Belonging is a fundamental human need that fosters connection, identity, and well-being within communities and relationships. It influences your emotional health and motivation by providing a sense of acceptance and support. Explore how cultivating belonging can transform your life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
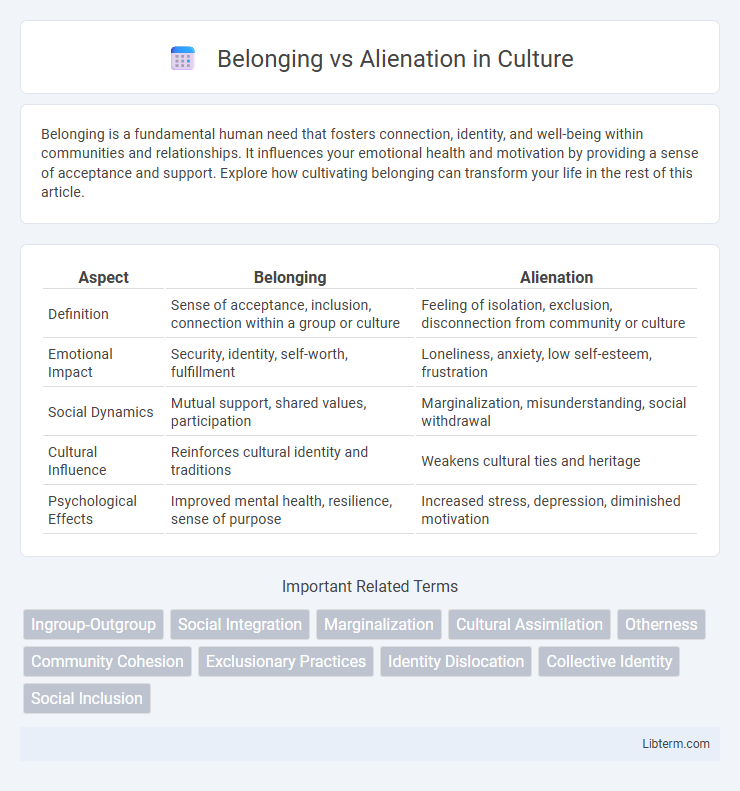
| Aspect | Belonging | Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sense of acceptance, inclusion, connection within a group or culture | Feeling of isolation, exclusion, disconnection from community or culture |
| Emotional Impact | Security, identity, self-worth, fulfillment | Loneliness, anxiety, low self-esteem, frustration |
| Social Dynamics | Mutual support, shared values, participation | Marginalization, misunderstanding, social withdrawal |
| Cultural Influence | Reinforces cultural identity and traditions | Weakens cultural ties and heritage |
| Psychological Effects | Improved mental health, resilience, sense of purpose | Increased stress, depression, diminished motivation |
Understanding Belonging: Definition and Importance
Belonging is the profound human need to feel accepted, connected, and valued within a group or community, fostering emotional security and personal identity. Understanding belonging involves recognizing its role in mental health, social cohesion, and motivation, as people deprived of belonging often experience loneliness and alienation. This concept is crucial in psychology, sociology, and education, where promoting belonging can enhance well-being, performance, and societal harmony.
What is Alienation? Key Concepts Explained
Alienation refers to a psychological and social state in which individuals feel disconnected or estranged from themselves, others, or society. Key concepts include existential alienation, where a person experiences a loss of meaning or purpose, and social alienation, characterized by feelings of isolation and powerlessness within a community or workplace. This phenomenon can lead to emotional distress, reduced motivation, and a weakened sense of identity or belonging.
Historical Perspectives on Belonging and Alienation
Historical perspectives on belonging and alienation reveal patterns of social inclusion and exclusion shaped by cultural, political, and economic forces. Societies throughout history have constructed identities through shared beliefs, rituals, and power dynamics, often marginalizing groups deemed "other" to reinforce collective belonging. Key examples include the caste systems in ancient India, racial segregation in the United States, and colonialism's impact on indigenous populations, highlighting how belonging and alienation have been instrumental in maintaining social hierarchies.
Psychological Impact of Belonging
A strong sense of belonging significantly enhances psychological well-being by fostering emotional security, reducing stress, and promoting resilience against mental health disorders like anxiety and depression. Neuroscientific studies show that social connectedness activates brain regions associated with reward and motivation, reinforcing positive behavioral patterns and emotional stability. Conversely, the absence of belonging triggers feelings of alienation, leading to increased cortisol levels and heightened vulnerability to psychological distress.
Effects of Alienation on Mental Health
Alienation profoundly impacts mental health by fostering feelings of isolation, loneliness, and decreased self-worth, often leading to anxiety and depression. Chronic experiences of social disconnection disrupt emotional well-being and can exacerbate stress-related disorders. Promoting inclusion and social support networks is critical in mitigating these negative psychological effects.
Social Factors Influencing Belonging and Alienation
Social factors such as community support, cultural inclusion, and shared values strongly influence feelings of belonging by fostering acceptance and identity affirmation. Conversely, social exclusion, discrimination, and lack of representation contribute to alienation, undermining individuals' sense of connection and self-worth. Interpersonal relationships and societal structures play critical roles in shaping whether people experience inclusion or isolation within their communities.
Belonging in the Digital Age: Opportunities and Challenges
Belonging in the digital age provides unprecedented opportunities for connection through social media platforms, online communities, and virtual collaborations, enabling individuals to find support and shared identity across geographical boundaries. However, digital belonging also presents challenges such as superficial interactions, algorithm-driven echo chambers, and the risk of cyberbullying, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation and alienation. The balance between authentic engagement and digital presence is crucial for fostering meaningful belonging in an increasingly interconnected world.
Overcoming Alienation: Strategies and Solutions
Overcoming alienation involves fostering genuine connections through active communication, empathy, and shared experiences that rebuild trust and inclusion. Implementing community-building initiatives and supportive social environments helps individuals regain a sense of belonging and purpose. Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can address feelings of isolation by reshaping negative thought patterns and promoting social engagement.
Belonging vs Alienation in the Workplace
Belonging in the workplace fosters employee engagement, productivity, and collaboration by creating an inclusive environment where individuals feel valued and accepted. Alienation, conversely, results in disengagement, reduced morale, and higher turnover rates due to feelings of isolation, exclusion, and lack of recognition. Organizations that prioritize diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives significantly enhance belonging, which directly impacts overall business performance and employee well-being.
Nurturing Communities: Fostering a Sense of Belonging
Nurturing communities cultivate a profound sense of belonging by promoting inclusion, empathy, and shared experiences among members. These environments reduce feelings of alienation by encouraging active participation and mutual support, which strengthens social bonds and individual identity. Research indicates that communities prioritizing belonging enhance mental well-being and resilience, highlighting the critical role of connectedness in human development.
Belonging Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com