Abstract portraits capture emotions and personality through unconventional forms, colors, and shapes rather than realistic representation. These artworks evoke deeper meaning by focusing on expression, mood, and artistic interpretation, allowing viewers to connect with the subject in unique ways. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques and inspirations for creating your own compelling abstract portrait.
Table of Comparison
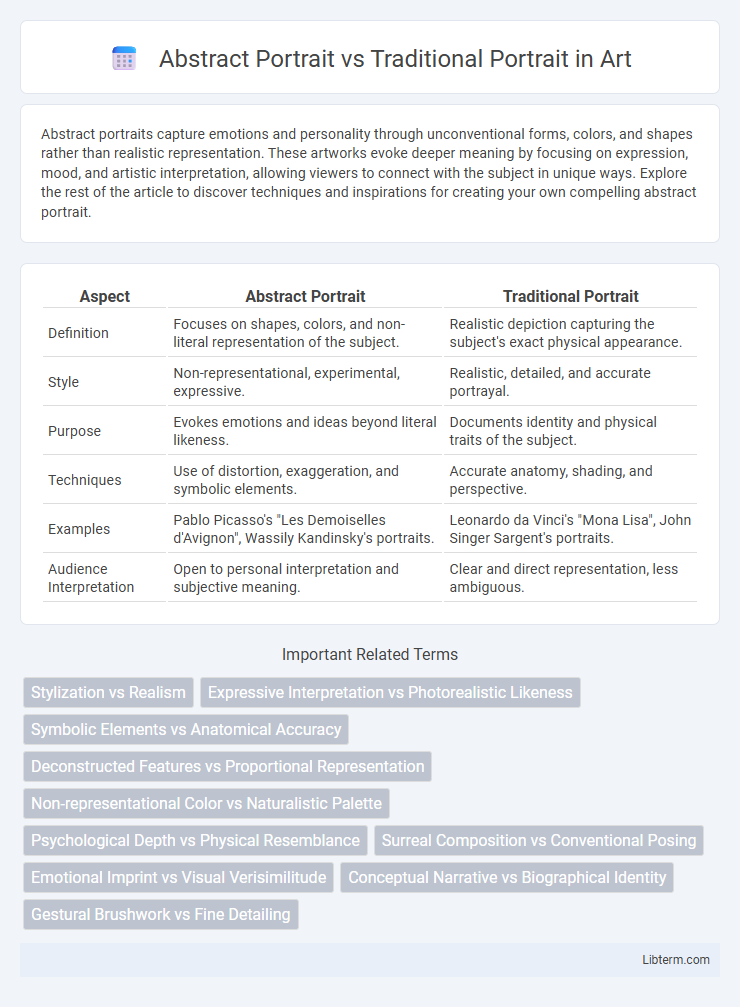
| Aspect | Abstract Portrait | Traditional Portrait |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on shapes, colors, and non-literal representation of the subject. | Realistic depiction capturing the subject's exact physical appearance. |
| Style | Non-representational, experimental, expressive. | Realistic, detailed, and accurate portrayal. |
| Purpose | Evokes emotions and ideas beyond literal likeness. | Documents identity and physical traits of the subject. |
| Techniques | Use of distortion, exaggeration, and symbolic elements. | Accurate anatomy, shading, and perspective. |
| Examples | Pablo Picasso's "Les Demoiselles d'Avignon", Wassily Kandinsky's portraits. | Leonardo da Vinci's "Mona Lisa", John Singer Sargent's portraits. |
| Audience Interpretation | Open to personal interpretation and subjective meaning. | Clear and direct representation, less ambiguous. |
Understanding Portrait Art: Abstract vs Traditional
Abstract portrait art distorts or simplifies facial features to evoke emotions and conceptual ideas, often using bold colors and unconventional shapes. Traditional portrait art emphasizes realistic representation, capturing fine details and true likeness to preserve identity and personality. Understanding these approaches highlights how abstract portraits explore psychological depth while traditional portraits focus on accurate visual documentation.
Defining Characteristics of Abstract Portraits
Abstract portraits emphasize distorted shapes, vibrant colors, and symbolic elements to convey emotions and ideas rather than realistic likeness. They often use geometric forms, exaggerated features, and unconventional techniques to challenge traditional representation. This approach prioritizes subjective interpretation and artistic expression over precise anatomical accuracy found in traditional portraits.
Key Elements of Traditional Portraits
Traditional portraits emphasize realistic representation, capturing precise facial features, expressions, and textures to convey personality and emotion. Key elements include accurate proportion, lighting, and detail, often set against a complementary background that enhances the subject's presence. These portraits prioritize lifelike depiction and formal composition to reflect identity and status.
Techniques Used in Abstract Portraiture
Abstract portraiture employs techniques such as distortion, exaggeration, and non-representational color to convey emotional or conceptual depth beyond physical likeness. Artists often use mixed media, layering, and textured brushstrokes to evoke mood and movement, differentiating it from the precise, realistic rendering seen in traditional portraiture. This approach prioritizes expression and interpretation, allowing greater creative freedom in form and structure.
Techniques Used in Traditional Portraiture
Traditional portraiture relies on techniques such as chiaroscuro to create depth and volume through the careful manipulation of light and shadow, emphasizing realism. Artists employ precise brushwork and layering methods like glazing to achieve detailed textures and lifelike skin tones, enhancing the subject's individuality. The use of classical proportions and anatomical accuracy remains fundamental in capturing the subject's true likeness and personality.
Emotional Expression in Abstract vs Traditional Portraits
Abstract portraits emphasize emotional expression through distorted forms, vibrant colors, and exaggerated features that evoke subjective feelings and inner experiences. Traditional portraits prioritize realistic representation and accurate facial details to convey the sitter's emotions in a more literal and recognizable manner. The emotional impact in abstract portraits often relies on symbolic interpretation, while traditional portraits depend on precise visual cues and facial expressions.
Historical Evolution of Portrait Styles
Abstract portraiture emerged in the early 20th century as artists like Picasso and Kandinsky challenged traditional realism by emphasizing emotional expression through distorted forms and vibrant colors. Traditional portraits, rooted in ancient civilizations and flourishing during the Renaissance, focused on lifelike representations to convey status, identity, and social narratives. The historical evolution from precise depiction to abstract interpretation reflects shifting cultural values and artistic philosophies over centuries.
Popular Artists: Abstract vs Traditional Portraitists
Abstract portrait artists like Pablo Picasso and Francis Bacon revolutionized portraiture by emphasizing emotional expression and fragmented forms, diverging from the realistic representation favored by traditional portraitists such as John Singer Sargent and Thomas Gainsborough, who prioritized lifelike detail and classical techniques. The abstract approach uses color, shape, and brushstroke to evoke psychological depth, contrasting with the traditional focus on capturing the subject's physical likeness and social status. This distinction highlights the evolving purpose of portraiture from mere representation to a medium for exploring identity and emotion.
Impact on Contemporary Art Trends
Abstract portraits disrupt conventional representation by emphasizing emotion and form over realism, significantly influencing contemporary art trends toward experimentation and subjective interpretation. Traditional portraits maintain a focus on accurate, detailed depiction, shaping ongoing appreciation for skill and historical context in art. The contrast between these styles drives innovation and diversity in modern artistic expression.
Choosing Between Abstract and Traditional Portraits
Choosing between abstract and traditional portraits depends on the emotional impact and stylistic preference desired. Abstract portraits emphasize artistic expression through unconventional shapes and colors, appealing to those seeking a unique and interpretive representation. Traditional portraits prioritize realistic likeness and detail, making them ideal for capturing precise facial features and formal settings.
Abstract Portrait Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com