Collage art combines various materials such as paper, fabric, and photographs to create unique, textured compositions that express creativity and storytelling. This artistic technique allows you to layer diverse elements, resulting in visually compelling and meaningful pieces. Explore the rest of the article to discover different collage methods and tips to enhance your craft.
Table of Comparison
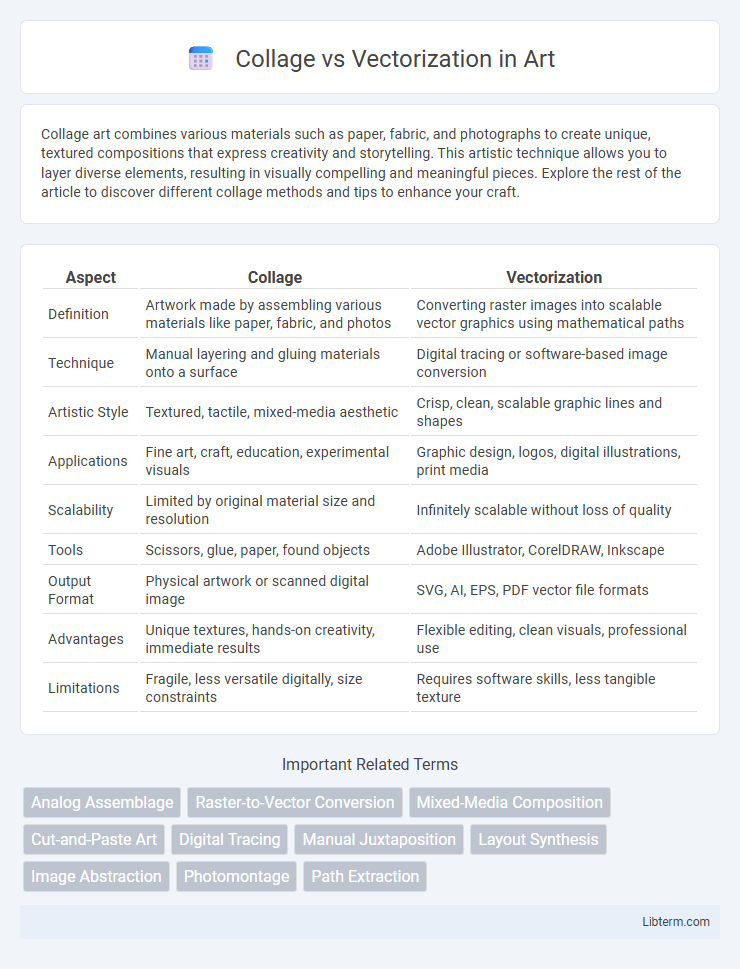
| Aspect | Collage | Vectorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artwork made by assembling various materials like paper, fabric, and photos | Converting raster images into scalable vector graphics using mathematical paths |
| Technique | Manual layering and gluing materials onto a surface | Digital tracing or software-based image conversion |
| Artistic Style | Textured, tactile, mixed-media aesthetic | Crisp, clean, scalable graphic lines and shapes |
| Applications | Fine art, craft, education, experimental visuals | Graphic design, logos, digital illustrations, print media |
| Scalability | Limited by original material size and resolution | Infinitely scalable without loss of quality |
| Tools | Scissors, glue, paper, found objects | Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, Inkscape |
| Output Format | Physical artwork or scanned digital image | SVG, AI, EPS, PDF vector file formats |
| Advantages | Unique textures, hands-on creativity, immediate results | Flexible editing, clean visuals, professional use |
| Limitations | Fragile, less versatile digitally, size constraints | Requires software skills, less tangible texture |
Understanding Collage Art: Definition and Techniques
Collage art involves assembling various materials such as paper, fabric, and photographs to create a unified composition that emphasizes texture and layer interplay. Techniques include layering torn or cut elements, integrating mixed media, and manipulating scale to produce depth and contrast within the artwork. Understanding collage art requires recognizing its emphasis on physical materials and tactile arrangement, which contrasts with the digital precision found in vectorization methods.
