Essence captures the fundamental nature or intrinsic quality that defines something's true character. Understanding the essence of a concept or product helps you appreciate its core value and significance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how essence shapes perception and meaning across different contexts.
Table of Comparison
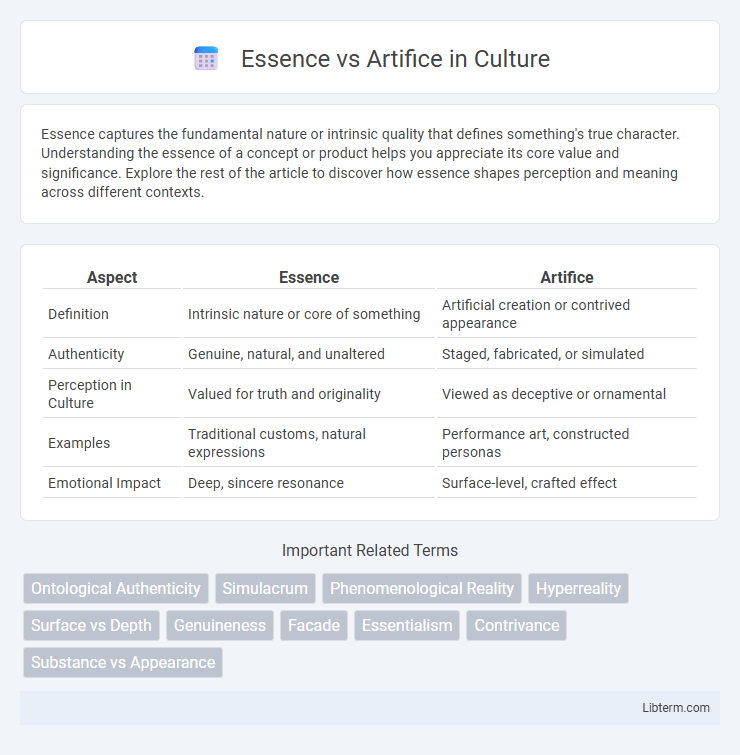
| Aspect | Essence | Artifice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intrinsic nature or core of something | Artificial creation or contrived appearance |
| Authenticity | Genuine, natural, and unaltered | Staged, fabricated, or simulated |
| Perception in Culture | Valued for truth and originality | Viewed as deceptive or ornamental |
| Examples | Traditional customs, natural expressions | Performance art, constructed personas |
| Emotional Impact | Deep, sincere resonance | Surface-level, crafted effect |
Understanding the Core: What is Essence?
Essence refers to the intrinsic nature or indispensable quality that defines an entity's true identity, distinguishing it from superficial attributes. It encompasses the fundamental characteristics that remain consistent despite external changes, serving as the core foundation of existence or concept. Understanding essence requires exploring these inherent properties that shape meaning beyond mere appearance or artificial constructs.
Defining Artifice: The Nature of Constructed Realities
Artifice represents the deliberate creation of constructed realities through human intention and design, contrasting with the inherent qualities of essence. It encompasses fabricated environments, narratives, or identities shaped by cultural, social, or technological influences. Understanding artifice involves analyzing the mechanisms by which reality is manipulated, highlighting the intersection between perception and manufactured experience.
Essence vs Artifice: Key Distinctions
Essence refers to the intrinsic, unchanging nature of a person, object, or concept, embodying authenticity and core identity. Artifice, by contrast, involves constructed appearances or deceptive elements designed to mask or alter reality for impression or manipulation. Understanding essence versus artifice is crucial for discerning genuine qualities from superficial or contrived ones in philosophy, literature, and everyday perception.
Historical Perspectives on Authenticity
Historical perspectives on authenticity analyze the tension between essence, representing inherent truth, and artifice, symbolizing constructed identity. Philosophers like Jean-Jacques Rousseau emphasized the value of natural essence in defining authentic human experiences, while Enlightenment thinkers highlighted how artifice could shape societal roles and cultural expressions. This ongoing dialogue reflects evolving concepts of identity and legitimacy shaped by historical, social, and political contexts.
Artifice in Modern Media and Technology
Artifice in modern media and technology manifests through sophisticated digital simulations, augmented realities, and algorithm-driven content creation that often blur the lines between genuine experience and manufactured perception. Platforms utilize deep learning and AI to generate hyper-realistic images, videos, and narratives, prioritizing engagement and influence over authenticity. This proliferation of artifice reshapes consumer trust and challenges traditional notions of truth in communication.
The Psychological Impact of Authenticity
The psychological impact of authenticity deeply influences mental well-being, fostering greater self-esteem and emotional resilience. Individuals who embrace their true essence experience reduced anxiety and enhanced satisfaction compared to those relying on artifice or external validation. Authenticity promotes genuine social connections and a coherent self-identity, crucial for psychological health.
When Artifice Enhances Experience
Artifice enhances experience by deliberately crafting details that elevate emotional engagement and sensory appeal, such as in theater, film, or digital media where staged elements create immersive realities. The strategic use of artifice can clarify concepts, evoke stronger responses, and enrich storytelling by guiding audience perception rather than relying solely on raw authenticity. In design and gastronomy, artificial enhancements improve functionality and pleasure, demonstrating how carefully applied artifice complements essence for optimal impact.
Navigating Social Interactions: Genuine vs Fabricated Personas
Navigating social interactions requires discerning genuine personas from fabricated ones to build trust and meaningful connections. Genuine personas reflect authentic values and emotions, fostering deeper empathy and cooperation in relationships. Fabricated personas often mask insecurities or social pressures, leading to misunderstandings and weakened bonds over time.
The Ethical Implications of Artifice
The ethical implications of artifice center on the distortion of authenticity and the potential manipulation of individual and societal values. When artificial elements obscure genuine intentions or identities, trust and moral accountability can erode, raising concerns in contexts like media, technology, and interpersonal relationships. Ethical frameworks must address the balance between innovation and the preservation of inherent human truths to mitigate the risks associated with artifice.
Embracing Essence in a World of Illusion
Embracing essence in a world of illusion requires discerning genuine values beneath superficial appearances and prioritizing authentic experiences over fabricated facades. This approach fosters deeper connections and clarity by anchoring identity in truth rather than external validations or deceptive constructs. Cultivating awareness of essence enhances personal growth and resilience amid pervasive artifice and societal pressures.
Essence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com