Traditional painting techniques, such as oil, watercolor, and acrylic, have been used for centuries to create timeless artworks that express creativity and cultural heritage. Mastering these methods can deepen your appreciation for the skill and patience involved in crafting detailed and vibrant pieces. Explore the rest of this article to discover how traditional painting continues to inspire modern artists and enrich your artistic journey.
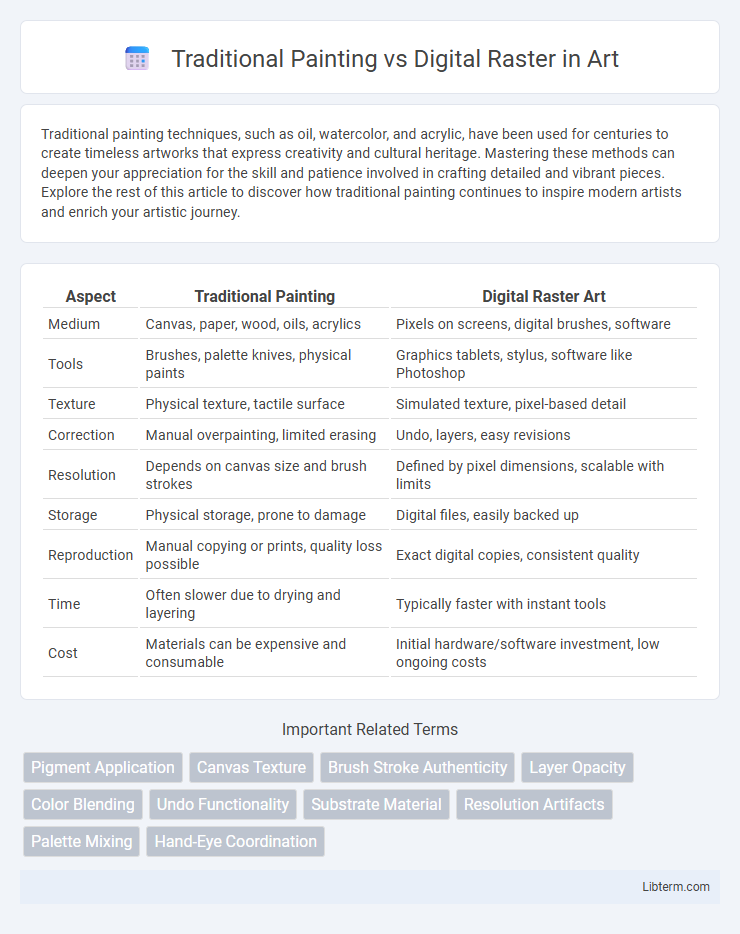
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Painting | Digital Raster Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Canvas, paper, wood, oils, acrylics | Pixels on screens, digital brushes, software |
| Tools | Brushes, palette knives, physical paints | Graphics tablets, stylus, software like Photoshop |
| Texture | Physical texture, tactile surface | Simulated texture, pixel-based detail |
| Correction | Manual overpainting, limited erasing | Undo, layers, easy revisions |
| Resolution | Depends on canvas size and brush strokes | Defined by pixel dimensions, scalable with limits |
| Storage | Physical storage, prone to damage | Digital files, easily backed up |
| Reproduction | Manual copying or prints, quality loss possible | Exact digital copies, consistent quality |
| Time | Often slower due to drying and layering | Typically faster with instant tools |
| Cost | Materials can be expensive and consumable | Initial hardware/software investment, low ongoing costs |
Introduction: Defining Traditional Painting and Digital Raster
Traditional painting encompasses techniques using physical materials such as oil, acrylic, or watercolor on surfaces like canvas or paper, emphasizing tactile brushstrokes and texture. Digital raster refers to images created and edited through pixel-based software like Adobe Photoshop, relying on resolution and color depth to define visual quality. Both mediums offer distinct creative processes and tools, influencing artistic expression and output style.
Historical Evolution of Artistic Mediums
Traditional painting, rooted in ancient civilizations, evolved through techniques like tempera, oil, and watercolor, each influencing artistic expression across centuries. The advent of digital raster graphics emerged in the late 20th century, revolutionizing art creation by utilizing pixel-based images that mimic traditional brushstrokes digitally. This transition highlights a significant shift from tactile, material-based mediums to versatile, software-driven tools, reflecting broader technological advancements in the art world.
Materials and Tools: Canvas vs. Computer
Traditional painting utilizes physical materials such as canvas, brushes, and various paint types like oil or acrylic to create tactile, textured artwork. Digital raster art relies on software programs, graphic tablets, and computers to manipulate pixels and colors, offering infinite undo options and layer controls. The tactile nature of canvas allows for organic brushstrokes and texture variations, while the computer provides precision, flexibility, and easy editing in digital raster creation.
Artistic Process and Workflow Differences
Traditional painting involves tactile interaction with physical materials like canvas, brushes, and pigments, which demands meticulous layering, drying time, and manual blending techniques. Digital raster painting utilizes software tools offering unlimited undo options, customizable brushes, and layers that streamline the creative process, enabling faster revisions and experimentation. Workflow in traditional art is linear and time-intensive, while digital art supports non-destructive editing and more efficient iteration cycles.
Texture, Depth, and Finish
Traditional painting offers rich texture and depth through physical brushstrokes and layering of pigments on canvas, creating a tactile finish that changes under varied lighting. Digital raster painting simulates texture and depth using pixel-based techniques and customizable brushes, allowing for precise control over surface details and finish. The finish in traditional art retains organic imperfections, while digital work provides clean, editable output suitable for diverse media formats.
Creative Flexibility and Undo Options
Traditional painting offers tactile control and unique texture effects but limits creative flexibility due to irreversible brushstrokes and drying times. Digital raster painting maximizes creative flexibility with infinite undo options, layer management, and customizable brushes, allowing artists to experiment freely without fear of permanent mistakes. This makes digital raster tools ideal for iterative workflows and complex compositions requiring frequent adjustments.
Reproducibility and Distribution
Traditional painting offers unique, one-of-a-kind artwork with limited reproducibility due to its physical nature, making each piece inherently valuable and exclusive. Digital raster images enable infinite reproducibility, allowing artists to distribute exact copies worldwide instantly through digital platforms, expanding accessibility and commercial reach. While traditional art relies on galleries and physical transport, digital raster formats leverage online marketplaces and social media, drastically enhancing distribution efficiency.
Learning Curves and Accessibility
Traditional painting demands mastery of physical materials and techniques, often requiring years of practice to develop precision and control over brushwork and color mixing. Digital raster art benefits from user-friendly software and tools like layers, undo functions, and customizable brushes, which significantly reduce the learning curve for beginners. Accessibility to digital art is enhanced by affordable tablets and free tutorial resources, whereas traditional painting involves ongoing costs for supplies and studio space.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Traditional painting relies on physical materials like canvases, paints, and solvents, often involving non-renewable resources and generating chemical waste that can harm the environment. Digital raster art reduces physical waste and chemical use, but depends heavily on electricity, electronic devices, and data storage, which contribute to electronic waste and carbon emissions. Sustainable practices in both mediums include using eco-friendly materials for traditional art and energy-efficient hardware for digital creation to minimize their environmental footprints.
Choosing Your Medium: Factors to Consider
Choosing between traditional painting and digital raster art depends on factors such as desired texture, flexibility, and workflow preferences. Traditional painting offers tactile experiences with rich, natural brushstrokes and unique material interactions, while digital raster art provides ease of editing, layering, and various digital effects. Consider your project goals, budget for supplies or software, and personal comfort with technology to select the most suitable medium.
Traditional Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com