Curvilinear design integrates smooth, flowing lines that create an elegant and dynamic aesthetic in architecture, art, and graphic design. These forms enhance visual interest and guide the viewer's eye naturally through the composition. Explore the rest of the article to discover how curvilinear elements can transform your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
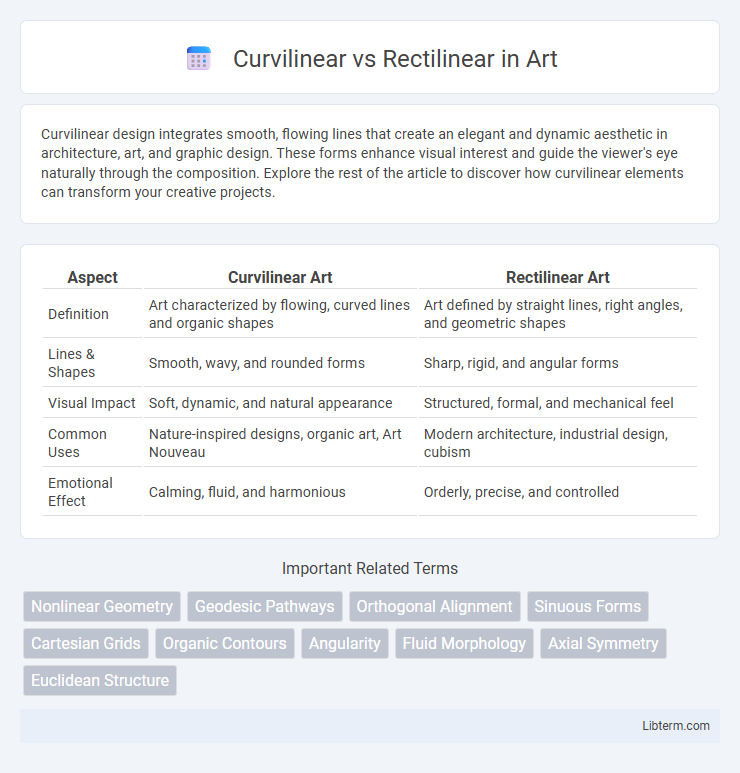
| Aspect | Curvilinear Art | Rectilinear Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art characterized by flowing, curved lines and organic shapes | Art defined by straight lines, right angles, and geometric shapes |
| Lines & Shapes | Smooth, wavy, and rounded forms | Sharp, rigid, and angular forms |
| Visual Impact | Soft, dynamic, and natural appearance | Structured, formal, and mechanical feel |
| Common Uses | Nature-inspired designs, organic art, Art Nouveau | Modern architecture, industrial design, cubism |
| Emotional Effect | Calming, fluid, and harmonious | Orderly, precise, and controlled |
Introduction to Curvilinear and Rectilinear Concepts
Curvilinear concepts involve smooth, flowing lines and shapes that mimic natural forms, creating dynamic and organic visual experiences. Rectilinear concepts embrace straight lines and right angles, emphasizing structure, order, and clarity in design and architecture. Understanding these fundamental differences aids in selecting appropriate styles for artistic, architectural, and graphic applications.
Defining Curvilinear: Meaning and Applications
Curvilinear refers to shapes, lines, or designs characterized by smooth, flowing curves rather than straight edges or angles, commonly found in natural forms and organic designs. It is applied extensively in architecture, automotive design, and digital graphics to create visually dynamic and aesthetically pleasing structures that evoke movement and fluidity. This style enhances ergonomics and spatial efficiency, making it ideal for modern interiors and product designs focused on human-centered usability.
Understanding Rectilinear: Key Characteristics
Rectilinear design emphasizes straight lines and sharp angles, creating a sense of order and structure in visual compositions. This style is characterized by geometric forms, such as rectangles and squares, which contribute to clarity and precision in architectural layouts, graphic design, and user interfaces. The predictability and symmetry of rectilinear elements often evoke stability, professionalism, and simplicity in spatial organization and visual hierarchy.
Core Differences Between Curvilinear and Rectilinear
Curvilinear designs feature smooth, flowing lines that create organic, natural shapes, whereas rectilinear designs emphasize straight lines and sharp angles, forming geometric and structured patterns. The core difference lies in their visual impact: curvilinear shapes evoke softness and movement, while rectilinear forms convey rigidity and order. These contrasting approaches influence functionality and aesthetics in fields such as architecture, graphic design, and art.
Visual Examples: Curvilinear vs Rectilinear Designs
Curvilinear designs feature flowing, organic shapes with smooth, rounded edges that create a sense of movement and softness, often seen in nature-inspired architecture and art nouveau patterns. Rectilinear designs emphasize straight lines, right angles, and geometric forms, producing a structured, orderly appearance commonly found in modernist buildings and minimalist interiors. Visual examples highlight the contrast between the dynamic fluidity of curvilinear forms and the precise rigidity of rectilinear compositions, influencing spatial perception and aesthetic impact.
Applications in Architecture and Design
Curvilinear forms in architecture enhance aesthetic fluidity and organic integration, often used in iconic buildings like the Guggenheim Museum and contemporary residential designs to evoke natural movement and soft spatial experiences. Rectilinear structures dominate urban architecture due to their efficient use of space, ease of construction, and alignment with modernist principles, prominently seen in skyscrapers, office complexes, and minimalist interiors. Both design approaches influence material selection, structural engineering, and environmental responsiveness, shaping functional and visual outcomes in built environments.
Impact on Motion and Physics
Curvilinear motion involves objects moving along curved paths, where velocity and acceleration vectors constantly change direction, affecting centripetal force and angular momentum dynamics. Rectilinear motion occurs along straight lines with constant direction of velocity, simplifying the analysis of linear momentum and uniform acceleration under Newtonian mechanics. Understanding the distinctions is crucial for applications in mechanics, robotics, and aerodynamics, where force distribution and trajectory prediction rely on accurately modeling motion types.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Curvilinear design enhances aesthetic appeal and user engagement by incorporating flowing, organic shapes but may pose challenges in manufacturing complexity and space efficiency. Rectilinear design offers simplicity, ease of construction, and optimal utilization of space, yet it can feel rigid and less inviting in certain applications. Choosing between curvilinear and rectilinear approaches depends on balancing creative expression with practical constraints in architecture, product design, or user interface development.
Choosing Between Curvilinear and Rectilinear: Decision Factors
Choosing between curvilinear and rectilinear designs depends on several decision factors such as spatial efficiency, aesthetic appeal, and structural requirements. Curvilinear forms offer organic shapes that enhance visual flow and natural movement, ideal for spaces emphasizing fluidity and creativity. Rectilinear designs prioritize functionality and simplicity, maximizing usable area and facilitating straightforward construction, making them suitable for practical and formal environments.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in curvilinear and rectilinear design emphasize the integration of advanced materials like flexible composites and smart surfaces to enhance structural adaptability and sustainability. Innovations such as parametric modeling and AI-driven design tools enable more efficient creation of complex curvilinear forms with optimized performance characteristics. The convergence of digital fabrication and bio-inspired design is expected to push the boundaries of both curvilinear and rectilinear architecture, fostering new possibilities in aesthetics and functionality.
Curvilinear Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com