Realism emphasizes accurate, detailed, and unembellished depiction of life, focusing on everyday scenes and genuine human experiences. This artistic and literary movement seeks to portray subjects as they truly are, avoiding idealization or romanticism. Discover how realism shapes your understanding of art and literature by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
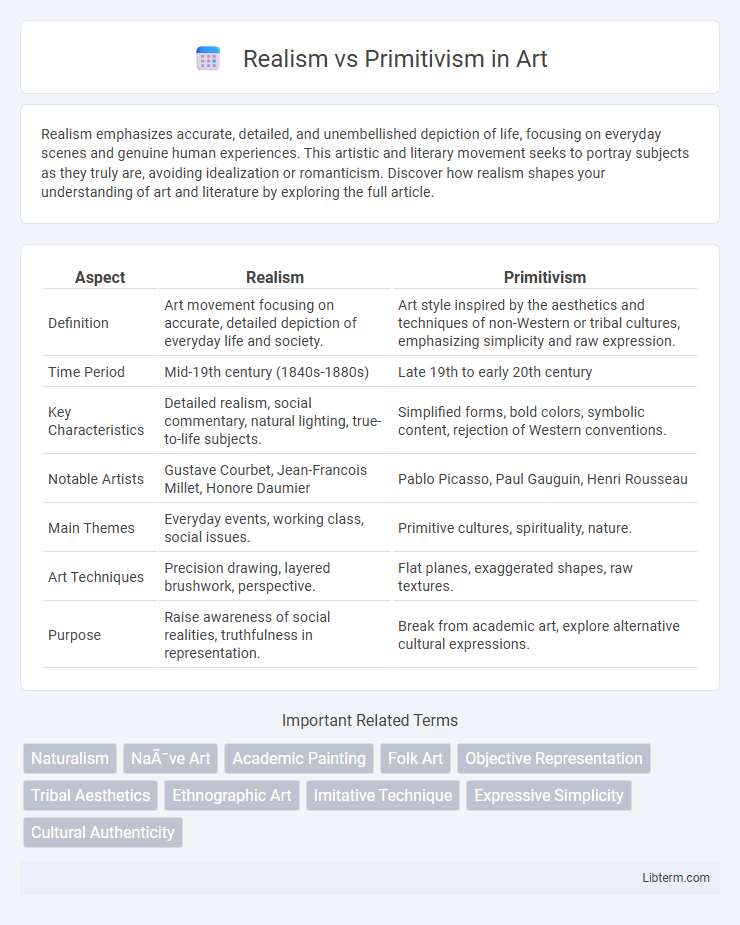
| Aspect | Realism | Primitivism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement focusing on accurate, detailed depiction of everyday life and society. | Art style inspired by the aesthetics and techniques of non-Western or tribal cultures, emphasizing simplicity and raw expression. |
| Time Period | Mid-19th century (1840s-1880s) | Late 19th to early 20th century |
| Key Characteristics | Detailed realism, social commentary, natural lighting, true-to-life subjects. | Simplified forms, bold colors, symbolic content, rejection of Western conventions. |
| Notable Artists | Gustave Courbet, Jean-Francois Millet, Honore Daumier | Pablo Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Henri Rousseau |
| Main Themes | Everyday events, working class, social issues. | Primitive cultures, spirituality, nature. |
| Art Techniques | Precision drawing, layered brushwork, perspective. | Flat planes, exaggerated shapes, raw textures. |
| Purpose | Raise awareness of social realities, truthfulness in representation. | Break from academic art, explore alternative cultural expressions. |
Understanding Realism: Key Principles and Origins
Realism, rooted in 19th-century European art, emphasizes accurate, detailed depictions of everyday life and ordinary people, rejecting the exaggerated emotionalism of Romanticism. Key principles of Realism include an objective perspective, attention to social conditions, and a commitment to visual truth, aiming to represent subjects as they appear without idealization. Originating as a response to political and social upheavals, Realism reflects a desire to portray the realities of contemporary society, often highlighting issues like labor, poverty, and class dynamics.
Defining Primitivism: Artistry and Influence
Primitivism in art is characterized by the deliberate incorporation of stylistic elements from non-Western or prehistoric cultures, emphasizing simplicity, raw expression, and a return to perceived authentic origins. This movement draws influence from indigenous art forms, African masks, Oceanic sculptures, and tribal artifacts, challenging the refined conventions of Western realism by celebrating spontaneity and symbolic depth. Artists such as Paul Gauguin and Pablo Picasso played pivotal roles in popularizing primitivism, shaping modern art through its fusion of primitive aesthetics and avant-garde techniques.
