Integration streamlines your business processes by connecting disparate systems and applications, enhancing data flow and operational efficiency. Effective integration reduces errors, saves time, and fosters better collaboration across teams. Discover how mastering integration can transform your organization by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
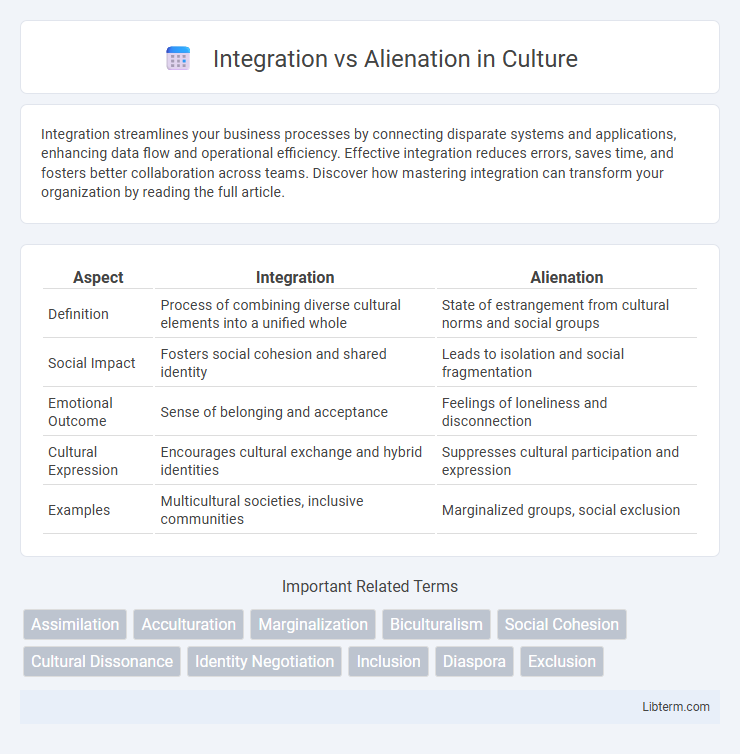
| Aspect | Integration | Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of combining diverse cultural elements into a unified whole | State of estrangement from cultural norms and social groups |
| Social Impact | Fosters social cohesion and shared identity | Leads to isolation and social fragmentation |
| Emotional Outcome | Sense of belonging and acceptance | Feelings of loneliness and disconnection |
| Cultural Expression | Encourages cultural exchange and hybrid identities | Suppresses cultural participation and expression |
| Examples | Multicultural societies, inclusive communities | Marginalized groups, social exclusion |
Understanding Integration and Alienation
Understanding integration involves recognizing the process by which individuals or groups become incorporated into a social system, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity. Alienation, in contrast, describes the experience of estrangement or disconnection from societal structures, often resulting in feelings of powerlessness or isolation. Sociologists analyze these concepts to explain how social cohesion or fragmentation impacts individual well-being and community dynamics.
Historical Context of Social Integration
The historical context of social integration reveals a shift from tribal and kinship-based groupings toward complex societies demanding institutional cohesion for stability. Industrialization accelerated social integration by fostering interdependence through labor specialization and urbanization, while alienation emerged as individuals felt disconnected from communal ties and production processes. Durkheim's theory emphasizes the role of collective conscience in maintaining social integration, contrasting with Marx's view of alienation as a consequence of capitalist exploitation.
Causes of Alienation in Modern Societies
Rapid technological advancements, urbanization, and industrialization contribute significantly to alienation in modern societies by disrupting traditional social bonds and creating fragmented communities. Economic inequality and labor market instability exacerbate feelings of powerlessness and social exclusion, undermining individuals' sense of belonging. The decline of communal institutions and weakened social networks further isolate individuals, fostering emotional and social detachment from society.
Cultural Identity and Belonging
Cultural identity shapes the sense of belonging within a community, influencing whether individuals feel integrated or alienated. Strong cultural integration promotes social cohesion by validating diverse traditions and shared values, while alienation arises when cultural expressions are marginalized or suppressed. The interplay between cultural recognition and social acceptance determines the depth of belonging and the stability of multicultural societies.
The Role of Education in Integration
Education plays a crucial role in fostering social integration by promoting shared values, cultural understanding, and civic responsibility among diverse populations. Schools serve as key environments where students from different backgrounds learn to collaborate, develop social skills, and build a sense of belonging within the community. Effective educational policies that emphasize inclusivity and equal access reduce alienation and contribute to cohesive, resilient societies.
Economic Factors Influencing Alienation
Economic factors influencing alienation include wage disparity, job insecurity, and lack of control over work processes, which contribute to workers feeling disconnected from the products of their labor. Capitalist production systems often prioritize profit over employee well-being, intensifying feelings of exploitation and powerlessness. This economic alienation manifests through monotonous tasks, insufficient recognition, and restricted opportunities for personal growth within the workplace.
Social Policies Promoting Inclusion
Social policies promoting inclusion aim to enhance integration by reducing social alienation through equitable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Programs targeting marginalized groups foster social cohesion by encouraging participation in community and civic activities. Effective inclusion policies address systemic barriers, promoting diversity and equal representation in decision-making processes.
Challenges in Achieving True Integration
Challenges in achieving true integration include overcoming systemic inequalities and deep-rooted social prejudices that hinder equal participation. Limited access to resources, education, and economic opportunities creates barriers that perpetuate alienation within marginalized communities. Effective integration demands sustained policy efforts, inclusive social frameworks, and genuine cross-cultural understanding to bridge divisions and foster cohesion.
Psychological Impacts of Alienation
Alienation negatively affects mental health by fostering feelings of isolation, helplessness, and decreased self-worth, which can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Psychological impacts include impaired social bonds and reduced motivation, often resulting in decreased productivity and engagement in both personal and professional contexts. Chronic alienation disrupts emotional well-being, hindering resilience and increasing vulnerability to various psychological disorders.
Building a Cohesive and Inclusive Society
Integration fosters social cohesion by promoting shared values and equal participation within diverse communities, reducing feelings of alienation among marginalized groups. Inclusive policies that encourage cultural exchange and access to resources empower individuals to contribute meaningfully to society. Building a cohesive society requires addressing systemic barriers and nurturing mutual respect to bridge gaps between different social identities.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com