Acrylic pouring creates unique, vibrant patterns by mixing acrylic paints with a pouring medium and pouring the mixture onto a canvas. This fluid art technique allows colors to flow and blend effortlessly, producing stunning abstract designs. Explore the rest of the article to master your acrylic pouring skills and unleash your creativity.
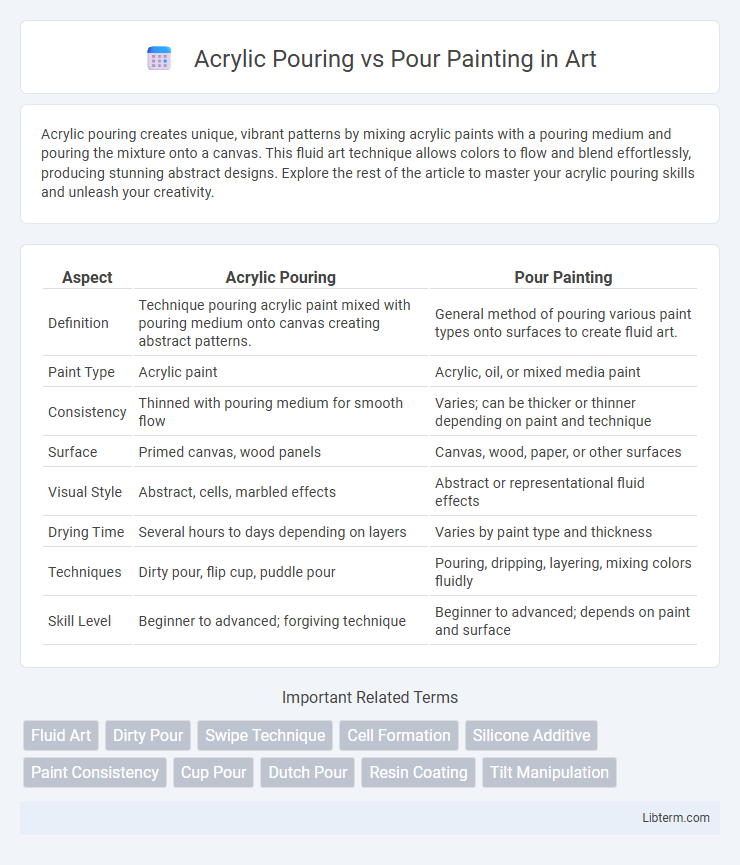
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Acrylic Pouring | Pour Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique pouring acrylic paint mixed with pouring medium onto canvas creating abstract patterns. | General method of pouring various paint types onto surfaces to create fluid art. |
| Paint Type | Acrylic paint | Acrylic, oil, or mixed media paint |
| Consistency | Thinned with pouring medium for smooth flow | Varies; can be thicker or thinner depending on paint and technique |
| Surface | Primed canvas, wood panels | Canvas, wood, paper, or other surfaces |
| Visual Style | Abstract, cells, marbled effects | Abstract or representational fluid effects |
| Drying Time | Several hours to days depending on layers | Varies by paint type and thickness |
| Techniques | Dirty pour, flip cup, puddle pour | Pouring, dripping, layering, mixing colors fluidly |
| Skill Level | Beginner to advanced; forgiving technique | Beginner to advanced; depends on paint and surface |
Introduction to Acrylic Pouring and Pour Painting
Acrylic pouring is a fluid art technique where acrylic paint is mixed with a pouring medium to create vibrant, abstract patterns poured onto a canvas. Pour painting, a broader category, encompasses various methods of pouring paint, including acrylic pouring, but can also involve other types of paints and substances. Both techniques emphasize the manipulation of liquid paint to achieve unique textures and color blends, making them popular for contemporary abstract art.
