Expressionism captures intense emotions through bold colors and distorted forms, reflecting the inner turmoil of artists. This movement revolutionized art by prioritizing subjective experience over realistic representation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Expressionism transforms your perception of modern art.
Table of Comparison
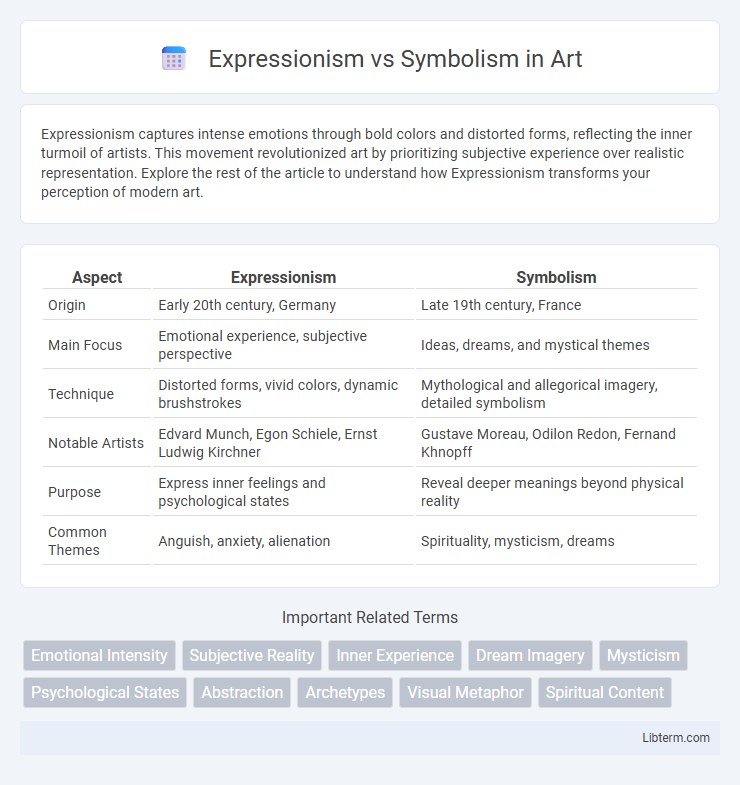
| Aspect | Expressionism | Symbolism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Early 20th century, Germany | Late 19th century, France |
| Main Focus | Emotional experience, subjective perspective | Ideas, dreams, and mystical themes |
| Technique | Distorted forms, vivid colors, dynamic brushstrokes | Mythological and allegorical imagery, detailed symbolism |
| Notable Artists | Edvard Munch, Egon Schiele, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner | Gustave Moreau, Odilon Redon, Fernand Khnopff |
| Purpose | Express inner feelings and psychological states | Reveal deeper meanings beyond physical reality |
| Common Themes | Anguish, anxiety, alienation | Spirituality, mysticism, dreams |
Introduction to Expressionism and Symbolism
Expressionism emerged in early 20th-century Europe as an art movement emphasizing emotional experience over physical reality, using vivid colors and distorted forms to convey subjective feelings. Symbolism, originating in the late 19th century, focused on representing ideas and emotions through symbolic imagery, often drawing on mythology, dreams, and spirituality. Both movements sought to transcend realism but diverged in technique and thematic focus, with Expressionism prioritizing emotional intensity and Symbolism emphasizing metaphysical meaning.
Historical Origins and Development
Expressionism emerged in early 20th-century Germany as a reaction against industrialization and urban alienation, focusing on intense emotional experience through distorted forms and vivid colors. Symbolism originated in late 19th-century France and Belgium, emphasizing mystical and dream-like imagery to convey ideas beyond the physical world, inspired by Romanticism and the philosophy of idealism. Both movements influenced modern art by challenging realism and emphasizing subjective perception, yet Expressionism prioritized raw emotional expression while Symbolism sought to reveal hidden spiritual truths.
