Value study is a systematic approach aimed at improving the value of products or processes by analyzing their functions and costs. This method identifies unnecessary expenses and suggests cost-effective alternatives without compromising quality or performance. Explore the full article to discover how you can apply value study techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Table of Comparison
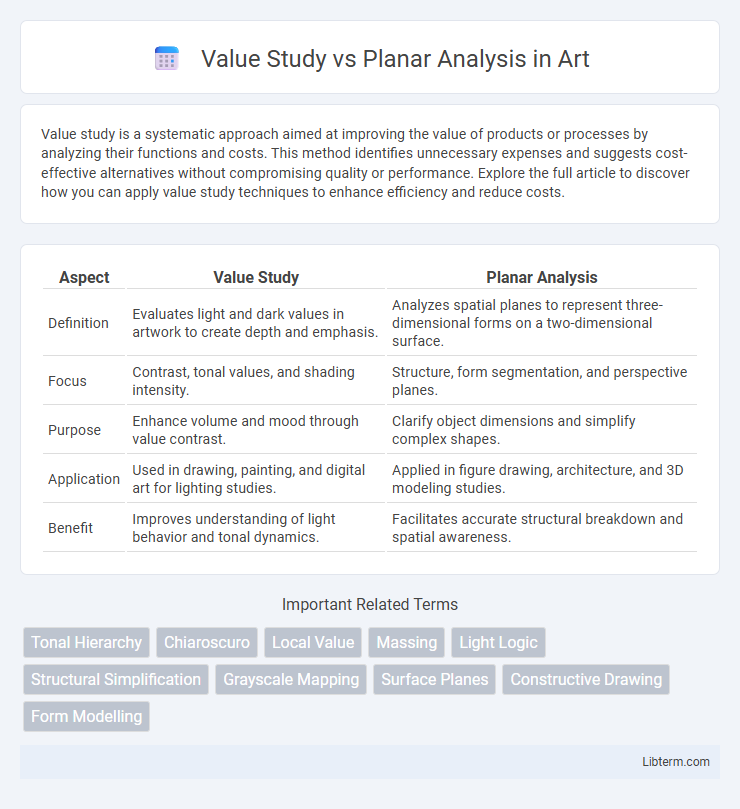
| Aspect | Value Study | Planar Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates light and dark values in artwork to create depth and emphasis. | Analyzes spatial planes to represent three-dimensional forms on a two-dimensional surface. |
| Focus | Contrast, tonal values, and shading intensity. | Structure, form segmentation, and perspective planes. |
| Purpose | Enhance volume and mood through value contrast. | Clarify object dimensions and simplify complex shapes. |
| Application | Used in drawing, painting, and digital art for lighting studies. | Applied in figure drawing, architecture, and 3D modeling studies. |
| Benefit | Improves understanding of light behavior and tonal dynamics. | Facilitates accurate structural breakdown and spatial awareness. |
Introduction to Value Study and Planar Analysis
Value Study focuses on systematically evaluating the worth of a product or process by analyzing its functions to optimize cost and performance, emphasizing function-oriented criteria and cost-saving opportunities. Planar Analysis involves examining two-dimensional geometric configurations to assess spatial relationships, structural integrity, and design efficiency, utilizing mathematical models and visual representations. Both methods enhance decision-making by providing distinct analytical frameworks tailored for functional and geometric assessments in engineering and design projects.
Defining Value Study in Art
Value Study in art is a focused examination of lightness and darkness in composition, emphasizing tonal contrast to create depth and dimensionality. Unlike Planar Analysis, which breaks down forms into geometric planes to understand structure and volume, Value Study concentrates on the distribution of values to enhance mood and visual interest. This method aids artists in mastering chiaroscuro and observational skills critical for realistic and expressive imagery.
Understanding Planar Analysis
Planar analysis examines the spatial relationships and geometric properties of surfaces within a given structure, providing detailed insights into load distribution and stress points. Unlike value study, which focuses on cost optimization and functional efficiency, planar analysis emphasizes the precise measurement and alignment of planar elements for structural integrity. Understanding planar analysis enables engineers to predict material behavior under various forces, ensuring safety and performance in architectural and mechanical designs.
Key Differences Between Value Study and Planar Analysis
Value Study emphasizes cost reduction and value improvement by analyzing functions and alternatives, focusing on optimizing product value without compromising quality. Planar Analysis involves evaluating planar structures or two-dimensional data to understand geometric, spatial, or structural properties for engineering or design purposes. The key difference lies in Value Study targeting functional cost-efficiency across product lifecycles, while Planar Analysis concentrates on spatial relationships and structural integrity within planar systems.
Importance of Value Study in Visual Art
Value Study in visual art emphasizes the exploration of light, shadow, and tonal contrasts to convey depth and form, crucial for creating realistic and emotionally compelling compositions. Unlike Planar Analysis, which breaks down complex forms into geometric planes to understand structure and perspective, Value Study prioritizes the manipulation of grayscale to enhance mood and focus. Mastery of Value Study enables artists to establish a strong visual hierarchy and dynamic range, essential for guiding viewers' attention and evoking specific responses.
Role of Planar Analysis in Form Depiction
Planar analysis plays a critical role in form depiction by breaking down complex shapes into simplified geometric planes, enhancing the understanding of light, shadow, and volume in a composition. Unlike value studies that primarily focus on tonal relationships and contrast, planar analysis emphasizes the structural foundation, aiding artists in capturing accurate proportions and spatial relationships. This method allows for more precise manipulation of form, facilitating improved realism and depth in visual art.
Techniques for Conducting a Value Study
Value Study techniques involve systematic functional analysis, focusing on identifying and evaluating the essential functions of a product or process to enhance value by reducing cost or improving performance. Planar Analysis techniques emphasize geometric and spatial assessment, analyzing planar sections or slices to assess structural integrity and material distribution efficiently. Both methods apply specific tools such as function-cost matrices in Value Study and cross-sectional imaging in Planar Analysis to optimize design and functionality.
Steps to Perform Planar Analysis
Planar analysis involves identifying and examining the planes of symmetry or rotational axes within a molecular or structural model to understand its geometry and symmetry properties. Key steps to perform planar analysis include selecting the reference plane based on the structure's geometry, calculating the orientation and position of atoms relative to this plane, and determining symmetry elements such as mirror planes or rotational axes. This method contrasts with value study, which focuses more on quantitative data evaluation rather than geometrical symmetry assessment.
Integrating Value Study and Planar Analysis in Artwork
Integrating Value Study and Planar Analysis in artwork enhances the artist's ability to accurately depict light, shadow, and form, creating a more dimensional and realistic composition. Value Study emphasizes tonal contrasts and gradients, while Planar Analysis breaks down complex shapes into flat planes, providing a structural foundation for rendering accurate light behavior. Combining these methods allows for precise control over visual hierarchy and spatial depth, improving the overall impact and readability of the artwork.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Value Study offers a comprehensive evaluation of a project's overall worth by integrating cost, benefits, and functional performance, making it ideal for optimizing resource allocation and design improvements. Planar Analysis emphasizes structural integrity and stress distribution within specific planes, providing precise insights crucial for engineering safety and material efficiency. Selecting the right approach depends on project goals: Value Study for strategic value optimization and Planar Analysis for detailed structural assessment.
Value Study Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com