Core culture represents the fundamental values and beliefs that define an organization's identity, while organizational culture encompasses the collective behaviors and practices shaped by those core principles. Understanding this distinction helps You align personal and professional goals with your workplace environment, fostering increased engagement and productivity. Explore the rest of the article to learn how these cultural elements impact organizational success and your career growth.
Table of Comparison
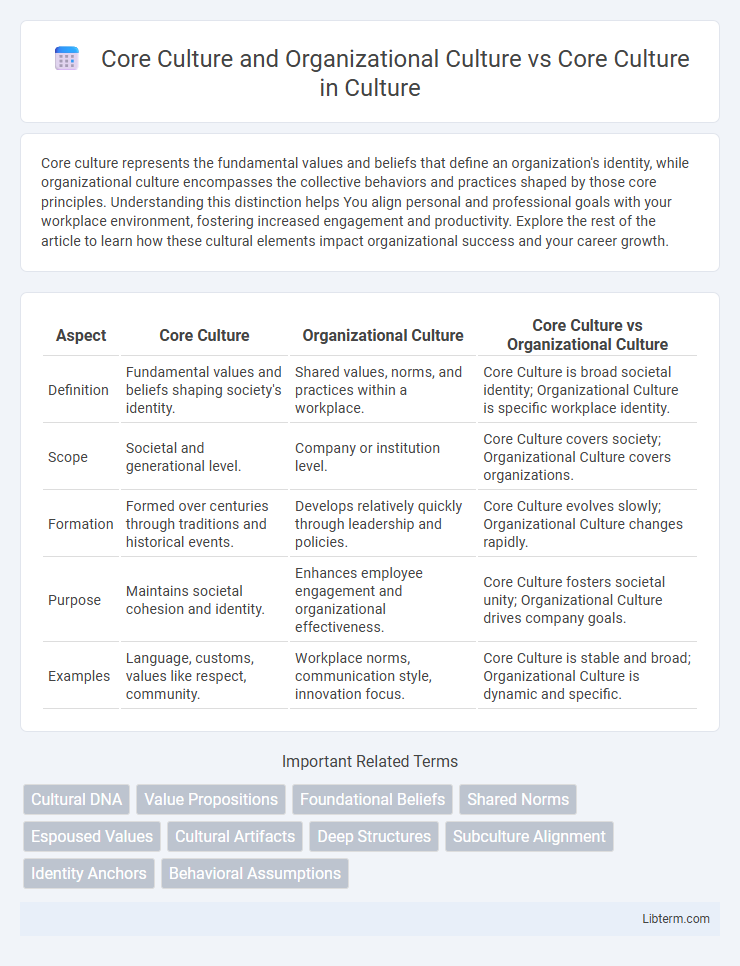
| Aspect | Core Culture | Organizational Culture | Core Culture vs Organizational Culture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental values and beliefs shaping society's identity. | Shared values, norms, and practices within a workplace. | Core Culture is broad societal identity; Organizational Culture is specific workplace identity. |
| Scope | Societal and generational level. | Company or institution level. | Core Culture covers society; Organizational Culture covers organizations. |
| Formation | Formed over centuries through traditions and historical events. | Develops relatively quickly through leadership and policies. | Core Culture evolves slowly; Organizational Culture changes rapidly. |
| Purpose | Maintains societal cohesion and identity. | Enhances employee engagement and organizational effectiveness. | Core Culture fosters societal unity; Organizational Culture drives company goals. |
| Examples | Language, customs, values like respect, community. | Workplace norms, communication style, innovation focus. | Core Culture is stable and broad; Organizational Culture is dynamic and specific. |
Introduction to Core Culture
Core Culture represents the fundamental values, beliefs, and assumptions that shape an organization's identity and guide employee behavior at the deepest level. Organizational Culture encompasses the broader set of shared norms, rituals, and practices that evolve from the core culture and influence everyday interactions within the workplace. Understanding Core Culture is essential for aligning an organization's strategic goals with its intrinsic values, fostering cohesion, and sustaining long-term success.
