Chladni plates reveal the fascinating patterns formed by vibrations on a solid surface, illustrating the principles of acoustics and resonance. By sprinkling fine particles on a metal plate and applying a frequency, you can visualize the nodal lines where the plate remains stationary. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Chladni plates work and their applications in science and art.
Table of Comparison
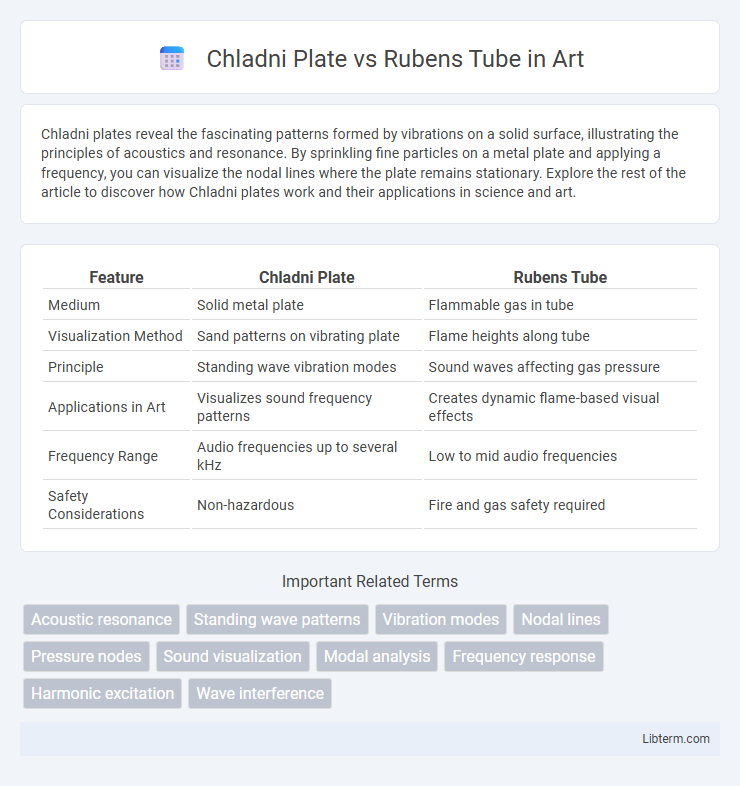
| Feature | Chladni Plate | Rubens Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Solid metal plate | Flammable gas in tube |
| Visualization Method | Sand patterns on vibrating plate | Flame heights along tube |
| Principle | Standing wave vibration modes | Sound waves affecting gas pressure |
| Applications in Art | Visualizes sound frequency patterns | Creates dynamic flame-based visual effects |
| Frequency Range | Audio frequencies up to several kHz | Low to mid audio frequencies |
| Safety Considerations | Non-hazardous | Fire and gas safety required |
Introduction to Chladni Plates and Rubens Tubes
Chladni plates visualize sound waves through sand patterns formed by vibrations on a metal surface, illustrating nodal lines of standing waves. Rubens tubes demonstrate sound wave behavior inside a gas-filled tube by producing flame patterns that correspond to pressure nodes and antinodes. Both devices serve as powerful tools for studying acoustics and wave phenomena by transforming invisible sound waves into visible patterns.
Historical Background and Invention
Chladni Plates, developed by Ernst Chladni in the late 18th century, visually demonstrated sound vibrations by creating intricate patterns from sand on metal plates. The Rubens Tube, invented by Heinrich Rubens in the early 20th century, utilized standing sound waves to manipulate flames within a tube, making acoustic waveforms visible through fire. Both devices significantly contributed to acoustic research by providing tangible representations of sound wave phenomena.
Principles of Sound Visualization
Chladni Plates visualize sound through the vibration of a metal plate covered with fine sand that arranges itself into patterns at nodal lines, revealing the resonance frequencies of the plate's surface. Rubens Tubes demonstrate sound visualization by creating standing acoustic waves in a gas-filled tube, where flames along the tube's perforations fluctuate in height according to pressure variations caused by sound waves. Both devices effectively illustrate acoustic phenomena by converting invisible sound waves into visible patterns, emphasizing the relationship between frequency, amplitude, and wave behavior.
How Chladni Plates Work
Chladni plates work by vibrating a metal plate at specific frequencies, causing particles like sand or salt to move and concentrate along nodal lines where the plate's surface remains still. These nodal patterns visualize standing wave formations created by the plate's oscillations. The vibration frequency directly influences the complexity and shape of the resulting Chladni figures.
How Rubens Tubes Operate
Rubens Tubes visualize sound waves by channeling flame through holes along a perforated tube, where pressure variations inside the tube cause flames to fluctuate in height, revealing standing wave patterns. As sound waves travel through the gas-filled tube, areas of high and low pressure modulate the intensity of the flames, effectively mapping the acoustic waveforms in real time. This visual representation helps in analyzing frequency, amplitude, and harmonic modes of sound waves in a tangible, observable manner.
Materials and Setup Comparison
Chladni plates typically use a metal or glass plate covered with fine sand and are vibrated using a violin bow or a frequency generator connected to a speaker. The Rubens tube consists of a perforated metal tube filled with flammable gas, with flames emerging from the holes influenced by sound waves produced from one end. While Chladni plates visualize vibrational modes with solid particles on a rigid surface, Rubens tubes demonstrate acoustic standing waves through flame patterns in a flammable gas medium, requiring safety precautions due to open flames.
Types of Waves Illustrated
Chladni plates visually demonstrate standing mechanical waves on solid surfaces, revealing nodal patterns created by vibrating metal plates with varying frequency. Rubens tubes illustrate standing sound waves in gases, showing pressure variations as visible flames along a perforated tube connected to a sound source. Both devices are essential for studying wave phenomena, with Chladni plates focusing on transverse waves on solids and Rubens tubes emphasizing longitudinal waves in gases.
Educational and Experimental Applications
Chladni Plates and Rubens Tubes serve as powerful educational tools to visualize sound waves and resonance phenomena through distinct physical representations. Chladni Plates demonstrate vibration patterns on metal surfaces using sand to reveal nodal lines, making complex wave behaviors tangible for students studying acoustics and physics. Rubens Tubes visually depict sound wave pressure variations within a combustible gas-filled tube, allowing experimental analysis of wave frequencies and standing waves in fluid dynamics and acoustical engineering classrooms.
Visual Impact and Demonstration Differences
Chladni Plates visualize sound waves through sand patterns forming distinct nodal lines on a vibrating metal surface, offering a static yet intricate display of resonance frequencies. Rubens Tubes, on the other hand, demonstrate acoustic standing waves with flames lit along a perforated tube, providing a dynamic and visually dramatic representation of pressure variations in real time. The Chladni Plate emphasizes precise geometric patterns of vibration modes, while the Rubens Tube delivers an engaging, fiery visualization of sound wave propagation and amplitude changes.
Choosing Between Chladni Plates and Rubens Tubes
Choosing between Chladni plates and Rubens tubes depends on the specific visualization of sound waves desired; Chladni plates effectively demonstrate nodal patterns on solid surfaces using sand or powder, while Rubens tubes visualize pressure variations in sound waves along a flammable gas column. For precise, static visualization of mode shapes in mechanical vibrations, Chladni plates offer clearer, detailed patterns suitable for educational and research purposes. Rubens tubes excel in dynamic demonstrations of acoustic standing waves and pressure fluctuations, providing a visually striking representation using flames, ideal for illustrating wave behavior in gases.
Chladni Plate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com