Key Differences Between Acrylic Pouring and Pour Painting
Acrylic pouring involves mixing acrylic paint with a pouring medium to create fluid, abstract designs, emphasizing the flow and blending of colors on the canvas. Pour painting, while similar, often includes a broader range of techniques and materials, focusing on controlled application and layering rather than purely fluid dynamics. Key differences lie in the medium consistency and artistic intent: acrylic pouring prioritizes spontaneity and cellular effects, whereas pour painting emphasizes precision and compositional structure.
Materials Needed for Each Technique
Acrylic pouring requires fluid acrylic paints, pouring medium, canvas or wood panels, and silicone oil to create cells and unique patterns. Pour painting often uses slightly thicker acrylic paints, water or flow improver, and a variety of tools like cups, sticks, and palettes to control paint flow and layering. Both techniques benefit from protective gear, disposable gloves, and a well-prepared workspace to handle the materials safely and efficiently.
Step-by-Step Process: Acrylic Pouring
Acrylic pouring involves mixing acrylic paints with a pouring medium to achieve a fluid consistency, then layering the mixture in a cup before pouring it onto a prepared surface. The artist tilts the canvas to spread the paint, allowing colors to blend organically and create unique cells and patterns. This process requires minimal brushwork, emphasizing fluid dynamics and controlled movement to produce vibrant, abstract designs.
Step-by-Step Process: Pour Painting
Pour painting involves preparing a canvas by applying a base layer of paint, followed by mixing acrylic paints with pouring medium to achieve fluid consistency. Artists layer multiple colors in a cup before pouring the mixture onto the canvas, allowing the paint to spread and blend naturally. The final step involves tilting the canvas to create dynamic patterns and using tools like heat guns or sticks to enhance cells and texture.
Popular Techniques Within Acrylic Pouring
Acrylic pouring encompasses popular techniques such as the Dirty Pour, Flip Cup, and Swipe methods, which create dynamic and fluid abstract art with vibrant color blends. Unlike pour painting, which broadly refers to the act of pouring paint, acrylic pouring specifically utilizes fluid acrylic paints mixed with pouring mediums to achieve cell formation and marbled effects. Mastery of these techniques allows artists to manipulate paint flow, producing unique textures and intricate patterns distinctive to acrylic pouring art.
Popular Techniques Within Pour Painting
Acrylic pouring and pour painting are popular fluid art techniques that involve manipulating liquid paint to create abstract designs. Key techniques within pour painting include dirty pour, where multiple colors are layered in one cup before pouring; flip cup, which involves flipping a paint-filled cup onto the canvas to spread colors; and puddle pour, where individual colors are poured sequentially to form concentric patterns. These methods highlight the versatility and dynamic effects achievable in fluid art, making pour painting a favored choice among artists.
Artistic Effects and Outcomes Compared
Acrylic pouring creates fluid, marbled patterns through the use of liquid acrylics manipulated by tilting or swirling the canvas, resulting in organic, unpredictable textures and cells. Pour painting involves layering multiple colors poured sequentially or simultaneously, producing vibrant, spontaneous designs with a balanced interplay of colors and sharper contrasts. Both techniques emphasize abstract visual effects, but acrylic pouring excels in creating intricate, cellular formations while pour painting offers more control over color distribution and composition.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Method
Acrylic pouring offers vibrant, fluid art with unpredictable patterns, enhancing creativity and ease for beginners, but it requires careful mixing and can result in thin, fragile layers. Pour painting provides greater control over designs through layering and brush techniques, allowing detailed compositions, though it demands more skill and time to master complex textures. Both methods enable unique abstract expressions, with acrylic pouring favoring spontaneity and pour painting emphasizing precision.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Art Style
Acrylic pouring and pour painting both offer fluid, abstract effects but differ in control and finish, making technique choice essential for your art style. Acrylic pouring emphasizes spontaneous blending of colors and dynamic cells, ideal for artists seeking organic, unpredictable patterns. Pour painting allows more intentional layering and design within the pour, perfect for creators wanting a balance between fluidity and guided composition.
Acrylic Pouring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com