Phthalo Blue is a vibrant, intense pigment widely used in art due to its brilliant hue and excellent lightfastness. Its versatility makes it ideal for creating rich, deep blues, and mixing with other colors to achieve a wide spectrum of shades. Discover how Phthalo Blue can enhance your artwork by exploring its unique properties and applications in this article.
Table of Comparison
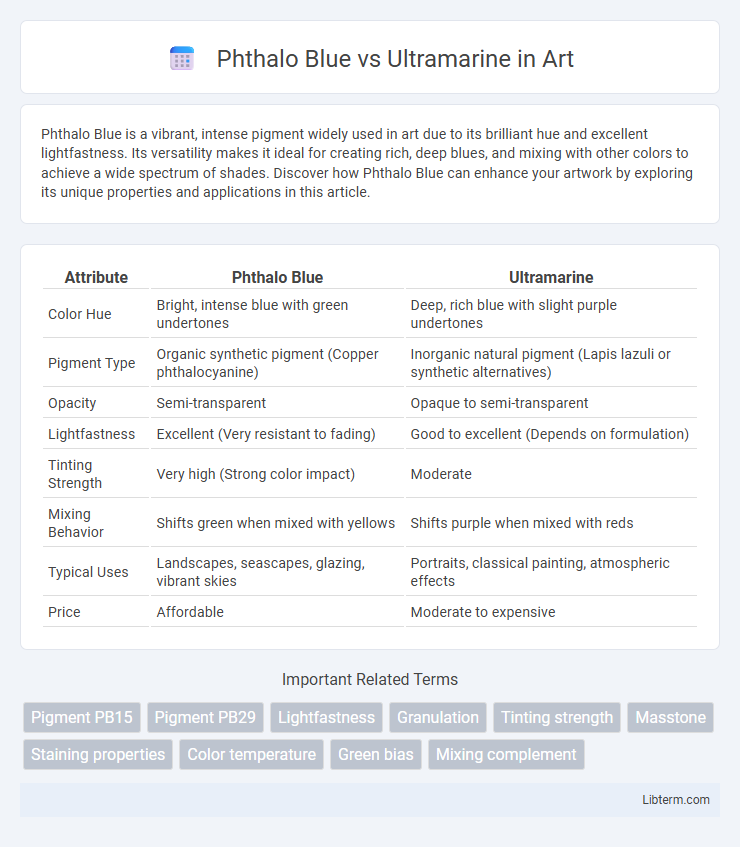
| Attribute | Phthalo Blue | Ultramarine |
|---|---|---|
| Color Hue | Bright, intense blue with green undertones | Deep, rich blue with slight purple undertones |
| Pigment Type | Organic synthetic pigment (Copper phthalocyanine) | Inorganic natural pigment (Lapis lazuli or synthetic alternatives) |
| Opacity | Semi-transparent | Opaque to semi-transparent |
| Lightfastness | Excellent (Very resistant to fading) | Good to excellent (Depends on formulation) |
| Tinting Strength | Very high (Strong color impact) | Moderate |
| Mixing Behavior | Shifts green when mixed with yellows | Shifts purple when mixed with reds |
| Typical Uses | Landscapes, seascapes, glazing, vibrant skies | Portraits, classical painting, atmospheric effects |
| Price | Affordable | Moderate to expensive |
Introduction to Phthalo Blue and Ultramarine
Phthalo Blue is a synthetic pigment known for its intense, vibrant hue and high tinting strength, commonly used in acrylic and oil painting for its durability and versatility. Ultramarine, derived from the semi-precious stone lapis lazuli, offers a deep, rich blue with a slightly warmer tone and excellent lightfastness, making it a staple in traditional and fine art applications. Both pigments serve distinct purposes in artistic techniques, with Phthalo Blue favored for brightness and mixing power, while Ultramarine is prized for its historical significance and subtle, natural depth.
