a blank surface, creating form through the direct application of pigment. Negative painting defines shapes by painting around the subject, using the background to reveal the intended forms through contrast. This fundamental difference influences composition, technique, and the artist's control over figure-ground relationships.
Materials and Tools for Each Approach
Additive painting relies on applying layers of pigment using brushes, palette knives, or sponges, often utilizing acrylics, oils, or watercolors to build color and texture. Negative painting involves removing or masking color, typically employing masking fluid, frisket film, or erasers alongside watercolors or inks to create contrast by revealing underlying paper or layers. Both techniques require precise tool selection to achieve the intended effects, with additive painting focusing on layering materials and negative painting emphasizing subtraction or preservation of the substrate.
Advantages of Additive Painting
Additive painting enhances control over color intensity and layering by building up pigments gradually, allowing for rich texture and depth in the artwork. This technique facilitates precise detail work and color mixing directly on the surface, resulting in vibrant and dynamic compositions. Compared to negative painting, additive painting offers greater versatility in achieving complex visual effects and a more intuitive approach for artists seeking to manipulate form through direct application.
Benefits of Negative Painting
Negative painting enhances depth and texture by emphasizing background elements, creating striking contrast and visual interest that additive painting may lack. This technique allows for greater subtlety and complexity in compositions, highlighting shapes through the absence rather than presence of color. Artists benefit from negative painting by achieving nuanced tonal variations and a unique interplay between light and shadow, enriching overall visual storytelling.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Additive painting and negative painting both present challenges such as achieving the desired color intensity and maintaining precise edges. Artists often struggle with controlling opacity in additive painting, requiring multiple layers to build up rich hues without muddying colors. Overcoming these issues involves mastering layering techniques, using high-quality, transparent pigments, and practicing patience to allow each layer to dry thoroughly before applying the next, ensuring clean lines and vibrant results.
Tips for Choosing the Right Technique
Additive painting builds images by layering colors and shapes from light to dark, while negative painting focuses on defining the subject by painting around it, emphasizing the background. To choose the right technique, artists should consider their desired visual impact: additive painting suits vivid, detailed subjects, whereas negative painting excels in creating strong contrasts and abstract forms. Experimenting with both methods on small canvas studies can help determine which approach best enhances the composition and mood of the artwork.
Inspiring Examples: Additive vs Negative Painting in Art
In art, additive painting involves applying layers of color to build up an image, as seen in the luminous works of Mark Rothko where color fields intensify emotion through accumulation. Negative painting, exemplified by traditional Southeast Asian batik, emphasizes outlining forms by painting around shapes, creating striking contrasts and defining figures through absence rather than direct application. These inspiring examples highlight how additive painting enhances presence by layering pigment, while negative painting relies on the deliberate preservation of background space to shape the composition.
Additive Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com