Collage art combines various materials such as photographs, paper, and fabric to create visually compelling and textured compositions. This technique allows artists to express creativity by layering diverse elements, resulting in unique and meaningful artwork. Discover how you can experiment with collage and transform your artistic vision by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
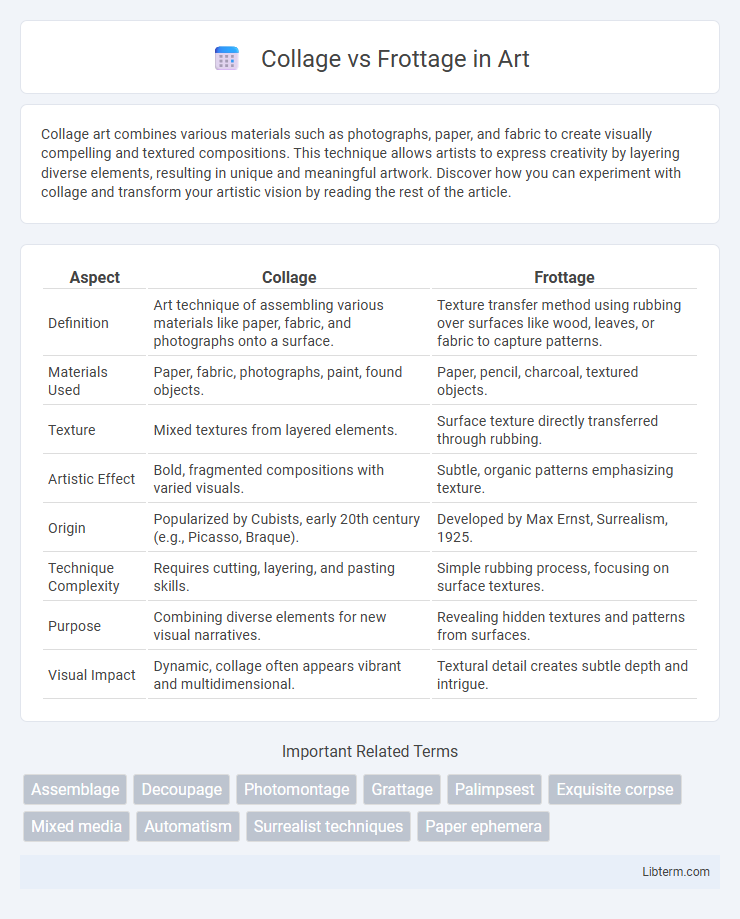
| Aspect | Collage | Frottage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art technique of assembling various materials like paper, fabric, and photographs onto a surface. | Texture transfer method using rubbing over surfaces like wood, leaves, or fabric to capture patterns. |
| Materials Used | Paper, fabric, photographs, paint, found objects. | Paper, pencil, charcoal, textured objects. |
| Texture | Mixed textures from layered elements. | Surface texture directly transferred through rubbing. |
| Artistic Effect | Bold, fragmented compositions with varied visuals. | Subtle, organic patterns emphasizing texture. |
| Origin | Popularized by Cubists, early 20th century (e.g., Picasso, Braque). | Developed by Max Ernst, Surrealism, 1925. |
| Technique Complexity | Requires cutting, layering, and pasting skills. | Simple rubbing process, focusing on surface textures. |
| Purpose | Combining diverse elements for new visual narratives. | Revealing hidden textures and patterns from surfaces. |
| Visual Impact | Dynamic, collage often appears vibrant and multidimensional. | Textural detail creates subtle depth and intrigue. |
Introduction to Collage and Frottage
Collage is an art technique involving the assemblage of various materials such as paper, photographs, fabric, and other ephemera onto a surface to create a unified composition. Frottage, developed by Max Ernst in the 1920s, is a texture-based printmaking method where paper is rubbed over a textured surface to capture its pattern. Both techniques emphasize visual texture and layering but differ in their approach: collage relies on the juxtaposition of physical elements, while frottage harnesses natural textures through rubbing.