Historical Context: Emergence of Realism and Primitivism
Realism and Primitivism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as contrasting artistic movements shaped by rapidly changing social and cultural landscapes. Realism developed as a response to industrialization and urbanization, emphasizing accurate depictions of everyday life and social conditions, rooted in 19th-century France with artists like Gustave Courbet. Primitivism arose as artists like Paul Gauguin and Pablo Picasso sought inspiration from non-Western and indigenous cultures, challenging classical art norms and reflecting Western anxieties about modernity and civilization's progress.
Visual Characteristics: Realist vs Primitivist Techniques
Realist techniques emphasize accurate, detailed representation with precise brushwork, natural color palettes, and meticulous shading that capture light and texture authentically. Primitivist techniques favor simplified forms, bold and flat colors, and exaggerated or stylized shapes, often drawing inspiration from folk art and non-Western indigenous aesthetics. The contrast highlights Realism's commitment to lifelike depiction against Primitivism's embrace of expressive, symbolic, and often naive visual elements.
Philosophical Foundations of Realism and Primitivism
Realism is grounded in the belief that states operate in an anarchic international system where power and security drive behavior, emphasizing rational actors pursuing national interests. Primitivism, often linked to Romanticism and critique of modernity, challenges the assumptions of progress and rationalism by valuing pre-civilizational social harmony and instinctual human nature. These contrasting philosophical foundations highlight realism's focus on pragmatic power politics versus primitivism's emphasis on natural human conditions and skepticism of industrial society.
Key Artists and Representative Works
Realism, exemplified by Gustave Courbet's "The Stone Breakers" (1849), emphasizes truthful, unidealized depictions of everyday life, while Primitivism, seen in Paul Gauguin's "Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?" (1897-1898), draws inspiration from non-Western art and cultures to challenge Western artistic conventions. Key Realist artists such as Jean-Francois Millet and Honore Daumier focused on social realities and working-class subjects, whereas Primitivists like Henri Rousseau incorporated exoticism and simplified forms to evoke a sense of purity and raw expression. The contrasting artistic approaches highlight Realism's commitment to factual representation and Primitivism's pursuit of emotional and symbolic depth through cultural reinterpretation.
Cultural Impact and Social Commentary
Realism and Primitivism offer contrasting cultural impacts through their artistic expressions and social commentaries. Realism emphasizes accurate, unembellished depictions of everyday life, highlighting social issues like poverty and class struggles to provoke public awareness and reform. Primitivism romanticizes non-Western and indigenous cultures, challenging industrialization's effects and questioning modern society's values by idealizing simplicity and authenticity.
Realism vs Primitivism in Modern Art
Realism in modern art emphasizes accurate, detailed depictions of everyday life, reflecting objective realities and social conditions without idealization. Primitivism, by contrast, draws inspiration from non-Western and tribal art forms, valuing raw, simplified aesthetics and emotional expression over precise representation. The tension between Realism and Primitivism in modern art highlights a crucial dialogue about authenticity, cultural influence, and the boundaries of artistic innovation.
Critical Debates and Reception Over Time
Realism and Primitivism have sparked critical debates centered on authenticity, cultural appropriation, and artistic value, with realism praised for its faithful representation of reality while primitivism faces scrutiny for exoticizing non-Western cultures. Over time, realism's reception remains grounded in its technical precision and social commentary, whereas primitivism's reception has evolved, increasingly interrogated through postcolonial and ethical perspectives. Scholars continue to analyze how these movements reflect broader socio-political contexts and the shifting dynamics of artistic influence and power.
Legacy and Influence on Contemporary Art
Realism's legacy in contemporary art is evident through its commitment to depicting everyday life with precise detail and social critique, influencing genres like photorealism and social documentary art. Primitivism inspired modern artists by valuing the raw, unrefined aesthetics of non-Western cultures, shaping movements such as Cubism and Fauvism and prompting a reevaluation of cultural hierarchies in art. Both movements fundamentally reshaped artistic expression by challenging academic conventions and fostering diverse visual languages that continue to resonate in today's global art scene.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com