What Is Vectorization? An Overview
Vectorization is a graphic technique that converts raster images into smooth, scalable vector graphics using mathematical equations to define shapes, lines, and colors. It enables images to be resized without loss of quality, making it essential for logos, illustrations, and digital art requiring precision and flexibility. This process contrasts with collage, which involves combining various visual elements often in raster form, lacking the scalability and editability offered by vectorization.
Key Differences Between Collage and Vectorization
Collage combines various images or materials into a single composition, emphasizing texture and layered visual elements, while vectorization converts raster images into scalable vector graphics using mathematical paths and shapes. Collage relies on physical or digital manipulation of discrete pieces, resulting in an often tactile, textured appearance; vectorization produces clean, resolution-independent images ideal for logos and illustrations. Key differences include the artistic approach--collage as assemblage versus vectorization as technical image transformation--and output scalability, with vector graphics maintaining quality at any size.
Tools and Materials Used in Collage Creation
Collage creation relies on a diverse range of tools and materials such as scissors, glue, paper, magazines, fabric, and found objects to assemble layered compositions with tactile textures. Artists often incorporate mixed media elements like paint, ink, and markers to enhance visual depth and contrast. In contrast, vectorization uses digital software like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW to transform images into scalable vector graphics without physical materials.
The Digital Process Behind Vectorization
Vectorization transforms raster images into scalable vector graphics using algorithms that detect edges and shapes to create paths defined by mathematical equations. This digital process involves tracing pixels to generate smooth curves and lines, enabling infinite resizing without loss of quality. Unlike collage, which combines different visual elements manually or digitally, vectorization automates image conversion for precise and editable artwork.
Artistic Expression: Collage vs. Vector Graphics
Collage combines diverse materials and textures, enabling artists to create layered, tactile compositions that evoke rich emotional responses. Vector graphics utilize mathematical paths to produce crisp, scalable images ideal for precision and clarity in digital art. This contrast highlights collage's organic, expressive potential versus vector graphics' clean, versatile visual communication.
Advantages of Collage in Modern Art
Collage in modern art offers unparalleled textural richness and dimensionality by integrating diverse materials such as paper, fabric, and found objects, which enhances visual complexity beyond flat surfaces. This technique encourages spontaneous creativity and experimental composition, allowing artists to juxtapose contrasting elements for unique narratives and emotional depth. Unlike vectorization, collage embraces imperfection and materiality, fostering tactile engagement and authentic expression in contemporary artworks.
Benefits of Vectorization for Digital Design
Vectorization enhances digital design by enabling infinitely scalable graphics without quality loss, ensuring crisp images across all screen sizes and resolutions. It facilitates easy editing and manipulation of design elements, saving time and increasing efficiency for designers. Vector files also offer smaller file sizes compared to collages made from raster images, improving storage and faster loading times for web and multimedia use.
Choosing the Right Approach: Collage or Vectorization?
Choosing between collage and vectorization depends on the project's goals and desired visual style; collage offers a tactile, layered aesthetic ideal for mixed media and expressive art, while vectorization provides clean, scalable graphics perfect for logos, branding, and digital illustrations. Collage excels in conveying texture and depth through physical or digital assembly of diverse materials, whereas vectorization ensures precision, smooth lines, and adaptability across various resolutions and platforms. Assessing factors such as output medium, detail requirements, and stylistic preferences guides designers in selecting the most effective method for impactful visual communication.
Future Trends in Collage Art and Vectorization
Future trends in collage art emphasize digital integration, using AI-powered tools to enhance creative layering and texture blending for more immersive visual experiences. Vectorization advances focus on real-time, high-precision conversion of raster images into scalable vectors, driven by machine learning algorithms that optimize path accuracy and reduce manual editing. Both fields converge toward hybrid workflows, enabling artists to seamlessly combine handmade collage aesthetics with precise vector graphics for innovative multimedia projects.
Collage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com