Defining Collage: Techniques and Materials
Collage is an artistic technique that involves assembling various materials such as paper, fabric, photographs, and found objects onto a surface to create a unified composition. Artists use adhesives, layering, cutting, and overlapping to combine textures, colors, and images, resulting in visually dynamic and tactile artworks. Unlike frottage, which captures textures through rubbing, collage emphasizes the arrangement and integration of diverse materials to convey meaning and aesthetic depth.
What is Frottage? Origins and Methods
Frottage is an art technique developed by surrealist artist Max Ernst in the 1920s, involving creating rubbings of textured surfaces to produce abstract patterns and imagery. This method uses materials like paper and pencil or charcoal to capture the texture of objects such as wood grain, fabric, or leaves by rubbing over them. Unlike collage, which assembles various materials onto a surface, frottage emphasizes texture transfer and chance effects as a foundational creative process.
Key Differences Between Collage and Frottage
Collage involves assembling various materials like paper, photographs, or fabric onto a surface to create a unified artwork, emphasizing layering and juxtaposition. Frottage is a texture-based technique where artists rub pencil or other media over paper placed on textured objects, highlighting surface impressions and tactile patterns. The key differences lie in collage's emphasis on combining diverse visual elements versus frottage's focus on capturing and reproducing textures directly from physical surfaces.
Artistic Expression in Collage
Collage utilizes the assembly of various materials such as paper, photographs, and fabric to create layered compositions that emphasize texture, color contrast, and spatial relationships. This technique enables artists to explore themes of fragmentation, memory, and identity by juxtaposing disparate elements in innovative ways. Frottage, by contrast, relies on rubbing textures from surfaces onto paper, focusing more on capturing the physical qualities of objects rather than combining mixed media for complex visual narratives.
The Unique Textures of Frottage
Frottage employs the technique of rubbing pencil or charcoal over textured surfaces, creating unique, organic patterns that cannot be replicated, offering richness in tactile detail distinct from the layered assemblages of collage. Unlike collage, which builds images by adhering diverse materials like paper, fabric, and photographs, frottage captures the direct impressions of objects such as wood grain, leaves, or rough surfaces, emphasizing natural texture and spontaneity. This method reveals the hidden qualities of everyday materials, producing visually engaging textures that invite closer inspection and inspire abstract interpretation.
Famous Artists Who Used Collage
Famous artists known for using collage include Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, pioneers of Cubism who integrated fragmented images to create dynamic compositions. Hannah Hoch and Kurt Schwitters advanced collage by incorporating found objects and newspaper clippings, influencing Dada and Constructivism movements. Contemporary artists like Robert Rauschenberg and Romare Bearden expanded collage with mixed media, blending painting, photography, and textiles to explore cultural and social themes.
Iconic Works in Frottage Art
Frottage, popularized by Max Ernst, is characterized by textures created through rubbing paper over surfaces, with iconic works like "The Entire City" (1923) displaying intricate textures and surreal landscapes. Unlike collage, which assembles disparate materials and images, frottage emphasizes automatic techniques that reveal subconscious patterns and organic forms. Ernst's pioneering frottage pieces significantly influenced surrealism, showcasing innovative textural expressions unattainable through traditional collage methods.
Which Technique is Right for You?
Collage, involving the assembly of various materials like paper, photographs, and fabric, offers a versatile and tactile approach ideal for artists seeking to combine textures and layers for a multidimensional effect. Frottage, created by rubbing a pencil or crayon over textured surfaces to capture their patterns, suits those who prefer spontaneous, texture-based compositions with an emphasis on natural or found surfaces. Choosing between collage and frottage depends on your artistic goals: collage for structured, mixed-media expression and frottage for organic, surface-driven texture exploration.
Conclusion: Collage vs Frottage in Contemporary Art
Collage and frottage both play pivotal roles in contemporary art as methods that challenge traditional textures and compositions. Collage merges diverse materials and imagery to create layered, multidimensional narratives, while frottage emphasizes texture through rubbing techniques, often revealing subconscious patterns. Contemporary artists leverage these techniques to explore materiality, memory, and abstraction, establishing collage and frottage as complementary practices that enrich visual storytelling.
Collage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com