Key Philosophies and Themes
Expressionism emphasizes intense emotional experience and subjective perspective, often portraying inner turmoil and existential angst through distorted forms and vivid colors. Symbolism focuses on representing ideas and emotions through symbolic imagery, exploring mysticism, dreams, and the unconscious mind to evoke deeper meanings beyond the visible world. Both movements reject realism but differ in approach: Expressionism channels raw, often chaotic feelings, while Symbolism seeks to reveal hidden spiritual truths through metaphor and allegory.
Major Figures and Influential Artists
Expressionism features major figures like Edvard Munch and Egon Schiele, whose intense emotional portrayals emphasized raw human experience and psychological depth. Symbolism, represented by artists such as Gustave Moreau and Odilon Redon, focused on mysticism, dream imagery, and metaphysical themes through intricate symbolism and allegory. Both movements influenced modern art by challenging realistic representation and exploring inner realities through distinct visual languages.
Artistic Techniques and Stylistic Differences
Expressionism employs bold, exaggerated brushstrokes and distorted forms to evoke intense emotional responses, emphasizing subjective experience over realistic representation. Symbolism utilizes intricate, often mystical imagery and symbolic motifs to convey deeper, abstract meanings, focusing on metaphor and suggestion rather than direct depiction. While Expressionism thrives on raw, dynamic energy and vivid colors, Symbolism leans toward refined detail and a more subdued, contemplative palette to evoke spiritual and psychological depth.
Expressionism in Visual Arts and Literature
Expressionism in visual arts and literature emphasizes the portrayal of raw emotional experience over physical reality, characterized by distorted forms, bold colors, and intense brushstrokes to evoke inner turmoil and subjective perception. Artists like Edvard Munch and Egon Schiele used exaggerated visuals to convey psychological depth, while writers such as Franz Kafka explored existential angst through fragmented, surreal narratives. This movement contrasts with Symbolism's reliance on metaphor and mystical imagery, as Expressionism seeks direct emotional impact and a visceral connection with the audience.
Symbolism in Visual Arts and Literature
Symbolism in visual arts and literature emphasizes the use of symbolic images and indirect suggestion to express mystical ideas, emotions, and states of mind, contrasting with the more direct emotional intensity of Expressionism. Originating in the late 19th century, Symbolism seeks to evoke deeper meanings through motifs like mythological figures, dreams, and abstract forms, often prioritizing mood and atmosphere over realistic representation. Key Symbolist artists include Gustave Moreau and Odilon Redon, while literary figures like Charles Baudelaire and Stephane Mallarme crafted poetry rich in metaphor and allegory to explore themes of spirituality and existential mystery.
Impact on Modern and Contemporary Art
Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing emotional experience through bold colors and dynamic brushstrokes, directly influencing movements like Abstract Expressionism and Neo-Expressionism. Symbolism, with its focus on mythic and dream-like imagery, laid the groundwork for Surrealism and contributed to the exploration of subconscious themes in contemporary art. Both movements challenged traditional realism, expanding the boundaries of artistic expression and shaping the narrative of 20th and 21st-century art.
Comparative Analysis: Expressionism vs Symbolism
Expressionism emphasizes raw emotional experience through distorted visuals and intense colors, aiming to evoke subjective feelings, whereas Symbolism utilizes metaphorical imagery and allegory to convey deeper spiritual or philosophical meanings. Expressionism's dynamic, often chaotic forms contrast with Symbolism's structured, dreamlike compositions, reflecting psychological tension versus mystical exploration. Both movements challenge realism but differ in intent: Expressionism seeks personal emotional impact, while Symbolism aspires to reveal hidden truths beyond the visible world.
Legacy and Cultural Significance
Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing emotional intensity and subjective experience, profoundly influencing 20th-century painting, theater, and cinema. Symbolism's legacy lies in its use of metaphor and myth to explore the unconscious and spiritual, shaping movements like Surrealism and inspiring literature, visual arts, and psychoanalytic theory. Both movements significantly impacted cultural narratives, challenging traditional realism and deepening the exploration of inner realities in artistic expression.
Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com