Cultural generalities are broad patterns or traits shared by a majority within a culture, helping to understand common behaviors and values. These generalities offer valuable insights but should not be mistaken for absolute rules, as individual variations always exist. Explore the rest of the article to learn how recognizing cultural generalities can improve your intercultural communication skills.
Table of Comparison
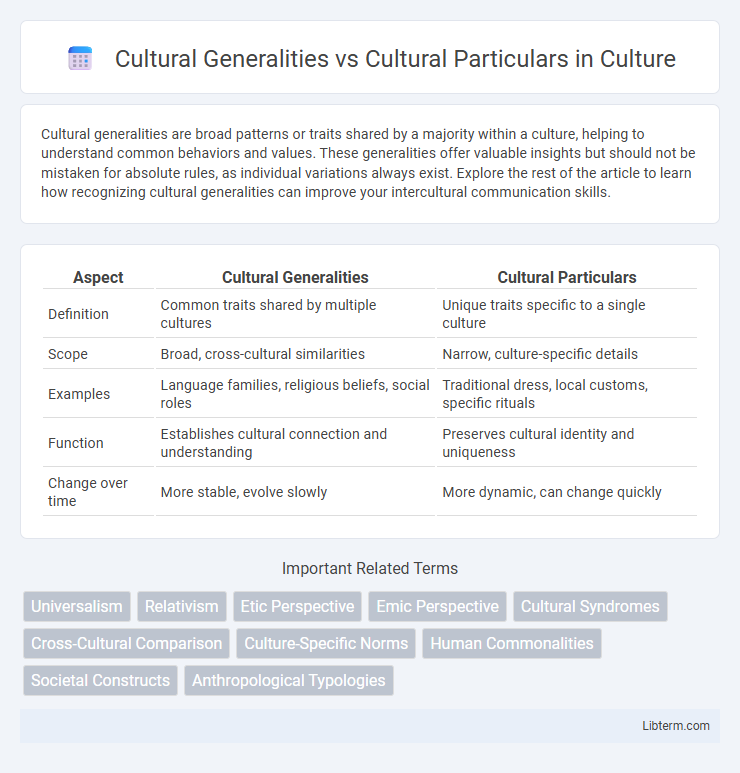
| Aspect | Cultural Generalities | Cultural Particulars |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Common traits shared by multiple cultures | Unique traits specific to a single culture |
| Scope | Broad, cross-cultural similarities | Narrow, culture-specific details |
| Examples | Language families, religious beliefs, social roles | Traditional dress, local customs, specific rituals |
| Function | Establishes cultural connection and understanding | Preserves cultural identity and uniqueness |
| Change over time | More stable, evolve slowly | More dynamic, can change quickly |
Understanding Cultural Generalities
Understanding cultural generalities involves recognizing common patterns and practices shared by members of a culture, such as language, social norms, and values, which provide a framework for predicting behavior and facilitating communication. These generalities help reduce uncertainty in intercultural interactions by highlighting typical cultural traits while acknowledging variability within groups. Emphasizing cultural generalities supports effective cross-cultural understanding without stereotyping individuals based on singular cultural characteristics.
Exploring Cultural Particulars
Exploring cultural particulars involves examining the unique, context-specific customs, behaviors, and practices that define individual cultures and differentiate them from others. These particulars include language nuances, traditional rituals, and social norms that are deeply rooted in a community's history and environment. Understanding cultural particulars enhances cross-cultural communication by highlighting the importance of localized knowledge and respect for cultural diversity.
Key Differences: Generalities vs Particulars
Cultural generalities refer to common traits, values, or practices shared by several but not all cultures, such as language families or agricultural methods, highlighting patterns that cross multiple societies. Cultural particulars are unique aspects or customs specific to a single culture, like specific rituals, traditional clothing, or localized beliefs that distinguish one group from another. The key difference lies in the scope of applicability: generalities reflect broader similarities across cultures, while particulars emphasize distinctive features unique to a specific cultural identity.
Historical Roots of Cultural Patterns
Cultural generalities refer to shared traits and practices that emerge across multiple societies, reflecting broad historical developments such as migration, trade, and technological diffusion. Cultural particulars arise from unique historical events, localized experiences, and distinct environmental conditions that solidify specific ethnic, national, or regional identities. The interplay between generalities and particulars demonstrates how cultural patterns evolve through both widespread historical influences and singular, context-driven transformations.
The Role of Society in Shaping Culture
Society plays a pivotal role in shaping culture by establishing shared norms, values, and customs that guide collective behavior, reflecting cultural generalities common across communities. At the same time, unique social structures and historical contexts give rise to cultural particulars, distinguishing one group's traditions and practices from another. The dynamic interplay between societal influences and individual experiences ensures that culture remains both universally recognizable and distinctly diverse.
Impact on Communication and Relationships
Cultural generalities, such as shared language or common values, facilitate smoother communication by providing a common framework for understanding, while cultural particulars--unique customs, rituals, and expressions--require careful attention to avoid misunderstandings. Misinterpreting cultural particulars can lead to miscommunication and strained relationships, highlighting the importance of cultural competence in diverse interactions. Recognizing both generalities and particulars enhances empathy, fosters trust, and improves collaboration across different cultural contexts.
Cultural Generalities in Globalization
Cultural generalities refer to common practices or traits shared by several but not all cultures, such as language family groups or social norms like hospitality, which facilitate cross-cultural understanding and global interaction. In globalization, cultural generalities promote communication and cooperation by providing a foundation of shared values or behaviors that transcend individual societies. These generalities help multinational businesses, international organizations, and global communities navigate cultural diversity more effectively while respecting unique cultural expressions.
Case Studies: Traditions Around the World
Case studies of traditions around the world illustrate cultural generalities, such as common themes of rituals marking life milestones, alongside cultural particulars that highlight unique expressions shaped by geography, language, and history. For instance, wedding ceremonies universally celebrate union but vary widely in customs, dress, and symbolism--from the red attire in Indian weddings to the white gowns in Western ceremonies. These examples emphasize how cultural particulars provide rich, context-specific nuances within broader cultural commonalities that define human social practices globally.
Challenges in Recognizing Cultural Nuances
Cultural generalities, such as shared language or customs within a group, often mask cultural particulars that include unique traditions, beliefs, or social norms specific to subgroups or individuals. Recognizing these cultural particulars presents challenges because assumptions based on generalities can lead to misunderstandings or stereotyping, impeding effective communication and collaboration. In cross-cultural interactions, sensitivity to nuanced cultural differences is essential to avoid oversimplification and to foster genuine respect and inclusivity.
Embracing Diversity: Balancing Both Perspectives
Cultural generalities provide a broad framework to understand shared traits across groups, while cultural particulars highlight unique customs and traditions within specific communities. Embracing diversity requires balancing these perspectives to foster mutual respect and avoid stereotypes by recognizing both universal patterns and individual cultural expressions. Effective intercultural communication depends on appreciating this duality to promote inclusivity and deeper cross-cultural understanding.
Cultural Generalities Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com