Origins and Chemical Composition
Phthalo Blue, also known as Phthalocyanine Blue, originated in the early 20th century as a synthetic pigment with a striking intense blue hue formed from copper phthalocyanine complexes. Ultramarine is a natural or synthetic pigment derived from the mineral lapis lazuli, characterized by its vibrant deep blue color primarily consisting of sodium aluminum silicate with sulfur compounds. The chemical composition of Phthalo Blue includes a complex aromatic macrocycle with copper ions at its center, whereas Ultramarine's blue color arises from trapped sulfur radicals within its aluminosilicate lattice.
Color Characteristics and Undertones
Phthalo Blue offers a vibrant, intense hue with strong green undertones, making it ideal for mixing bright, vivid shades in painting. Ultramarine Blue features a deeper, more muted tone with warm reddish undertones, providing richness and depth in color applications. Artists often select Phthalo Blue for its high tinting strength and transparency, while Ultramarine Blue is preferred for its subtle warmth and natural earthiness.
Lightfastness and Permanence
Phthalo Blue exhibits exceptional lightfastness and permanence, making it a preferred choice for artists seeking longevity and vibrant color stability in their work. Ultramarine, while also lightfast, tends to be less permanent and can fade or shift color over extended exposure to light. The superior durability of Phthalo Blue ensures consistent performance in archival projects where resistance to fading and chemical degradation is critical.
Mixing Properties and Color Range
Phthalo Blue offers a vibrant, intense hue with strong staining properties and excellent tinting strength, making it ideal for creating bold, vivid color mixtures, especially greens and teals. Ultramarine Blue provides a softer, more muted tone with a granulating texture, delivering smoother transitions and subtle variations when mixed, particularly effective in blending with reds and earth tones for natural, atmospheric effects. Both pigments contribute uniquely to an artist's palette, with Phthalo Blue excelling in bright, saturated mixes and Ultramarine Blue favored for its depth and rich, complex color range.
Applications in Different Mediums
Phthalo Blue offers vibrant, intense color ideal for acrylics and oils, excelling in glazing and mixing due to its high tinting strength and transparency. Ultramarine Blue, prized in watercolors and oil paints for its rich, deep hue and granulating texture, adds natural variation and depth to landscapes and skies. Both pigments perform distinctively across mediums, with Phthalo Blue favored for bold, modern works and Ultramarine preferred for classic, textured effects.
Transparency and Opacity Comparison
Phthalo Blue exhibits high transparency, making it ideal for glazing and layering techniques where light passes through the pigment to create depth and luminosity. Ultramarine, by contrast, generally has a more opaque quality, providing stronger coverage and richer, denser color application on the canvas. Artists often choose Phthalo Blue for its brilliant transparency and mixing versatility, while Ultramarine is preferred for bold, solid strokes and subtle shifts in opacity.
Common Uses in Art and Design
Phthalo Blue is favored in art and design for its vibrant, intense hues and strong tinting strength, making it ideal for creating vivid skies, water scenes, and bold color mixing. Ultramarine Blue, prized for its rich, deep, and slightly reddish tones, is commonly used in classical paintings, landscapes, and mood-driven compositions to evoke depth and warmth. Both pigments play essential roles in palettes, with Phthalo Blue offering brightness and versatility, while Ultramarine Blue provides subtlety and a traditional feel.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Pigment
Phthalo Blue offers intense color strength and excellent transparency, making it ideal for glazing and mixing vibrant greens, but it can be overpowering and difficult to control in delicate washes. Ultramarine provides a rich, deep blue with a slightly granulating texture that enhances visual interest and is preferred for atmospheric effects, though it has lower tinting strength and can dull when mixed with certain colors. Both pigments have excellent lightfastness, but their distinct properties suit different artistic techniques and color mixing needs.
Choosing Between Phthalo Blue and Ultramarine
Phthalo Blue offers intense tinting strength and a vibrant, cool tone ideal for mixing vivid greens and strong shadows, while Ultramarine provides a richer, warmer blue with subtle reddish undertones suited for natural skies and gentle gradients. Artists frequently select Phthalo Blue for bold, high-contrast work requiring durability and chemical stability, whereas Ultramarine is favored for its granulating texture and softer blending capabilities in traditional and landscape painting. The choice depends on the desired color intensity, mixing versatility, and the specific atmospheric effects an artist aims to achieve.
Phthalo Blue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com