Defining Organizational Culture
Organizational culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape how employees interact and perform within a company, forming a unique internal environment. Core culture refers to the fundamental principles and assumptions at the heart of an organization's identity, influencing decision-making and strategic direction. Defining organizational culture involves identifying these core elements, including artifacts, espoused values, and underlying assumptions that collectively drive workplace norms and employee engagement.
Core Culture vs Organizational Culture: Key Differences
Core Culture represents the fundamental beliefs and values that shape an organization's identity and long-term vision, while Organizational Culture encompasses the shared behaviors, practices, and norms that emerge from these core values in daily operations. Core Culture drives strategic decision-making and influences employee mindset, whereas Organizational Culture manifests in workplace environment and interaction patterns. Understanding the distinction between Core Culture and Organizational Culture is essential for aligning business strategy with employee engagement and operational effectiveness.
The Role of Core Culture in Business Success
Core culture serves as the foundational set of shared values, beliefs, and principles that shape employee behavior and drive organizational identity, directly influencing innovation, decision-making, and customer satisfaction. Organizational culture encompasses the broader, observable practices and norms derived from core culture but may evolve with external influences and operational changes. Strong alignment between core culture and organizational behavior fosters cohesive teamwork, enhances brand reputation, and sustains competitive advantage, proving essential for long-term business success.
Elements That Shape Organizational Culture
Core culture consists of the fundamental values, beliefs, and assumptions that drive an organization's identity and decision-making processes. Organizational culture is shaped by elements such as leadership style, communication patterns, rituals, and shared norms that influence employee behavior and collaboration. These elements together form a unique environment that supports the organization's mission and impacts its overall performance and adaptability.
Aligning Core Culture with Organizational Goals
Aligning core culture with organizational goals ensures that shared values and beliefs directly support strategic objectives, enhancing overall performance and employee engagement. Core culture reflects the deep-rooted principles driving behavior, while organizational culture encompasses the broader environment shaped by policies and practices. Synchronizing these elements creates a cohesive framework that fosters innovation, accountability, and sustained growth.
Impact of Core Culture on Employee Behavior
Core Culture shapes employee behavior by embedding fundamental values and beliefs that guide decision-making, communication, and teamwork within an organization. Unlike broader Organizational Culture, which includes visible practices and rituals, Core Culture represents the underlying principles that consistently influence employee attitudes and motivation. This deep-rooted value system fosters alignment, commitment, and ethical conduct, driving productivity and reinforcing a positive workplace environment.
Challenges in Maintaining Core and Organizational Culture
Maintaining core culture and organizational culture faces challenges such as resistance to change, misalignment between stated values and employee behavior, and difficulties in consistently communicating cultural principles across diverse teams. Conflicts often arise when core culture, which represents foundational beliefs, clashes with evolving organizational practices aimed at adaptation and growth. Sustaining cultural coherence requires ongoing leadership commitment, transparent communication, and mechanisms to reinforce desired behaviors amidst dynamic business environments.
Strategies to Strengthen Core Culture
Core culture represents the fundamental values and beliefs that define an organization's identity, while organizational culture encompasses the broader behaviors, practices, and norms shaping daily interactions. Strategies to strengthen core culture include consistent communication of core values, embedding these values into leadership development, and aligning recruitment processes to attract talent that reflects the core culture. Reinforcing core values through recognition programs and continuous feedback loops ensures sustained commitment and enhances overall organizational cohesion.
Future Trends in Core and Organizational Culture
Future trends in core culture emphasize adaptability, innovation, and inclusivity as organizations navigate rapid technological advancements and global challenges. Organizational culture is evolving to prioritize employee well-being, diversity, and remote collaboration, reshaping traditional work environments. Data-driven decision-making and continuous learning are critical components shaping both core and organizational culture in modern enterprises.
Core Culture and Organizational Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com